Do you know what ipc electronics standards are?For those who work in the electronics industry or PCB assembly may wonder if there is a fixed standard to ensure the quality of my products and if there is a common language for this industry. The solution to all these problems is the IPC standard.
So what is the IPC standard and who developed it? Are there any benefits to using it? What should I know about my electronics? Next we will describe these issues in detail.
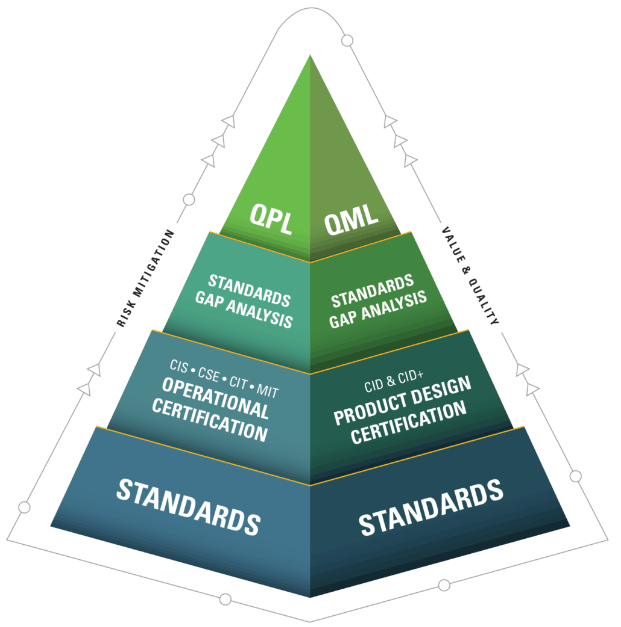
Who developed the IPC standard?
Before we can understand the IPC standard, we first need to know who developed it. It comes from the IPC Association, a trade association whose goal is to standardize the assembly and production requirements for electronic devices and components. Founded in 1957, it was formerly known as the Institute of Printed Circuits.
Its name was changed to the Institute for the Interconnection and Packaging of Electronic Circuits to highlight the expansion from bare boards to packages and electronic assemblies. 1999 saw the organization’s official name change to IPC, with the tagline “Association Connecting Electronics Industries “.
From the history of the IPC Association, we can briefly understand that the IPC standard has included the requirements for the manufacturing and assembly of electronic products.
What is the IPC standard?
The IPC standard is the most widely recognized acceptability code in the electronics industry. The organization publishes standards for virtually every stage of the electronic product development cycle, including design, procurement, assembly, packaging, and more.
So another thing we know from this short introduction is that IPC standards refer to everything in the electronics industry and are essential knowledge for designers and manufacturers alike.
Just like the IPC standards tree, there are a huge number of standards that have been developed for different aspects and all of them are for end products. For example, IPC-A-610, which focuses on the acceptability of electronic assemblies, is used worldwide by OEMs and EMS companies.
Why use IPC standards?
After reading the IPC standard tree, some of you may reject this standard because of its complexity and triviality. This kind of thinking is not desirable. We must be clear about the benefits that IPC standard can bring.
(1) Quality Assurance and Product Reliability
As we said before, the IPC standard touches on everything in electronic products, such as IPC-A-600 for the acceptability of printed boards, and even lists the material requirements for copper foils, soldermasks, and stencil designs in IPC-4562, IPC-SM-840, and IPC-7525, 7526, and 7527, respectively. Because it establishes standards from all aspects, as long as they are applied to the production process of electronic products, manufacturers only need to follow the standards strictly, product quality and reliability are naturally guaranteed.
(2) facilitate communication
IPC electronics standard is the most widely used terminology in the electronics industry, which describes and demonstrates almost all the engineering problems. ipc standard with the computer industry common C language, in the electronics industry also has a similar status. Because it is widely used, people can understand each other well, thus ensuring that communication is barrier-free.
(3) Guarantee production
Generally speaking, each PCB manufacturer formulates its own production and quality standards accordingly to the IPC standard. All production line workers are trained in technical knowledge, so workers in each position can basically understand and comply with the production guidelines. As for all managers, they have received professional education on IPC standards and have experienced so many projects in their career. From all these aspects, all production processes are operated by professionals and tested in all aspects according to IPC standards as a way to ensure smooth production.
(4) Cost Savings
Due to the wide applicability and acceptance of the IPC standard, engineers and designers know how to test the finished product, and manufacturers know what requirements they have to fulfill and meet the agreed upon special standards. Almost all companies have a QC department and all employees have a deep understanding of what the product should look like. For consensus and mandatory requirements, we don’t need to engage in constant experimentation to know which materials are appropriate, and can avoid excessive trial and error costs, resulting in a significant savings.
(5) Branding effect
Affected by the sluggish market environment, we are always exploring new things and expanding our supplier network. But we were also concerned about the qualifications of our new suppliers and were not sure if they were reliable. Suddenly, we know that they have established a quality management system in accordance with IPC standards. In this case, we are slightly reassured that we can give them a try. This is the brand effect brought by IPC standard, which can realize the strategic goal and create a win-win situation, bringing more business to suppliers and better competitiveness to buyers.
What is the essential knowledge of IPC standard?
Before answering this question, we must understand the necessary processes for the production of PCBA. PCBA, an acronym for Printed Circuit Board Assembly, is an electronic product or production process by placing electronic components on a bare board or PCB. The main technologies used are SMT and DIP. almost all IPC standards are applied throughout the production process. For example, there are standards for stencil design and the materials used in SMT.
According to the definition of IPC standards, products can be categorized into three levels.
IPC Level 1 standards, which are primary standards, have the shortest lifespan and simplest functionality.
IPC Level II standards, which represent service electronics or specialized products with high performance, high reliability and long life.
IPC tertiary standards, which represent high-performance electronic products, are used in special industries such as military, medical and aerospace.
The Scope and Importance of Specific IPC Standards
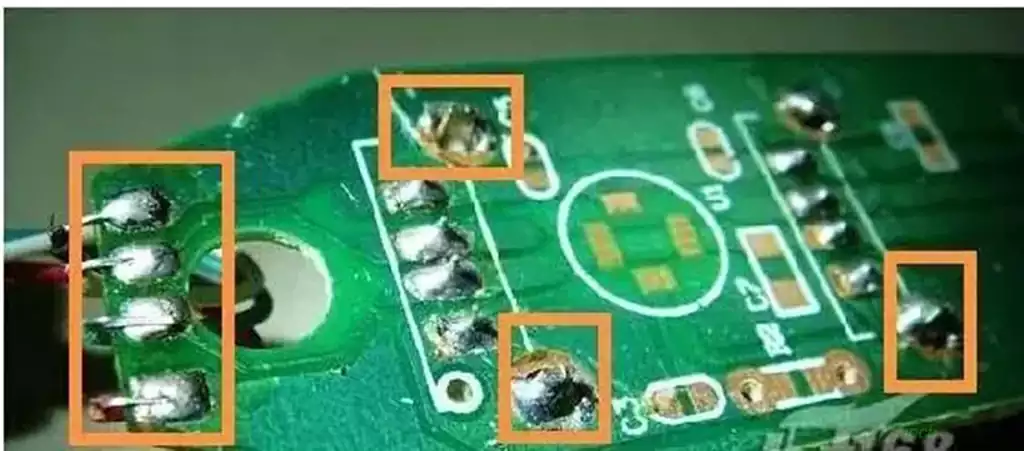
1. IPC-A-600: Acceptability of Printed Boards IPC-A-600 is a crucial standard that details the acceptability criteria for printed circuit boards (PCBs). It provides comprehensive visual representations and explanations of the criteria for a PCB to be considered acceptable. This includes criteria for base materials, holes, plated-through holes, conductors, and coatings. Adhering to IPC-A-600 ensures that the PCBs meet the highest quality standards, which is essential for the reliability and longevity of electronic devices.
2. IPC-A-610: Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies One of the most widely used standards, IPC-A-610, defines the acceptability criteria for electronic assemblies. It covers various aspects such as soldering criteria, component placement, and cleanliness. This standard is crucial for ensuring that assembled electronics meet the required quality and performance specifications, thereby reducing the risk of failures in the field.
3. IPC-6012: Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards IPC-6012 sets the performance and qualification requirements for rigid printed boards. This standard includes specifications for material properties, electrical performance, and mechanical integrity. Ensuring compliance with IPC-6012 helps manufacturers produce boards that can withstand the rigors of their intended applications, whether in consumer electronics, automotive, or industrial equipment.
4. IPC/WHMA-A-620: Requirements and Acceptance for Cable and Wire Harness Assemblies This standard specifies the requirements and acceptance criteria for cable and wire harness assemblies. It covers materials, methods, tests, and acceptability criteria for these assemblies, which are critical components in many electronic devices. Adhering to IPC/WHMA-A-620 ensures that cable and wire harness assemblies meet the necessary reliability and performance standards.
5. IPC-2221: Generic Standard on Printed Board Design IPC-2221 provides generic requirements for the design of PCBs and other forms of component mounting or interconnecting structures. This standard covers various aspects such as design layout, materials, mechanical and electrical parameters, and testing requirements. Following IPC-2221 helps designers create robust and reliable PCB layouts that meet industry standards.
The Role of IPC Certification
1. Certification Programs IPC offers various certification programs for individuals and companies. These programs include Certified IPC Trainer (CIT), Certified IPC Specialist (CIS), and Certified Interconnect Designer (CID). These certifications are recognized globally and demonstrate a high level of expertise and commitment to industry standards. Companies with IPC-certified staff can assure their customers of the quality and reliability of their products.
2. Continuous Improvement and Updates The IPC standards are continuously reviewed and updated to keep pace with technological advancements and industry needs. This ensures that the standards remain relevant and effective in addressing current and emerging challenges in electronic manufacturing. Staying updated with the latest versions of IPC standards helps companies maintain a competitive edge and meet the evolving demands of the market.
Challenges and Future of IPC Standards
1. Complexity and Implementation While IPC standards provide significant benefits, their complexity can pose challenges for implementation. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) might find it challenging to fully comply with all the detailed requirements. However, investing in proper training and certification can mitigate these challenges and ensure smooth implementation.
2. Global Adoption and Harmonization IPC standards are widely recognized and adopted globally. However, harmonizing these standards with local regulations and standards can be challenging. Efforts are ongoing to promote the global adoption and harmonization of IPC standards, which will further enhance their effectiveness and reduce barriers to international trade.
3. Technological Advancements As technology advances, new challenges and requirements emerge in the electronics industry. IPC continuously works on developing new standards and updating existing ones to address these advancements. Emerging technologies such as flexible electronics, wearable devices, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are areas where IPC standards will play a crucial role in ensuring quality and reliability.
4. Sustainability and Environmental Considerations Sustainability and environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important in the electronics industry. IPC electronics standards is actively working on incorporating sustainability aspects into its standards. This includes guidelines for environmentally friendly materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and recycling and disposal of electronic components.
In addition to the above division of different product levels, due to the complexity and diversity of PCB assembly, ensuring product quality is the most basic. Hope the above information is helpful to you.