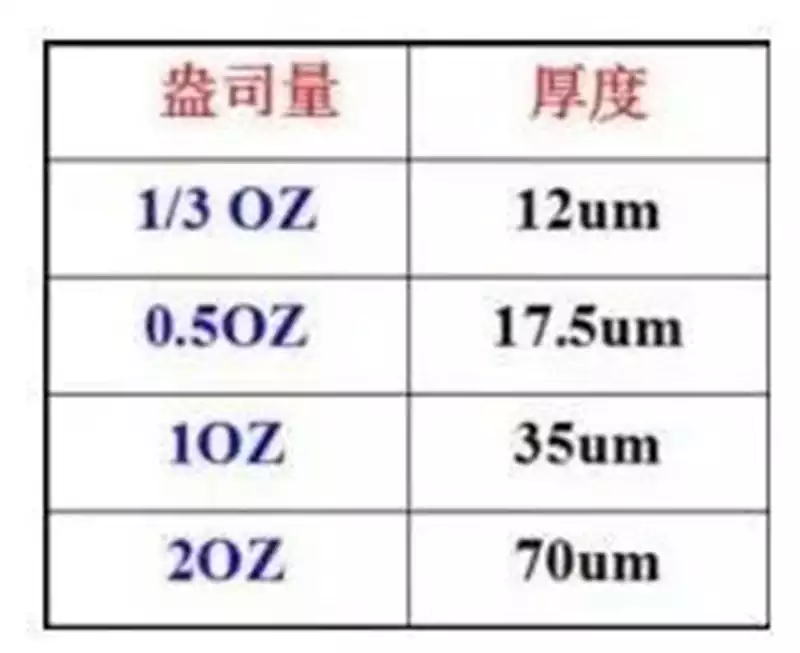
Printed circuit board (PCB) as a core component of modern electronic equipment, its quality and reliability of the performance of the entire electronic system plays a vital role. However, during the manufacturing, storage and use of PCBs, they are affected by various factors such as temperature, humidity, contaminants and process operations, and often suffer from a variety of defects. These defects not only affect the function and life of the circuit board, and may even lead to equipment failure, serious irreversible damage to the entire system. Therefore, understanding and mastering the causes of common printed circuit board defects, to improve manufacturing quality and ensure the stable operation of electronic products is of great significance.
1.Temperature
In the storage and component installation process, printed circuit board will experience temperature changes, especially in extreme environments, multiple temperature fluctuations may become a hidden danger of component or solder joint failure. The maximum and minimum operating temperatures of the PCB circuit board should be taken into full consideration during design, as the expansion and contraction caused by temperature changes will accelerate the aging and failure of the printed circuit board.
2.Humidity
Printed circuit board in the manufacturing and preservation process if exposed to a humid environment, easy to trigger short-circuit phenomenon, may also lead to different types of damage to components in the circuit. Moisture in the environment can damage the solder and lead to corrosion problems, thus affecting the normal operation of the circuit board.
3.Contaminants
In the manufacturing and subsequent storage process, dust. The intrusion of pests and other contaminants may make the printed circuit board defective, weakening its performance and reliability. These external contaminants can affect the quality of the PCB and reduce its service life.
4.Impact
Impacts on printed circuit boards can be disastrous in the manufacturing, storage and transport of PCBs. Storage and transport can be disastrous. PCB circuit board that are dropped violently or not manufactured in the normal way can cause excessive vibration, and as a result, the printed circuit board loses flexibility, which in turn damages the PCB’s alignment.
5.Short and Open Circuits
Causes may include negligence at the design stage, such as too narrow a line spacing or layers are not properly aligned; manufacturing process etching is not complete. Drilling errors or solder resist residue in the pad area can also lead to such problems.
6.Soldermask defects
Uneven coating: If the soldermask is not evenly distributed when applied, it may expose the copper foil, thus increasing the risk of short circuit.
Incomplete curing: Due to poor control of baking temperature or time, solder resist may not be fully cured, affecting its protective effect.
7.Poor screen printing
Insufficient printing accuracy: Lower accuracy or improper operation of screen printing equipment can lead to fuzzy characters . Missing or positional offset.
Ink quality is not good: the use of poor quality ink or ink and substrate mismatch, will reduce the clarity of the logo and adhesion.
8.Welding defects
Void soldering phenomenon: due to component pins are not clean . Not fully tinned, or the circuit board is not adequately cleaned and flux quality problems, may trigger false soldering.
Abnormal solder buildup: too much or too little solder, usually with the quality of solder. Soldering temperature and iron withdrawal time.
Overheating and cold soldering: too much iron power or too long heating time will lead to overheating; solder is not solidified before the action of the jitter may cause cold soldering.
9.Hole Defects
Drilling Error: Worn out drill bits or inaccurate positioning can lead to oversized holes or deviation from the designed position.
Unclean debonding: Resin left after drilling is not thoroughly removed, affecting welding quality and electrical performance.
10.Interlayer separation and blistering
Thermal stress problem: During reflow soldering, the mismatch of expansion coefficients of different materials may trigger interlayer delamination.
Moisture intrusion: Insufficiently dried printed circuit board absorbs moisture before assembly, and water vapour forms vapour bubbles during soldering, leading to internal blistering.
11.Poor plating
Uneven plating: uneven distribution of current density or fluctuations in the composition of the plating solution can cause uneven thickness of copper plating.
Pollution problems: too many impurities in the plating solution affects the quality of the plating layer, resulting in defects.
Printed circuit board in the manufacture, storage and use of various links, may be due to temperature fluctuations, humidity effects, contaminants invasion and improper process control and other factors and produce a variety of defects. These problems not only affect the performance and reliability of the PCB, but also may directly lead to the failure of electronic equipment and performance degradation. Therefore, an in-depth understanding and effective control of the causes of various types of defects is of great significance to improve the manufacturing quality of PCB circuit boards and ensure the stable operation of electronic products.