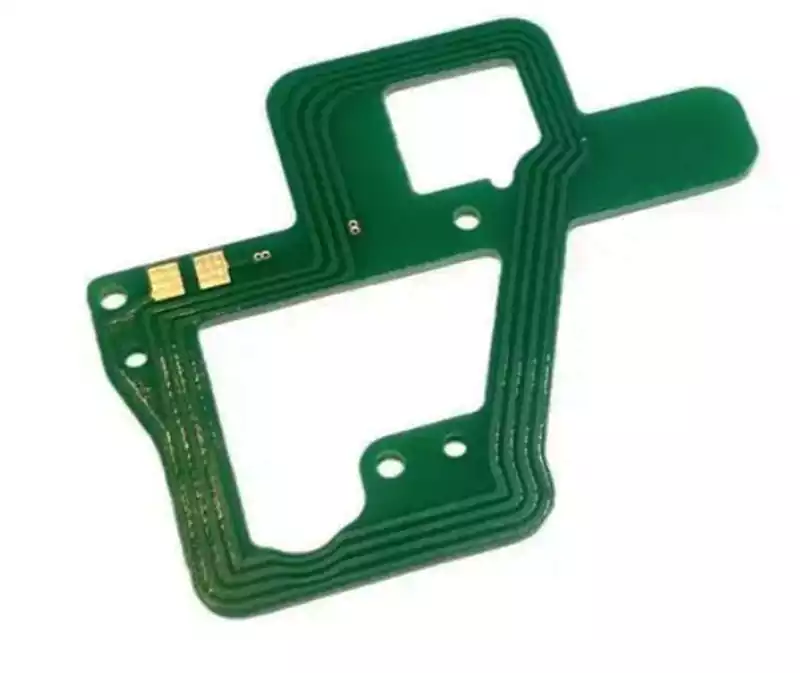
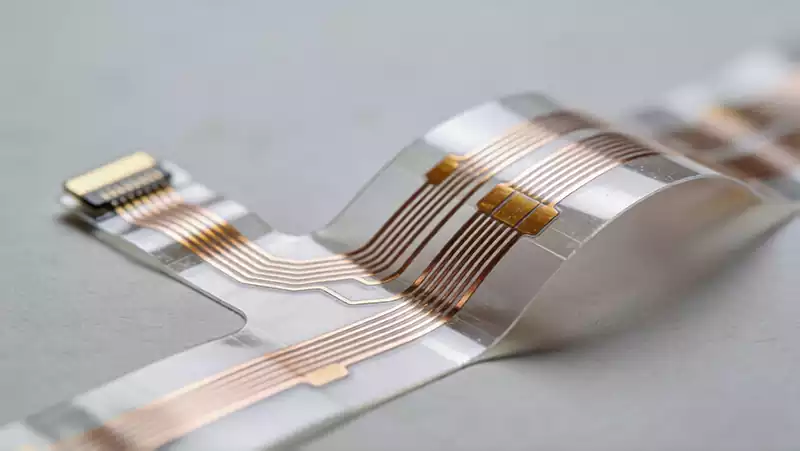
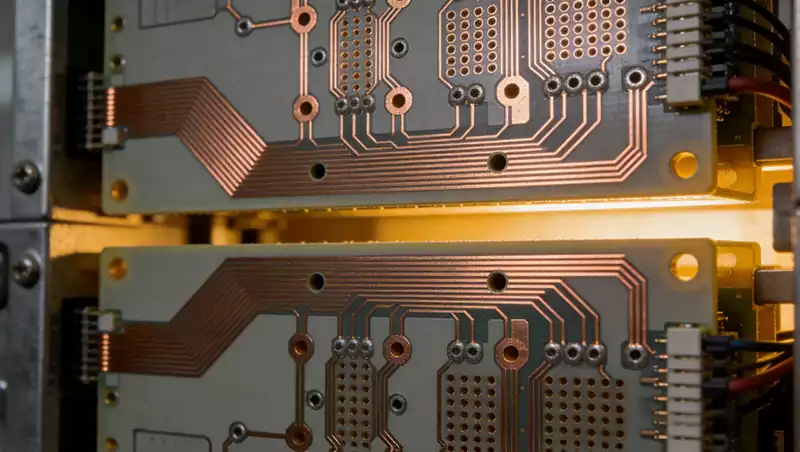
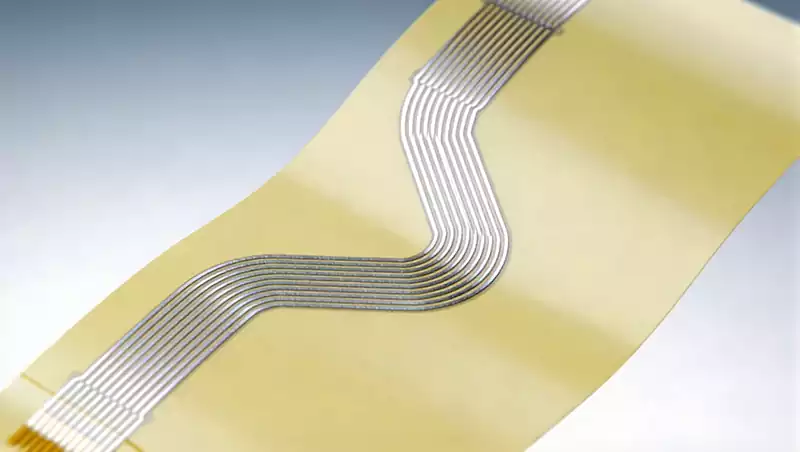
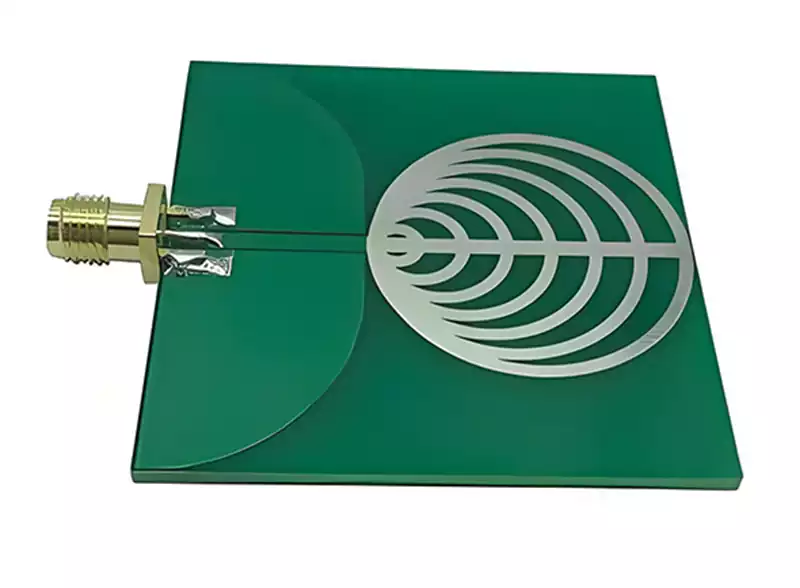
High frequency PCB via optimisation
The success or failure of signal transmission in high frequency PCBs is often determined by details imperceptible to the naked eye. Via holes, serving as the core conduits for interconnecting signals between PCB layers, may appear merely as minute apertures piercing through the board layers. Yet in high frequency scenarios, they become the ‘invisible killers’ […]