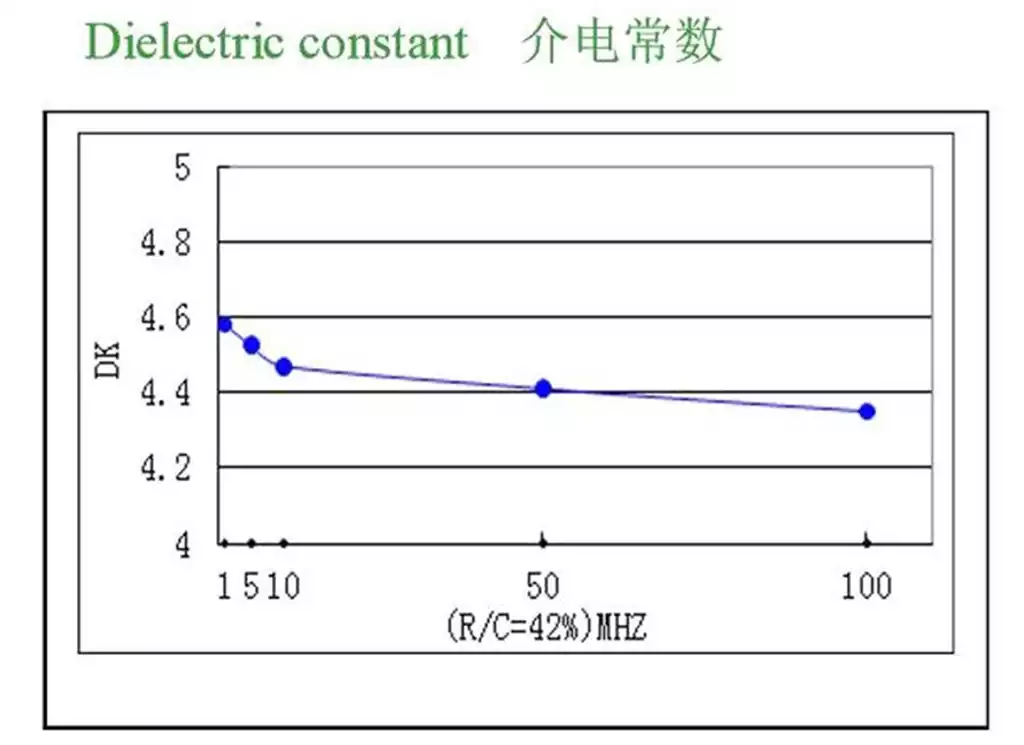
Introduction
With the continuous progress of automobile technology, the electronic systems in automobiles are becoming more and more complex. The role of printed circuit boards (PCBs) as a core component of automotive electronic systems is crucial. Whether it is the power system, infotainment system or safety control system, PCB plays an indispensable role. However, with the increasing number of electronic devices, PCB failure rates are on the rise. Therefore, understanding the functions of automotive printed circuit board repair, common types of failures, repair methods and preventive measures will help owners better maintain their vehicles.
The function of automotive PCB
The main functions of automotive PCB can be divided into the following aspects:
Signal transmission
There are many sensors and actuators in a car, and these devices need to be connected to the control unit through the PCB. For example, the sensors in the brake system will feedback the vehicle’s speed and brake status to the electronic control unit (ECU), so as to adjust the braking force to ensure the safety of the vehicle.PCB is not only responsible for the transmission of these signals, but also to ensure the integrity and timeliness of the signals in order to avoid delays and errors.
Power Management
Various electronic devices in the car need a stable power supply. PCB distributes the power from the battery reasonably to the navigation system, audio system, air-conditioning and other devices to ensure that these devices can run stably under different working conditions. Efficient power management can reduce energy consumption and improve the overall performance of the vehicle.
Control Logic
Many functions in modern automobiles rely on microcontrollers and integrated circuits, components that are often integrated on PCBs and are responsible for handling complex logic operations. For example, autonomous driving technology relies on a large amount of data processing and real-time decision-making, which cannot be achieved without the support of a PCB, which runs pre-programmed algorithms to realize intelligent control and ensure the safety and efficiency of the vehicle in a variety of situations.
Communication Interface
In modern automobiles, PCBs also undertake the task of data communication between different systems. Through communication protocols such as the CAN (Controller Area Network) bus, the vehicle’s various control modules are able to exchange information quickly and reliably. This efficient communication capability enables the vehicle to comfortably cope with various emergencies in a complex environment.
Safety Functions
Many safety systems, such as the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and Electronic Stability Program (ESP), rely on the PCB for real-time monitoring and regulation. the PCB is responsible for processing data from sensors and issuing timely commands to the braking system and the power system to ensure driving safety.
Common Failure Types
Although automotive PCB design is usually very robust, but in harsh environments, frequent temperature changes or improper use, PCB failure may still occur. Common failure types include:
Soldering defects
Solder joints are the connection points on the PCB. If the soldering quality is poor or if thermal expansion occurs due to heat or cold during use, the solder joints may deteriorate, fall off, or be falsely soldered. This condition can lead to circuit breakage, which in turn affects the function of the entire system. For example, a detached solder joint may cause the car stereo to not work or the navigation system to malfunction.
Short Circuit
A short circuit is the flow of current in an unintended path, usually due to moisture, dust or other contaminants. In humid environments, PCBs can short-circuit, causing electronic components to overload or even burn out. For example, if a car gets water in it, moisture may seep into the circuit board and cause a short circuit, which in severe cases can lead to a fire.
Component Damage
Electronic components (e.g. capacitors, resistors, chips) in a car may be damaged due to overheating, overvoltage or aging. Damaged components may cause certain functions of the circuit to fail, for example, a damaged capacitor may cause the car stereo to produce noise.
Corrosion
Prolonged exposure of the PCB to moisture and chemicals may lead to corrosion of the circuit, which in turn affects the conductivity. For example, in marine climates, salt and moisture may lead to corrosion of the metal parts of the circuit board, which can affect the stability of the entire circuit.
Thermal runaway
In high-temperature environments, certain components may overheat, resulting in reduced performance or permanent damage. Electronic devices around automobile engines are particularly susceptible to thermal runaway. Excessive temperatures may cause plastic parts on the circuit board to melt or warp.
Physical Damage
PCBs can be physically damaged due to accidental impact, vibration, or other external factors. This damage may result in circuit breakage or short circuits, affecting the normal operation of electronic equipment. For example, excessive vibration while traveling on a rugged road may cause damage to the connecting parts of the circuit board.
When the automobile PCB fails, timely repair is the key. The repair process usually includes the following steps:
Detection and diagnosis
Use a multimeter: check the continuity of the circuit to determine the location of the fault. By measuring voltage and current, you can quickly determine whether the circuit is normal.
Oscilloscope testing: Use an oscilloscope to observe signal waveforms, look for abnormal waveforms, and assess the operational status of the circuit. For example, test the amplitude and frequency of the signal waveform to determine whether the signal transmission is normal.
Fault code reading: Read the fault code with the help of special diagnostic tools to understand the source of the fault. Modern automobiles are usually equipped with OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics), and fault codes can be read and cleared by connecting an OBD-II scanner.
Cleaning the PCB
Use appropriate cleaners and tools to remove dirt and corrosion and ensure that the surface of the circuit board is clean. Timely cleaning, especially after signs of moisture or corrosion have been detected, can prevent malfunctions from worsening.
For heavily corroded areas, you can treat them with a solvent such as isopropyl alcohol to help remove oxides and restore conductivity.
Replacing damaged components
Based on the failure analysis, determine which components need to be replaced. Examine the appearance of the component to determine if it is burned, deformed, or otherwise visibly damaged.
Use a heat gun or soldering equipment to carefully remove damaged components to avoid secondary damage to the PCB. When replacing, ensure that the new component matches the parameters of the original component.
Resoldering
Use appropriate solder and soldering equipment to ensure good soldering quality and avoid false soldering. Pay attention to temperature control when soldering, too high temperature may damage the PCB.
Check whether the solder joints are smooth and even to ensure good electrical connection. After soldering, you can use a multimeter to check the continuity of the solder joints again.
Function Test
Before installing back into the vehicle, perform a function test on the repaired PCB to ensure that everything is in order, including functions such as signal transmission and power distribution. Function testing can be verified by connecting the PCB to the appropriate electrical system to ensure that all functions are normal.
Preventive measures
In order to reduce the incidence of PCB failure, owners can take the following preventive measures:
Regular Inspection
It is recommended that the electrical system of the car be inspected on a regular basis to detect potential problems early and avoid small failures from evolving into big losses. Inspections can include cable connections, solder joint status and power supply.
Avoid extreme environments
Minimize PCB exposure to extreme temperatures or humid environments, especially during the rainy season and winter, and pay attention to protecting the electronic equipment in the car. For example, after driving in heavy rain, the interior circuits should be checked for water buildup.
Use high-quality components
When replacing electronic components, use durable and reliable high-quality parts to improve the reliability of the overall circuit. Try to choose components from well-known brands to ensure their stable performance.
Keep the interior clean
Regularly clean the interior of the car to avoid dust and moisture from entering the electronic components and to ensure that the PCB is dry and clean. Car owners can use a clean damp cloth to wipe down the electrical equipment inside the car regularly to keep it in good condition.
Professional Maintenance
Vehicle owners are advised to seek the help of professional technicians when carrying out complicated repairs to ensure the accuracy and safety of the repairs. Professional technicians can provide more comprehensive diagnostic and repair services to ensure that the vehicle functions properly.
Use waterproof protection
Circuit boards that are susceptible to moisture can be treated with waterproof materials to enhance their moisture resistance. Using materials such as waterproof covers and sealants can effectively stop moisture from entering the interior of the PCB.
Avoid prolonged non-use
If the vehicle is not used for a long period of time, the engine should be started regularly to keep the battery charged to avoid the circuitry from malfunctioning due to a long period of inactivity. It is recommended to start the car once a month to keep the battery active and the circuits working properly.
Conclusion
Automotive printed circuit boards are the core of modern automotive electronic systems, and their failure may seriously affect the performance and safety of the vehicle. By understanding the functions, common faults, repair methods and preventive measures of PCBs, vehicle owners can deal with problems more effectively when they occur. At the same time, regular maintenance and reasonable use can also effectively extend the service life of the PCB to ensure the safe and stable operation of the car. Understanding this knowledge allows us to better protect the automotive electronic system and improve driving safety.