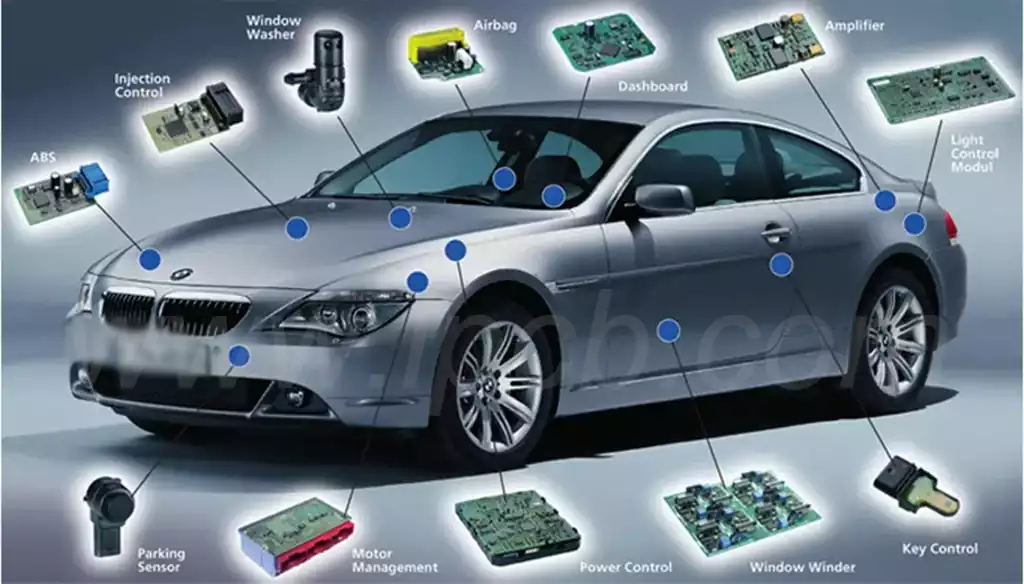
As a popular choice for meeting the needs of flexible electronic circuits, FPC flexible circuit boards are designed to replace traditional wire harnesses for a variety of complex electronic design solutions. While the performance of flexible PCBs is influenced by multiple factors, one of the key elements is undoubtedly the constituent materials. So, what exactly are the materials that make up an FPC flexible circuit board? From a structural point of view, FPC flexible circuit boards are mainly constructed from core materials such as flexible copper-clad laminate (FCCL), cover film and bonding film. The selection and use of these materials is essential to ensure the performance and reliability of FPC flexible circuit boards.
Substrate part:
The substrate, as an important support part of the FPC flexible circuit board, is mainly used in polyimide (PI) or polyester (PET) film materials. Polyimide because of its excellent high temperature resistance and chemical stability, in the high-end electronic products are favored; while polyester materials because of its lower cost and excellent flexibility, in the field of consumer electronics has been widely used.
Polyimide film, with its excellent chemical stability, mechanical strength and insulating properties, has become the material of choice for the production of circuit lines and cover films for FPC flexible circuit boards. The thickness of the film is usually between 12.5 and 50 μm, and different colors of polyimide film have slightly different performance, for example, yellow film is more excellent in high temperature resistance.
Polyester film, a high-quality transparent, insulating and mechanically strong polymer material, plays a key role in the production of FPC flexible circuit boards. Its thickness range is usually between 5 and 25 μm, different colors of polyester film in the performance of the difference, such as white polyester film in the insulation performance is better.
Conductive layer:
The conductive layer, as the core component of FPC, is mainly made of calendered copper foil or electrolytic copper foil. As a metal material, copper foil occupies an important position in FPC manufacturing due to its good conductivity and ductility. The thickness and conductivity of copper foil are directly related to the quality and performance of flexible circuit boards.
In the FPC manufacturing process, the thickness of copper foil is usually between 17 and 70 μm, and different thicknesses of copper foil have their own characteristics in terms of conductivity and processing performance. In addition, the surface treatment and cleanliness of the copper foil also have a significant impact on the quality of the FPC. After a series of processes, the copper foil is finally transformed into the circuit pattern designed by engineers.
Covering film section:
Covering film, mainly used to protect the conductive layer of FPC flexible circuit boards from erosion and damage by the external environment. The film consists of an organic chemical plastic film with an adhesive, commonly used materials include polyester resin and polyurethane.
Polyester resin film, with its excellent transparency, insulation and mechanical strength, provides good insulation protection for FPC flexible circuit boards. Its thickness usually ranges from 12.5 to 50 μm, and different colors of polyester resin films vary in performance.
Polyurethane film, on the other hand, provides strong waterproof and abrasion-resistant protection for FPC flexible circuit boards with its superior abrasion resistance, elasticity, and waterproof performance. Its thickness is usually between 10 and 30 μm, and different colors of polyurethane film also vary in performance.
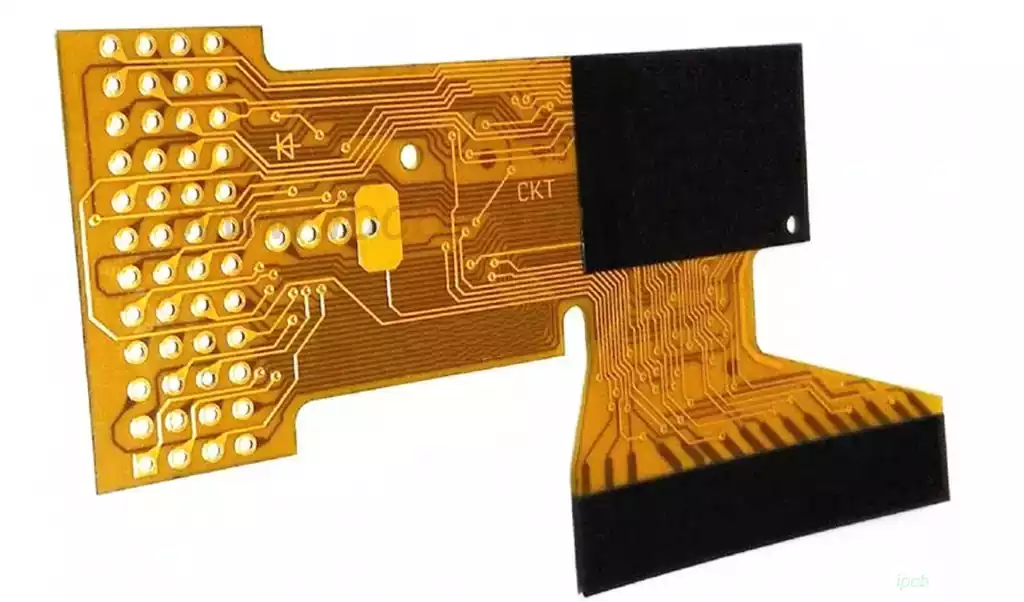
Reinforcement material section:
Reinforcement materials, mainly used to enhance the strength and stability of FPC, commonly used materials include fiberglass cloth and polyimide film. There are various types of reinforcement materials, such as PI reinforcement, PED reinforcement, FR4 reinforcement, steel sheet reinforcement, etc., and their thickness can be adjusted according to customer needs.
303 stainless steel, as a kind of easy-cutting and wear-resistant stainless steel material, is mainly used in applications requiring high precision and surface finish. In FPC fabrication, steel sheet reinforcement enhances the performance of flexible circuit boards by adding strength and stability, while also forming specific circuit patterns through the etching process. However, when using sheet metal reinforcement materials, due consideration needs to be given to their processability and cost-effectiveness.
Fiberglass cloth, as an inorganic non-metallic material, occupies an important position in FPC reinforcement materials with its excellent mechanical strength and insulation properties. It combines high temperature resistance, chemical resistance and abrasion resistance, and its thickness is usually between 0.05 and 0.2mm. Fiberglass cloth can effectively improve the strength and stability of FPC circuit boards, different colors of fiberglass cloth in the performance of the difference. However, in the use of glass fiber cloth reinforcement materials, you need to pay attention to its impact on the environment, especially in high-temperature conditions may produce harmful gas emissions, so you need to fully consider the environmental and safety factors in the selection and use.
Other auxiliary materials part:
In addition to the above main materials, the flexible circuit board manufacturing process also needs to use a series of auxiliary materials, such as cleaning fluid, developing fluid and etching fluid. These auxiliary materials play an important role in the manufacturing process of cleaning, developing and etching, etc., the quality and performance of the FPC has a non-negligible impact. Through the rational use of these auxiliary materials, you can ensure that the manufacturing process of FPC flexible circuit boards smoothly, and achieve the expected quality and performance requirements.
As an outstanding representative of modern electronic technology, the performance and reliability of flexible circuit boards cannot be separated from the careful selection and use of various materials. From the high temperature resistance and chemical stability of the substrate, to the good conductivity and ductility of the conductive layer, to the protective function of the cover film, as well as the reinforcing effect of the reinforcing material, every detail has condensed the wisdom and craftsmanship of the engineers.