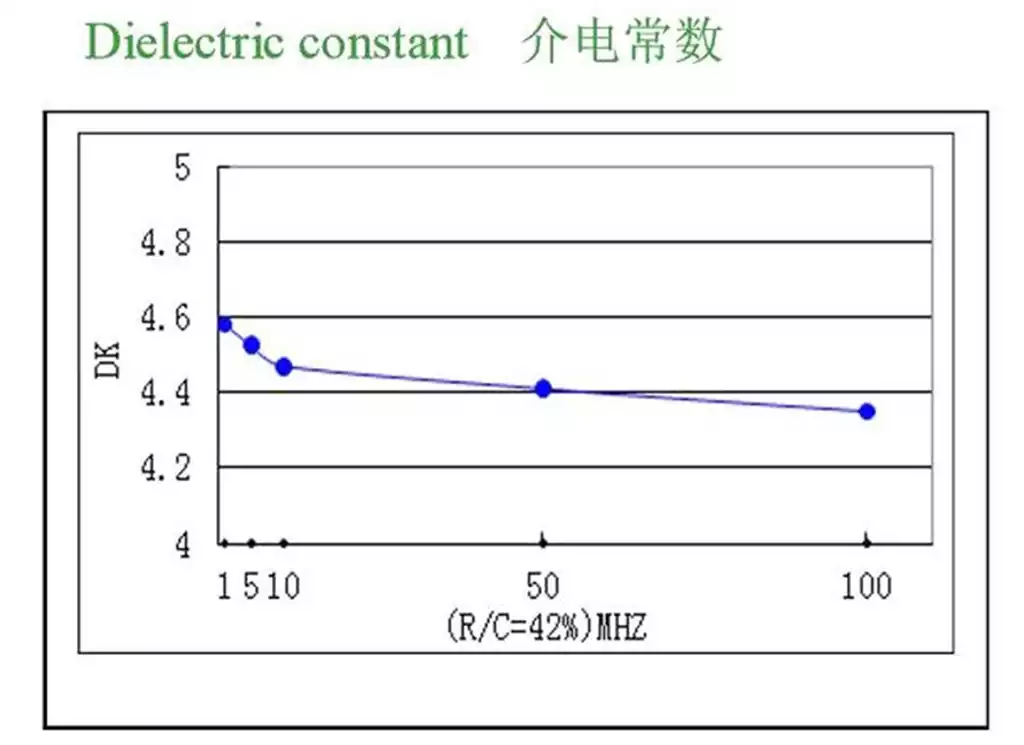
What is a Rigid Flex PCB? Rigid Flex PCB is a combination of flexible and rigid circuit boards, also known as R-FPCB. Rigid Flex PCB is a new type of printed circuit board that combines the durability of a rigid PCB with the adaptability of a flexible PCB. Among all types of PCBs, the combination of soft and hard is the strongest resistance to harsh application environments.
Because the Rigid-Flex PCB is a combination of FPC and PCB, the production of Rigid-Flex PCB should have both FPC and PCB production equipment. Usually, electronic engineers draw the circuit and shape of the flexible bonding board according to the requirements, and then send it to factories that can produce Rigid Flex PCB. After processing and planning the relevant documents by CAM engineers, they arrange the FPC production line to produce the required FPC and PCB production lines to produce PCBs. After these two types of soft and hard boards are produced, according to the planning requirements of the PCB engineer, the FPC and PCB are seamlessly pressed together by a pressing machine, and then go through a series of detailed steps to finally produce the Rigid Flex PCB. A very important step, because the Rigid Flex PCB is difficult and has many details, a full inspection is usually required before shipment.
Three Characteristics of Rigid Flex PCB
a. Materials (including rigid and flexible materials)
b. Line layer (more than 3 layers)
c. Containing PTH (Plating Through Hole) metallized pores, the layer connected to it is conductive; There is an electrical connection. On the other hand, NPTH (Non Plating Through Hole) non-metallic pores refer to the absence of copper on the inner side of the pores; Electrical partitions
Advantages of Rigid Flex PCB: Rigid Flex PCB combines the characteristics of FPC and PCB, so it can be used in some products with special requirements. It has both a certain flexible area and a certain rigid area, which is very helpful for saving internal space, reducing finished product volume, and improving product performance.
The disadvantages of Rigid Flex PCB: Rigid Flex PCB has multiple production processes, high production difficulty, low yield rate, and requires a lot of materials and manpower. Therefore, its price is relatively expensive and the production cycle is relatively long.
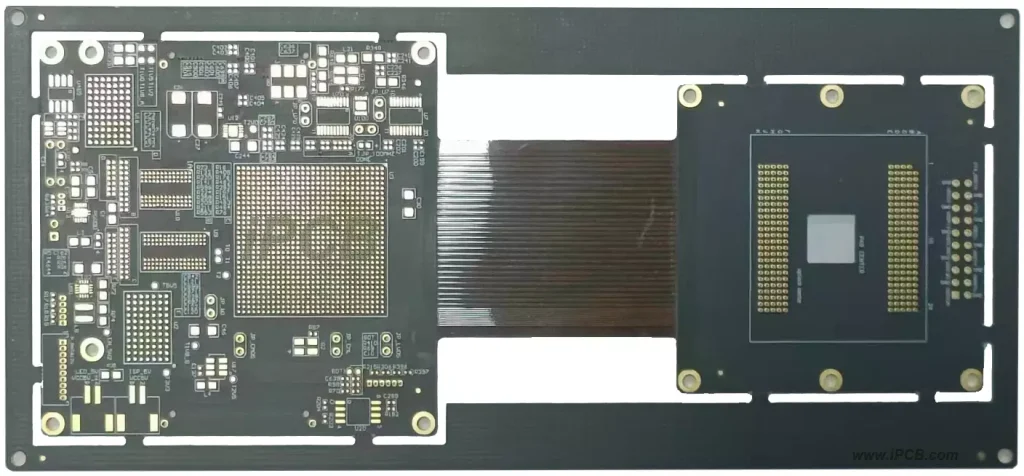
Application of Rigid Flex PCB
Industrial use – Industrial use includes Rigid Flex PCB used in industrial, military, and medical applications. Most industrial components require characteristics such as precision, safety, and low susceptibility to damage. Therefore, the requirements for Rigid Flex PCB are high reliability, high precision, low impedance loss, complete signal transmission quality, and durability. But due to the high complexity of the process, the output is small and the unit price is quite high.
Mobile phone – The application of Rigid Flex PCBs in mobile phones, commonly including the Hinge, Camera Module, Keypad, and RF Module of foldable phones. The advantages of using hardware and software in mobile phones include the integration of components and the consideration of signal transmission volume. At present, mobile phone products use soft and hard boards to replace the original combination of two connectors and a soft board. Its greatest significance in the product is to increase the durability and long-term reliability of the mobile phone’s folding point. Therefore, Rigid Flex PCBs are highly valued due to their high product stability. On the other hand, due to the popularity of camera phones, combined with the integration of multimedia and IT functions, the internal signal transmission volume of mobile phones has increased, leading to a demand for modularity.
Consumer electronics products – In consumer products, DSC and DV are representative of the development of Rigid Flex PCBs, and can be discussed on two main axes: performance and structure. In terms of performance, Rigid Flex PCBs can connect different PCBs and components in a three-dimensional manner. Therefore, under the same circuit density, the total usage area of PCBs can be increased, which can relatively improve their circuit carrying capacity and reduce the signal transmission limit and assembly error rate of contacts. On the other hand, due to the lightweight and thin nature of soft and hard boards, they can bend wiring, which is of substantial benefit in reducing volume and weight.
Cars – The use of Rigid Flex PCBs in cars often includes buttons on the steering wheel to connect to the motherboard, connection between the car’s video system screen and control panel, operation connection of audio or function keys on side doors, reverse radar imaging system, sensors (including air quality, temperature and humidity, special gas regulation, etc.), car communication system, satellite navigation, rear seat control panel and front end controller connection board, external detection system, and other purposes.
Wearable devices – With the popularity of wearable devices, there is an increasing demand for the softness and bendability of electronic materials. Rigid Flex PCB is an ideal choice for wearable devices due to its soft and flexible characteristics. It can achieve lightweight, comfortable, and good user experience for devices.
Flexible Display Screen – As an emerging display technology, flexible display screens have extremely high requirements for materials. Rigid Flex PCB has become one of the key materials for flexible display screens due to its soft and impact resistant properties. It can achieve morphological changes such as bending and folding of the display screen, bringing users a brand new visual experience.
Aerospace – In the aerospace field, electronic equipment needs to withstand extreme environmental conditions, such as high radiation, high pressure, etc. Rigid Flex PCB, with its high temperature resistance and reliability, can meet these special needs. It can provide stable and reliable electrical connections for aerospace electronic equipment, ensuring the normal operation of the equipment.
The basic process flow of Rigid Flex PCB
Material selection->Control of production process flow and key parts ->Production process flow ->Graphic transfer of inner layer single chip ->Multi layer positioning of flexible materials ->Lamination ->Drilling ->Removal of drilling stains and protrusions ->Chemical copper plating and electroplating ->Surface resistance welding and weldability protection layer ->Appearance processing
Why choose a Rigid Flex PCB?
a. The Rigid Flex PCB can solve the reliability issue of FPC installation.
Connecting FPC through connectors brings installation costs, inconvenience, and reliability issues, as well as issues such as short circuits and detachment. I saw the phenomenon of repairing welding between FPC and PCB after FPC installation in a design of a mass-produced barrel machine on Hikvision. The Rigid Flex PCB solves the reliability issue of FPC installation.
b. The overall cost may be lower.
Rigid-Flex PCB Although the price per unit area has increased, it has saved connector costs, reduced installation time, reduced repair rates, improved productivity and reliability. The use of products with massive shipments often effectively reduces costs.
So, comprehensive cost = Rigid Flex PCB area * Rigid Flex PCB unit price – processing time cost – FPC loosening repair cost * loosening probability – whether the management cost caused by fewer types of boards is greater than the original PCB area * PCB unit price+FPC price+connector price
c. Effectively improving signal quality
Due to not connecting through connectors, the wiring continuity is better and the signal integrity is better.
With the continuous progress of electronic technology and the continuous expansion of the market, the application fields of Rigid Flex PCB will be more extensive. In the future, Rigid Flex PCBs will play a more important role in various fields. Meanwhile, with the continuous improvement and optimization of electronic manufacturing processes, the performance of Rigid Flex PCBs will also be further enhanced, providing more solid support for the development of electronic devices.