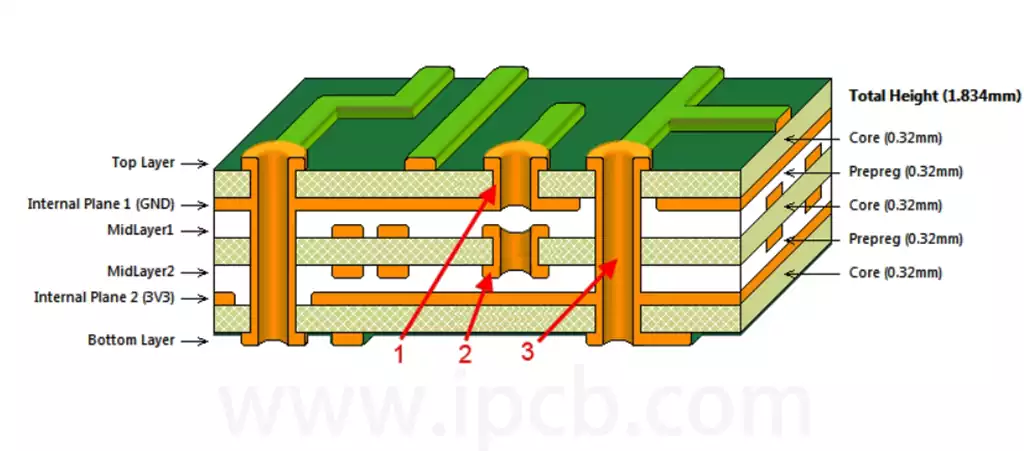
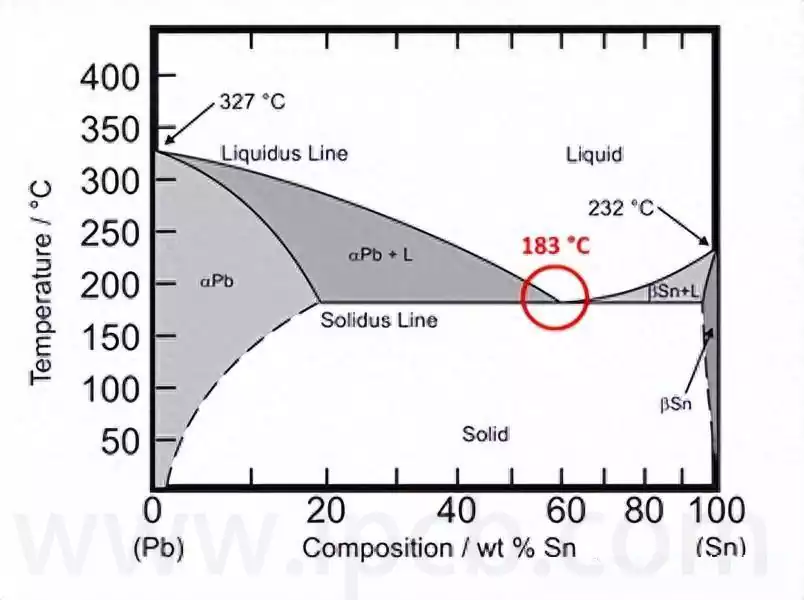
In the field of modern electronic manufacturing, the welding process is an important step to realize the functions of electronic equipment. In the welding process, soldering pins, as one of the core tools, undertake multiple functions such as connection, testing, and signal transmission.
In the welding process, soldering pins, as one of the core tools, undertake multiple functions such as connection, testing, and signal transmission.From circuit board design to finished product debugging, the use of soldering pins runs through the entire production process of electronic products.
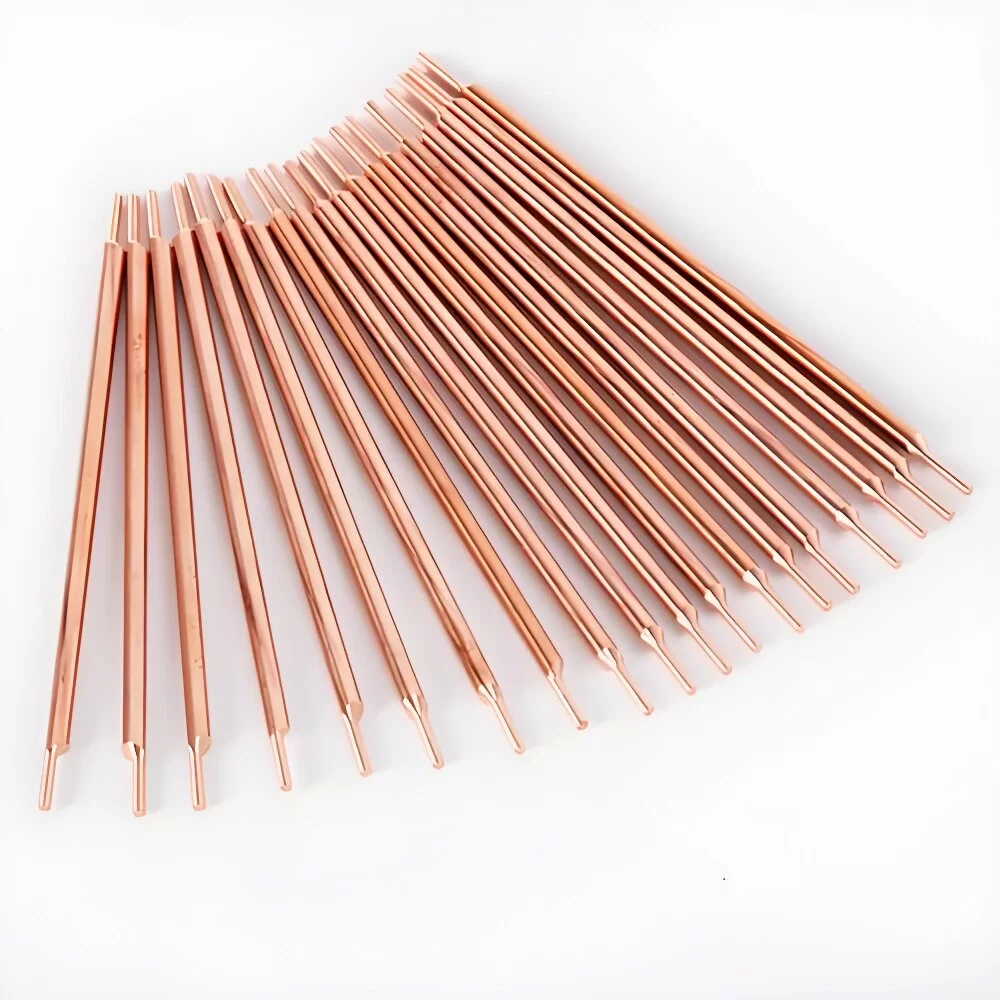

This article will analyze the definition, type, working principle, application scenarios, and future technology development direction of soldering pins in detail, so that readers can have a more comprehensive understanding of this seemingly simple but significant gadget.
Basic concept of soldering pins
Soldering pins are a common tool in electronic manufacturing, mainly used to connect circuits, test signals or assist in welding operations. They are mostly made of highly conductive metals such as copper alloys, stainless steel or tungsten alloys, and are often surface treated to enhance durability. The unique design of soldering pins enables them to operate stably for a long time in high-temperature welding and complex electrical environments.
Soldering pins are not only a medium for connecting circuits, but also an important tool for precise positioning. During the welding process, soldering pins need to withstand repeated pressure, friction and high temperature. It can ensure the stability of signal transmission and avoid poor contact. Especially in high-speed PCB manufacturing, the accuracy of soldering pins directly determines the welding quality.
Classification of soldering pins
Depending on the purpose and design, soldering pins can be divided into the following categories:
- Classification by purpose:
Test soldering pins:
Test soldering pins are mainly used for functional testing after the circuit board is soldered. By connecting the test equipment to the solder joints of the circuit board, it can quickly detect open circuits, short circuits and other welding defects. For example, in automated testing equipment, the soldering pin can accurately contact each test point, thereby greatly improving the detection efficiency.
Connection soldering pins:
This type of soldering pin is usually used to temporarily connect two-point circuits for signal debugging or short-term functional verification. They are often designed to be plug-in and unplug-convenient, which is convenient for multiple use.
Grounding soldering pins:
During circuit operation, the ground wire is the basis for maintaining circuit stability. Grounding soldering pins are usually used exclusively for current discharge or anti-interference processing, and their materials usually need to take into account both conductivity and wear resistance.
- Classification by structure:
Fixed pins:
Fixed pins have the characteristics of strong rigidity and stable structure, and are suitable for long-term high-intensity welding scenarios. Its design is simple, but it can provide high welding stability, and it is the first choice for traditional welding applications.
Spring needle:
The welding needle with a built-in spring can adjust the contact pressure through the elastic structure to adapt to welding points of different heights. This type of welding needle is widely used in multi-point contact test systems.
Needle tip needle:
The needle tip needle is particularly suitable for the operation of tiny welding points due to its extremely fine tip design. It is commonly used in the manufacture of high-precision electronic products, such as smart watches or medical devices.
- Classification by material:
Stainless steel welding needle:
Stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance and strength, and is suitable for use in high humidity or chemical environments.
Tungsten alloy welding needle:
Tungsten alloy is an ideal choice for frequent use scenarios due to its high hardness and excellent electrical conductivity.
Beryllium copper welding needle:
This material is light and has good electrical conductivity and flexibility. It is mostly used in lightweight test instruments.
Main materials and processes of welding needles
The material of the welding needle directly affects its performance and service life. Common welding needle materials include beryllium copper, tungsten alloy, stainless steel, etc. Each material has its unique characteristics and applicable scenarios.
Beryllium copper: Beryllium copper has extremely high electrical conductivity and good oxidation resistance, and is the main material for manufacturing high-precision soldering pins. It is often used in circuit boards that require high-frequency signal transmission, especially in the communications and computer industries. The elasticity and toughness of beryllium copper also enable it to maintain a long service life in high-temperature environments.
Tungsten alloy: As a high-melting-point metal, tungsten alloy is often used to manufacture soldering pins that withstand high-temperature environments. Tungsten alloy has extremely strong high-temperature resistance, so it is widely used in automotive, aerospace and other fields, and can provide stable performance under high temperature and high load.
Stainless steel: Stainless steel materials have excellent corrosion resistance and wear resistance, so they are suitable for welding some electronic products that need to be used for a long time. Its cost is relatively low, so it is widely used in mid- and low-end electronic products, especially in consumer electronic products.
In the manufacturing process of soldering pins, it usually goes through steps such as cutting, forming, gold plating, and surface treatment. Cutting and forming ensure the pin tip accuracy and shape, gold plating is used to enhance the pin’s conductivity and oxidation resistance, and surface treatment (such as silver plating, tin plating, etc.) makes the pin more corrosion-resistant.
Main performance parameters of solder pins
The pin performance directly affects the accuracy of soldering and testing. Here are several key parameters and their significance:
- Tip diameter:
The tip diameter determines the pin’s soldering accuracy. Smaller diameters are suitable for micro components, while larger diameters are more suitable for industrial applications. The need for precision has driven the development of smaller diameter pins to adapt to nanoscale circuit board manufacturing. - Working pressure:
The pin needs to provide a certain amount of pressure when contacting the solder joint, which is determined by an internal spring or fixed structure. Higher pressure can ensure stable contact, but too high pressure may damage the solder joint. - Conductivity:
The higher the conductivity of the pin, the more stable the signal transmission. This is especially important for high-frequency circuits and complex signal transmission. High-quality pins are usually improved in conductivity through processes such as gold plating. - Temperature resistance:
The soldering pin needs to withstand high temperature welding conditions. The higher the temperature resistance, the longer its life. Tungsten alloy or ceramic coated soldering pins perform particularly well under extreme conditions. - Service life:
The service life of the soldering pin is determined by the material hardness, wear resistance and surface treatment. A soldering pin used for a long time needs to maintain precise performance while withstanding high-frequency operation.
Quality control and inspection of soldering pins
In the production process of soldering pins, quality control is a crucial link. The accuracy and stability of soldering pins are directly related to the quality of the final product, especially in the production of high-precision electronic products, the quality control of soldering pins is particularly important. Manufacturers usually use advanced inspection technologies such as microscope inspection and X-ray inspection to ensure the accuracy and reliability of soldering pins.
Microscope inspection: Microscope inspection is mainly used to check the appearance of soldering pins, the shape of the needle tip and the smoothness of the pins. This is the first step to ensure the smooth progress of the welding process. Through the microscope, manufacturers can clearly observe whether there are defects or damage on the surface of the soldering pin.
X-ray detection: X-ray detection is used to detect the internal structure of the soldering pin, especially in the welding of small electronic components. X-rays can effectively detect whether the welding is uniform and whether the solder is fully penetrated. This is crucial for the production of high-end equipment.
In addition, manufacturers will regularly test the hardness, conductivity, corrosion resistance and other properties of the soldering pin to ensure that there will be no performance degradation during long-term use.
Maintenance and replacement of soldering pins
Although soldering pins play a very important role in electronic manufacturing, they also need regular maintenance and replacement. During long-term use, soldering pins may have problems such as wear and deformation, which will affect the quality of welding. Therefore, the maintenance and replacement of soldering pins should not be ignored.
Cleaning: After each use, the soldering pin needs to be cleaned in time to avoid the accumulation of solder residues and oxides. Generally, a cleaning agent or a special brush can be used to clean the surface of the soldering pin to ensure that it maintains good conductivity.
Inspection: The soldering pin should be checked regularly during use to check whether its needle tip is worn or bent. If obvious damage or deformation is found on the surface of the soldering pin, it should be replaced immediately to avoid affecting the welding effect.
Replacement standard: The service life of the welding pin is closely related to its material, frequency of use, working environment and other factors. When the welding pin is damaged or cannot be repaired, it should be replaced according to the recommended standards of the equipment manufacturer. Generally, when the wear of the welding pin reaches a certain level, replacement becomes more urgent.
Application of welding pins in different fields
The application field of welding pins is extremely wide, covering multiple industries such as communications, consumer electronics, automobiles, and medical equipment. In these fields, the role and technical requirements of welding pins are different.
Communication field: With the continuous development of 5G communication technology, the welding accuracy requirements of communication equipment are becoming more and more stringent. Welding pins play a vital role in the manufacture of 5G base stations, communication modules and other equipment. Due to the high frequency of 5G equipment, welding pins need to have extremely high conductivity and anti-interference ability to ensure stable signal transmission. Especially in high-frequency circuit boards and complex components, the precision welding of welding pins can ensure the stable performance of communication equipment.
Consumer electronics field: In the production process of consumer electronic products such as smartphones, tablets, and home appliances, welding pins are one of the key components. Modern consumer electronic products require not only extremely small size, but also high-density circuit design, so soldering pins need to be precisely soldered in a limited space. For high-precision mobile phone motherboards, headphone circuit boards and other products, the precision of soldering pins is directly related to the performance and stability of the products.
Automotive field: With the increasing degree of automotive electronics, the welding quality of automotive circuit boards is crucial to the overall safety and reliability of the car. Soldering pins play an irreplaceable role in the welding of automotive electronic modules, especially in battery management systems, autonomous driving technology and vehicle-mounted communication equipment, the stability and high temperature resistance of soldering pins cannot be ignored.
Medical field: Medical equipment has extremely high requirements for the stability and reliability of electronic components. Soldering pins are widely used in high-end medical devices such as pacemakers, blood glucose monitoring equipment, and medical imaging equipment. In these applications, soldering pins need to have extremely high precision and anti-interference capabilities to ensure the long-term stable operation of the equipment.
Future development trend of soldering pins
The advancement of soldering pin technology will help the electronics manufacturing industry cope with increasingly complex technical challenges. Here are several major trends:
- Miniaturization and high precision:
As the trend of miniaturization of electronic components intensifies, soldering pins need to achieve smaller sizes and higher welding precision. This requires production processes to break through traditional limits, such as the application of nano-processing technology will become more common. - Intelligent technology:
Future soldering pins will integrate intelligent sensing functions to achieve real-time monitoring and data feedback. For example, when the temperature of the solder joint is too high or the contact is poor, the intelligent soldering pin can issue an early warning to further improve production efficiency. - New material development:
Soldering pins such as graphene coatings or composite materials will improve conductivity and durability, providing more possibilities for emerging industrial applications. - Environmental protection and sustainability:
Soldering pin manufacturing will pay more attention to environmental protection, using recyclable materials and energy-saving processes. Recycling soldering pins not only reduces resource waste, but also reduces manufacturing costs.
Summary
Although soldering pins are small tools in electronic manufacturing, their role cannot be ignored. From circuit design to product production, soldering pins run through the entire process, providing a guarantee for production efficiency and product quality. As technology continues to advance, soldering pins will play an irreplaceable role in more complex and higher-precision manufacturing environments.