Flexible Copper Clad Laminate (FCCL) refers to a kind of flexible insulating materials such as film on one or both sides, through a specific process, and copper foil bonded together with the formation of copper cladding board, FCCL is a flexible circuit board (Flexible Printed Circuit, FPC) processing substrate, according to the structure of the product is divided into three-layer flexible copper clad laminate (3L-FCCL) and two-layer flexible copper clad laminate (2L-FCCL) two categories. FCCL is a substrate for Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC), which is divided into two categories, 3L-FCCL and 2L-FCCL, with a thickness of up to 5.5 μm. This substrate has a high degree of flexibility and plasticity, and can be adapted to a variety of complex electronic product design requirements. FCCL plays a key role in the manufacturing of the electronics industry, and provides a flexible and reliable circuit solution for a variety of applications.
Features of Flexible Copper Clad Laminate
- Characterized by lightness, thinness, shortness and smallness.The flexible substrate is composed of a thin film, which replaces the higher density glass fiber reinforcement with a lower density insulating base film. Therefore, the quality of flexible copper-clad laminates is lighter than rigid copper-clad laminates, and the thickness is much thinner than the thickness of the sheet.
- Static and dynamic flexing can be realized.Flexibility is flexible copper-clad laminates from the most significant features of rigid copper-clad laminates, the number of times it can be flexed up to 107 times. FCCL can be folded into any shape still maintain the metal layer and the substrate layer does not break, in any three-dimensional space for any arrangement of wiring. As for RCCL, even if it is as light and thin as FCCL, when it is subjected to external stress, it will be easily fractured, resulting in a short circuit or circuit breakage.
- Three-dimensional construction. Three-dimensional (3D) interconnection construction, increasing the freedom of spatial design and wiring, maximizing the function of the PCB.
Flexible copper cladding board is composed of three main categories of materials:
Insulating base film materials: flexible copper-clad laminate with insulating base film materials are polyester (PET) film, polyimide (PI) film, polyesterimide film, fluorocarbon vinyl film, amide fiber paper, polybutylene to phthalate film, etc.. Among them, the most widely used are polyester film (PET film) and polyimide film (PI film).
Metal conductor foil: Metal conductor foil is the conductor material for flexible copper-clad laminates, and there are copper foil (ordinary electrolytic copper foil, high ductility electrolytic copper foil, calendered copper foil), aluminum foil and copper-beryllium amalgamated gold foil. The vast majority of copper foils are used, among which are electrolytic copper foil (ED) and calendered copper foil (RA).
Adhesive: Adhesive is an important part of the three-layer method of flexible copper-clad laminates, which directly affects the product performance and quality of flexible copper-clad laminates.The main adhesives used for flexible copper-clad laminates are polyester adhesives, acrylic adhesives, epoxy or modified epoxy adhesives,polyimide adhesives,phenolic – butyral adhesives,etc.In the three-layer flexible copper-clad laminates method, the adhesives are mainly used for the production of flexible copper-clad laminates. In the three-layer method of flexible copper-clad laminate industry,adhesives are mainly divided into two major schools of acrylic adhesives and epoxy adhesives.
They are a kind of composite material made of metal conductor material and dielectric substrate material, which are bonded together by adhesive. This product can be randomly wound into a shaft type without breaking the metal conductor or dielectric substrate. In the case of rigid copper-clad laminates, even when very thin, the dielectric substrate material is susceptible to rupture when bent by an external force.
The total thickness of most flexible laminates is less than 0.4mm, usually between 0.04-0.25mm thick. Flex copper-clad laminates require a flexing capability that must meet the end-product usage requirements or the process requirements of the flex circuit board molding and processing time.
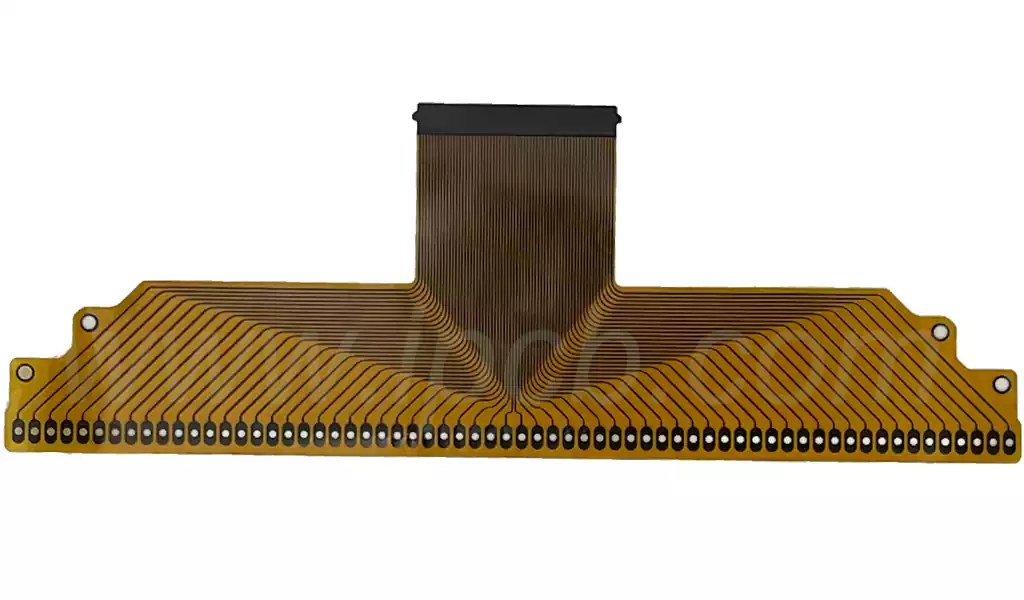

Flexible Copper Clad Laminate Production ProcessMaterial Preparation
The materials for flexible copper-clad laminates mainly include substrates, copper foils, glues and inks. Among them, the substrate is the main component of the flexible circuit board, usually using polyimide film or polyimide composite materials. Copper foil is the conductive layer of the flexible circuit board, generally choose the thickness of 9um to 18um between the copper foil. Glue and ink are used to protect the surface of the circuit board and the circuit pattern.
Printed Circuit Patterns
Circuit patterns on flex circuit boards are usually produced using printing techniques. The process of producing printed circuit diagrams involves applying a layer of adhesive and a layer of copper foil to the substrate, then using photolithography to storm the circuit pattern onto the copper foil, and etching to remove the unwanted copper foil, leaving the circuit pattern.
Copper Cladding
Copper cladding on pcb boards consists of two types of copper cladding: full copper cladding and partial copper cladding. Full copper cladding refers to coating the entire surface of the circuit board with a layer of copper foil, while partial copper cladding refers to coating the circuit pattern with a layer of copper foil. The purpose of copper cladding is to protect the surface of the board and to improve conductivity.
Drilling
Drilling is an important step in the production of flexible circuit boards. The purpose of drilling is to drill connection holes in the circuit board to make the board more compact. The accuracy and quality of the drilled holes directly affects the reliability and performance of the entire board.
SMD
SMD is the final step in the production process of flex circuit boards. The purpose of SMD is to attach electronic components to the circuit board to complete the circuit connection. The quality of the various components used in SMD has a significant impact on the reliability and performance of the board.
Testing
After the production of flexible circuit boards is completed, a series of tests need to be conducted to ensure the quality and reliability of the board. Tests mainly include electrical performance, soldermask coverage and pad inspection. The test results will directly determine whether the flexible circuit board is qualified.
Flexible copper-clad laminates, as the core of flexible electronics technology, with its excellent flexibility and high performance, is promoting the development of electronic products in the direction of smaller, lighter and smarter. In the future, it will continue to play an important role in the electronics industry, leading technological innovation.