A board electronics with holes is a substrate used for the layout of electronic components and its function is to connect electronic components. It is a design element on a circuit board, which is a hole set up to facilitate the insertion, connection and soldering of circuit board components.
The core principle behind the functioning of board electronics with holes lies in the design of the metal or plastic grids used in their construction. These grids can be connected to each other to create a variety of circuit layouts, such as resistors, capacitors, inductors and other components. By connecting the grids as required, users can assemble complex circuits that can be experimented with and tested. During the experimental phase, users can also adjust the parameters of some components to observe the changes in the operating status and performance of the circuit.
According to the material differences and different areas of application, board electronics with holes can be subdivided into the following categories:
Metal-based hole boards: These boards are usually made of copper or aluminium, and have excellent electrical and thermal conductivity properties, making them ideal for use in high-frequency circuit construction and power amplifiers and other high-energy devices.
Plastic-based holey boards: They are mainly made of lightweight and durable plastic materials such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polypropylene (PP), and are suitable for building low-frequency circuits and simple logic circuit systems, and are easy to carry and use.
Ceramic-based hole boards: made of alumina or other high-performance ceramic materials, they are widely used in applications requiring high reliability and stability due to their excellent insulating properties and high-temperature resistance.
Comprehensive hole boards: These boards incorporate a variety of grid designs and connector types designed to accommodate diverse user needs. Some of the integrated boards are additionally equipped with LED indicators or other auxiliary components to facilitate the user’s intuitive demonstration and functionality.
Manufacturing process of board electronics with holes:
Material selection: According to the specific needs and actual conditions, select the appropriate substrate materials, such as plastic or cardboard;
Circuit design: according to the circuit schematic diagram, planning the circuit layout of the required board, and clear hole board size specifications;
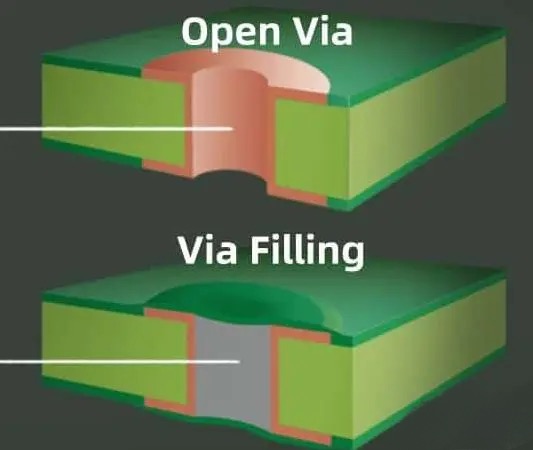
Moulding: transferring the designed circuit layout to the selected substrate, and accurately punching holes in the substrate through drilling machines or manual operations;
Stamping and moulding: using press-fit machinery, the copper layer around the holes is stamped and removed to form through-holes for circuit connections;
Copper coverage: to ensure the integrity of the circuit connections, a layer of copper is uniformly coated on the substrate so that the copper layer covers the entire substrate and fills the through-holes;
Corrosion treatment: the copper coated substrate is placed in an etching solution to remove the excess copper layer, leaving only the copper in the lines and through-holes that form the circuit;
Anti-corrosion film formation: the substrate is immersed in an acidic solution to create a yellow-green copper oxide protective film on its surface, which enhances the durability and chemical stability of the circuit;
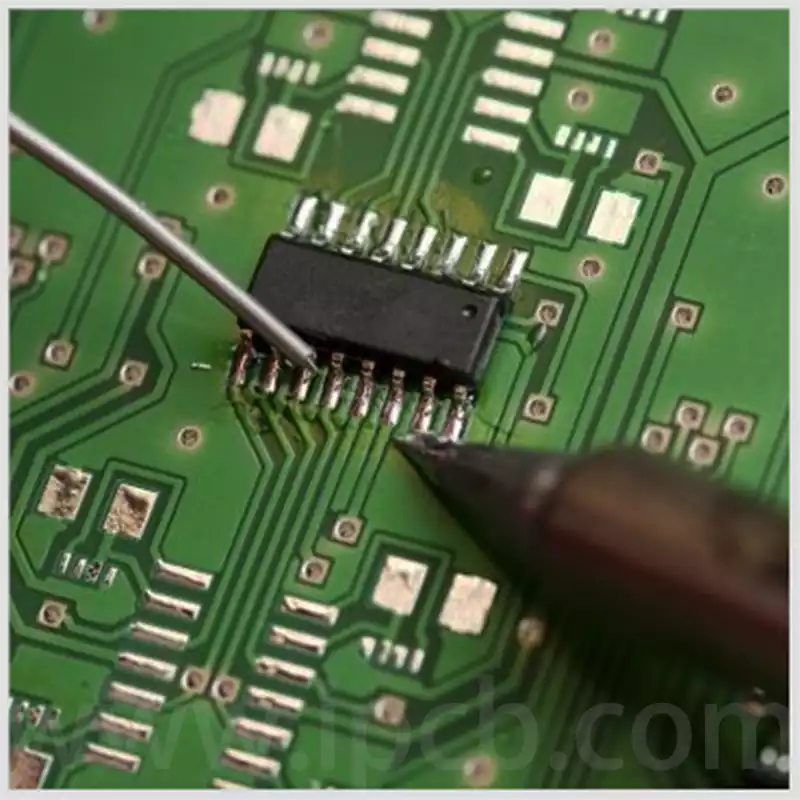
Component soldering: Finally, through the solder or other electronic components, the required electronic devices will be fixed and soldered to the designated location of the hole board.
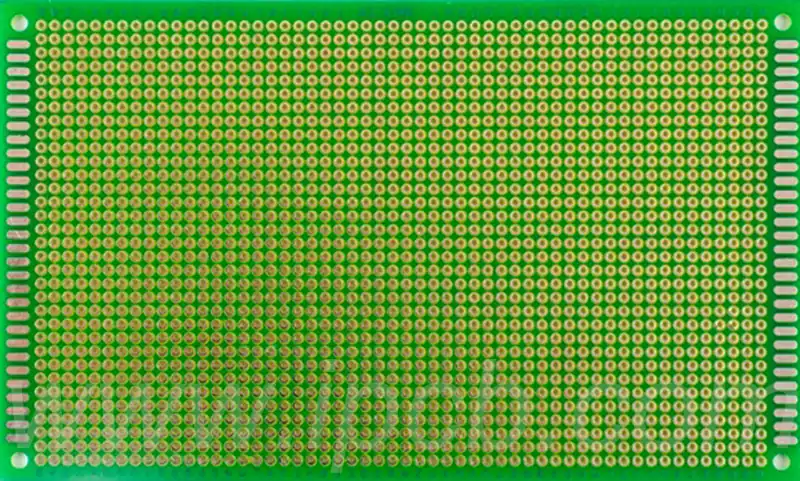

Functions of board electronics with holes:
Wire bridging: the board electronics with holes provides a mechanism that allows wires to cross its surface to make connections from one side to the other, thus building pathways between circuits.
Component Assembly Soldering: It allows the pins of electronic components to pass through the holes and be tightly bonded to the board by soldering to achieve an effective connection between the component and the circuit.
Thermal Management: board electronics with holes also play the role of a heat sink, either through natural air flow or the role of an auxiliary fan, to help dissipate the heat that gathers around the components, thus maintaining the safe operation of the electronic components.
Board electronics with holes in the circuit board design and manufacturing of the diverse applications:
Component Layout Organisation: Hole-in-the-wall boards can efficiently connect the pins of multiple individual components (e.g. resistors and capacitors) so that they are arranged in an orderly manner on the board.
Wiring Flexibility: Compared to fixed electrical paths on printed circuit boards, holey boards offer a higher degree of wiring freedom and the ability to flexibly adjust the circuit layout as needed.
Thermal Conductive Design: Through careful planning of the layout and density of the holey boards, heat dispersion and conduction on the board can be effectively achieved.
Plug-in Soldering Adaptation: Hole-in-the-wall boards are designed to be compatible with the soldering requirements of a variety of plug-ins, including board card connectors, D-shaped plug-ins (round and rectangular), etc., which provides a convenient way of fixing and connecting plug-ins.
With its flexibility and versatility, the board electronics with holes play an irreplaceable role in circuit board design and manufacturing. Whether it is component layout, wiring adjustment, or heat dissipation management, electronic hole boards have demonstrated their excellent performance, injecting new vitality into the development of the electronics industry.