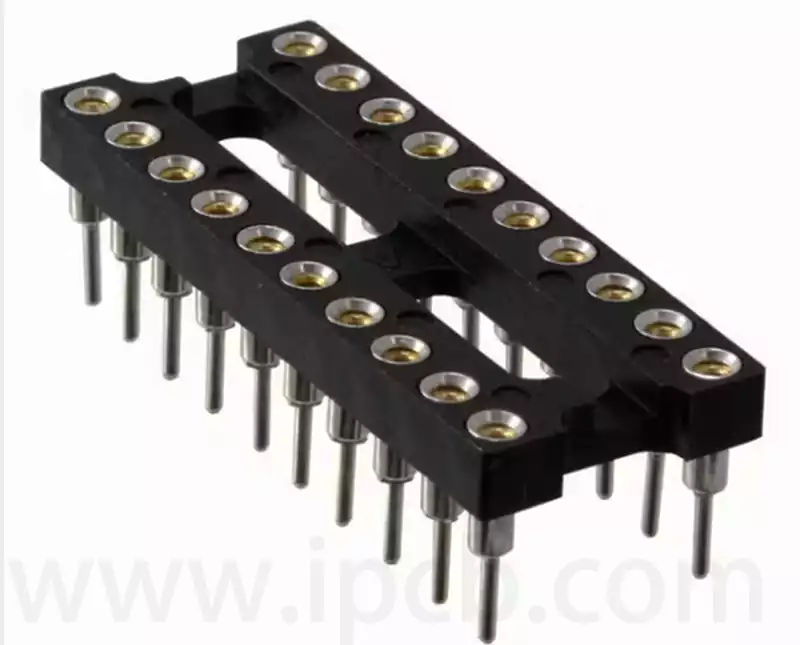
An integrated circuit socket, also known as an IC socket, is an interface used to connect integrated circuits. It allows integrated circuits to be easily inserted and removed, facilitating testing and replacement. This type of socket is widely used in various electronic devices, particularly those that require frequent replacement or testing of integrated circuits.
An integrated circuit socket is a connector designed to facilitate the connection between integrated circuits and circuit boards. It enables integrated circuits to be easily inserted and removed from circuit boards by matching the sockets on the circuit board with the pins on the integrated circuit package. Typically, an integrated circuit socket consists of two parts: the base and the plug.
The base is the foundation of an integrated circuit socket, typically made of insulating material. It securely mounts to the circuit board and provides support for the socket core. The underside of the base usually features small metal pins that help maintain the socket core’s position within the integrated circuit socket.
The socket is the second part of the IC socket, typically made of metal. It features electrodes that match the pins on the IC package, enabling it to be inserted into the IC and establish a connection with the circuit. The socket can be easily inserted into and removed from the base, allowing the IC to be replaced with ease.
An IC socket is a socket designed to accommodate IC pins, available in various specifications such as 8, 16, 18, and 20 pins. Through the IC socket, chips on the circuit can be directly inserted and removed without the need for a soldering iron for desoldering. This not only enhances flexibility during chip assembly, facilitates maintenance and replacement, streamlines assembly procedures, and saves labor and time, but also improves contact performance and conductivity, enabling circuit layout miniaturization and high density.
An 8-pin IC socket has a specific pin arrangement that corresponds to the pins on the integrated circuit. Typically, the number of pins on an IC socket is determined by the number of pins on the connected integrated circuit. In an 8-pin IC socket, “8-pin” refers to the fact that the socket has 8 pins, designed to connect to an integrated circuit with 8 pins.
The design of integrated circuit socket is typically directional, meaning that the integrated circuit must be inserted into the socket in the correct orientation to ensure that each pin is accurately connected to its corresponding interface. This directionality is achieved through the physical design of the socket and the arrangement of the pins.
The basic operating principle of an IC socket is to use elastic metal contacts to form a reliable electrical connection with the IC pins, thereby ensuring signal transmission and power supply between the IC and the PCB.
The pins or contacts of IC sockets typically use a spring-loaded structure to apply sufficient pressure, ensuring good contact between the IC pins and the socket, thereby reducing contact resistance and improving signal integrity. Additionally, some IC sockets are equipped with locking mechanisms to prevent the IC from becoming loose due to external impacts.
In high-frequency applications, signal integrity is critical for IC sockets. To minimize the effects of parasitic inductance and capacitance, the pins of IC sockets are typically designed with a short and thick structure, and ground connections are optimized to reduce signal loss.
Classification of IC Sockets
IC sockets can be categorized based on different classification criteria, including packaging type, installation method, and insertion/removal method.

Classification by Package Type
IC sockets must be compatible with specific IC packages, so they can be categorized based on the IC’s package type as follows:
DIP Socket (Dual In-line Package Socket): Used for ICs in DIP packages, typically employed in traditional through-hole mounted circuit boards. The pins of the DIP socket align with the pads on the PCB, allowing the IC to be easily inserted and removed.
SOP/SOIC Socket (Small Outline Package/Small Outline Integrated Circuit Socket): Used for ICs in SOP or SOIC packaging, these sockets are generally used in surface mount technology (SMT) applications.
QFP Socket (Quad Flat Package Socket): Used for ICs in QFP packaging, suitable for high-pin-count, high-density integrated circuits.
BGA sockets (Ball Grid Array Socket): Used for ICs in BGA packaging, primarily applied in high-end microprocessors and high-speed data transmission fields.
Classified by installation method
Through-hole sockets (Through-hole Socket): IC sockets suitable for through-hole soldering, typically used for ICs in DIP packaging.
Surface Mount Socket: Used for SMT processes, suitable for ICs in surface mount packages such as SOP and QFP.
Classified by insertion/removal method
Zero Insertion Force Socket (ZIF): Allows ICs to be inserted or removed without applying excessive force, suitable for high-end testing and development environments.
Low Insertion Force Socket (LIF): Requires a certain amount of force to insert the IC, but is relatively easy to remove.
Spring-loaded Socket: Uses spring contacts to connect with IC pins, suitable for applications requiring frequent insertion and removal.
Main Functions of Integrated Circuit Socket
- Facilitates IC Replacement
Integrated circuit socket serves as connectors between ICs and circuit boards. Since IC sockets can be easily inserted and removed, ICs can be conveniently replaced. When an IC malfunctions or requires an upgrade, there is no need to replace the entire circuit board; simply replacing the IC saves significant time and cost. - Protection of integrated circuits
Integrated circuit socket also protects integrated circuits. Since they can be easily inserted and removed, they prevent damage to integrated circuits during installation and removal. Additionally, another important function of integrated circuit sockets is to protect the pins of integrated circuits. If integrated circuits are directly soldered to the circuit board, their pins are prone to damage from heat, but integrated circuit sockets prevent this from occurring. - Facilitating Maintenance and Testing
Another important benefit of using integrated circuit socket is that they facilitate maintenance and testing of circuit boards. If an integrated circuit on the circuit board malfunctions, technicians can easily remove the integrated circuit and identify the issue through testing. Without integrated circuit sockets, this task would be extremely challenging.
Integrated circuit socket plays a crucial role in electronic devices by providing connection, protection, and ease of maintenance. They not only simplify the process of replacing and testing chips but also effectively ensure the safety and signal quality of integrated circuits. As technology advances, IC sockets will continue to play a key role in electronic design and applications, driving industry development.