“GND” stands for “ground” in electronic circuits, and is the abbreviation of “Ground”. It can also be called zero point or system ground. It usually connects other components in the circuit to the ground potential to form part of the circuit. Ground is the reference point in the circuit. Its potential is zero relative to other potentials in the circuit. It is used to connect various parts in the circuit and as the basis for signal connection to ensure that they are at the same potential.
In circuit design, GND is usually used as a zero potential point to connect power, signals and other components. In addition, GND can also be used to return the current in the circuit to the power supply so that the circuit can work normally.
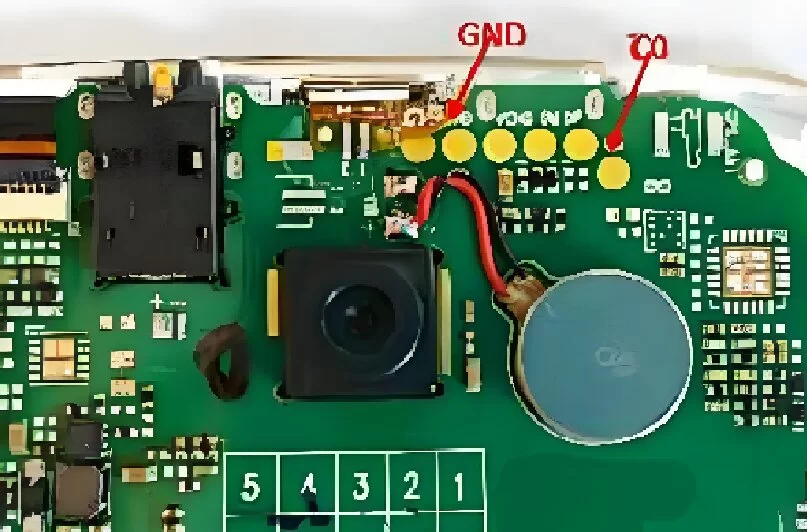

At present, there are two forms of “ground” for electronic equipment:
One is to connect to the “earth”, with the earth as the zero potential, and connect the metal shell of the electronic equipment to the earth to protect the equipment and personnel, such as protective grounding and lightning protection grounding. This is generally called “safety ground”.
One is the “reference ground”. This “ground” does not have to be connected to the “earth”. It may be a reference mark for convenient circuit analysis Q to reduce the difficulty of circuit signal analysis; of course, when necessary, it will also be connected to the “earth”. This is generally called “signal ground”.
At present, in daily applications, circuit systems that exceed the safety voltage must be connected to the “ground” to improve safety; in weak current systems (voltage is lower than the safety voltage: AC below 36V, DC below 24V), on the final PCB board, various “signal grounds” in the circuit are generally connected back to the negative pole of the common power supply in a certain way.
Since there are many grounding points in a circuit, in order to distinguish different sub-circuit parts, the grounding points of each sub-circuit part will use different logos.
Safety ground
1) Earth ground wire-EGND grounding protection
Grounding protection is generally used on lightning rods and electrical enclosures to protect buildings from lightning strikes and prevent people from electric shock.
The principle of grounding protection is to build a “low impedance current channel” between the object and the ground, allowing the current to flow to the ground through this channel, thereby preventing the current from flowing through the building or the human body to achieve the purpose of protection.
Signal ground
1) Power ground – GND
GND (abbreviation of Ground, meaning common end, that is, the common end of the circuit.) In early circuits, various “grounds” were generally represented by GND, but with the development of circuit research, people need to distinguish circuit parts with different functions, so different marks are used for different circuit parts. Now, GND is generally used to represent the power ground.
Different types of ground wires will eventually be gathered together as the 0V reference ground wire of the entire circuit. This ground wire is called the power ground wire GND. The power supply is the energy source of all circuits. The voltage and current required for all circuits to work come from the power supply. Therefore, the ground wire GND of the power supply is the 0V voltage reference point of all circuits. Generally, the GND of the power supply will be used as the negative pole of the circuit loop.
2) AC ground wire – CGND
The AC ground wire CGND is generally present in circuit projects containing AC power, such as AC-DC AC to DC power supply circuit
The AC-DC power supply circuit is divided into two parts. The front stage of the circuit is the AC part, and the back stage of the circuit is the DC part, which forces the formation of two ground wires, one is the AC ground wire and the other is the DC ground wire.
The AC ground wire is used as the 0V reference point of the AC circuit part, and the DC ground wire is used as the 0V reference point of the DC circuit part. Usually, in order to unify the ground wire GND in the circuit, engineers will connect the AC ground wire to the DC ground wire through a coupling capacitor or inductor. Through this coupling capacitor, interference between the AC circuit and the DC circuit is prevented.
3) Analog ground wire–AGND
The analog ground wire AGND is mainly used in the analog circuit part, such as the ADC acquisition circuit of the analog sensor, the operational amplifier proportional circuit, etc.
In these analog circuits, since the signal is an analog signal and a weak signal, it is easily affected by the large current of other circuits. If it is not distinguished, the large current will produce a large voltage drop in the analog circuit, which will distort the analog signal and may seriously cause the analog circuit to fail.
4) Digital ground – DGND
Digital ground DGND is obviously relative to analog ground AGND, and is mainly used in digital circuits, such as key detection circuits, USB communication circuits, single-chip circuits, etc.
The reason for setting up digital ground DGND is that digital circuits have a common feature, which is that they are all discrete switching signals, and only digital “0” and digital “1” are distinguished. In the process of jumping from digital “0” voltage to digital “1” voltage, or from digital “1” voltage to digital “0” voltage, the voltage changes. According to Maxwell’s electromagnetic theory, a magnetic field will be generated around the changing current, which will form EMC radiation to other circuits.
5) Power ground – PGND
Whether it is analog ground AGND or digital ground DGND, they are all low-power circuits. In high-power circuits, such as motor drive circuits, solenoid valve drive circuits, etc., there is also a separate reference ground, which is called power ground PGND.
High-power circuits, as the name suggests, are circuits with relatively large currents. Obviously, large currents can easily cause ground offsets between circuits with different functions.
The above is my simple sharing, I hope it will be helpful to you.