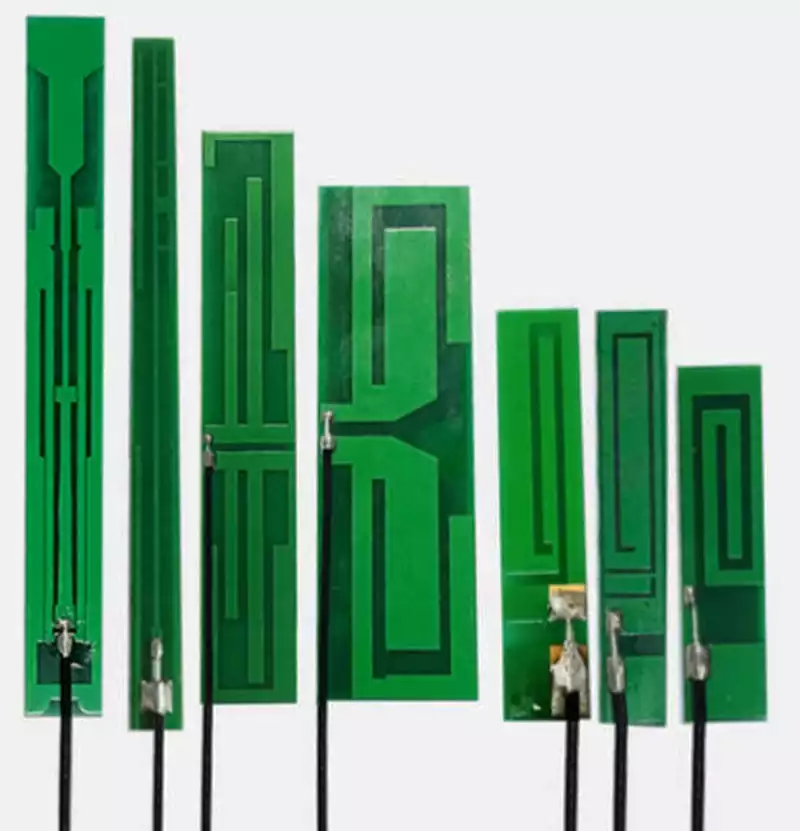
Differences in Frequency Bands for Automotive Radar PCB Antenna Design
All design differences between 24 GHz and 77 GHz automotive radar PCB antenna boards fundamentally stem from the distinct physical characteristics of the frequency bands themselves. Frequency determines wavelength, and wavelength directly affects antenna size, signal loss, and radiation efficiency—thereby driving adjustments across every stage of PCB design. The wavelength at 24 GHz is approximately […]