Patch antenna is a commonly used antenna for wireless communication and is widely used in many small electronic devices. It has the advantages of miniaturisation, easy fabrication, easy integration and higher operating frequency band.
The principle of patch antenna is based on electromagnetic induction and electromagnetic radiation. It is made of a metal sheet, which can be a conductive material such as copper or aluminium. This metal sheet is pasted or soldered on the surface of the circuit board, so it is called ‘patch’ antenna.
When a patch antenna is connected to an RF source in a circuit, a current is passed through the metal sheet in the antenna. This current generates an electromagnetic field on the metal sheet, which is radiated and, according to Ampere’s law, forms an electromagnetic wave similar to that of the RF signal source.
When a patch antenna is connected to an RF source in a circuit, a current is passed through the metal sheet in the antenna. This current generates an electromagnetic field on the metal sheet, which is radiated and, according to Ampere’s law, forms an electromagnetic wave similar to that of the RF signal source.
Types of Patch Antennas
According to different application scenarios, patch antennas can be classified into various types, such as:
- PIFA Antenna: the abbreviation of Planar Inverted F Antenna, it is a kind of board-mounted antenna, which is commonly used in mobile phones, televisions, routers and other devices.
- Coated Patch Antenna: This type of antenna coats a metal foil directly onto the surface of an electronic device in order to reduce manufacturing costs and footprint.
- PCB Antenna: Abbreviation for Printed Circuit Board, it is a printed circuit board antenna, which is widely used in scenes such as rail transport.
Applications of Patch Antennas
Patch antennas have been used in a variety of electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, networking devices, wireless routers, and so on. With patch antenna, these devices do not need external antenna, which is more convenient to carry and use. At the same time, the small size of patch antenna can also reduce the size of electronic devices, more convenient to carry.
A microstrip antenna is an antenna structure that uses a microstrip line as a radiator. It consists of three main parts: a metal patch, a dielectric substrate and a ground plane. The metal patch acts as a radiator and connects to the feed point through the microstrip line; the dielectric substrate provides the support structure and isolation layer; and the ground plane acts as a reflector and insulator.
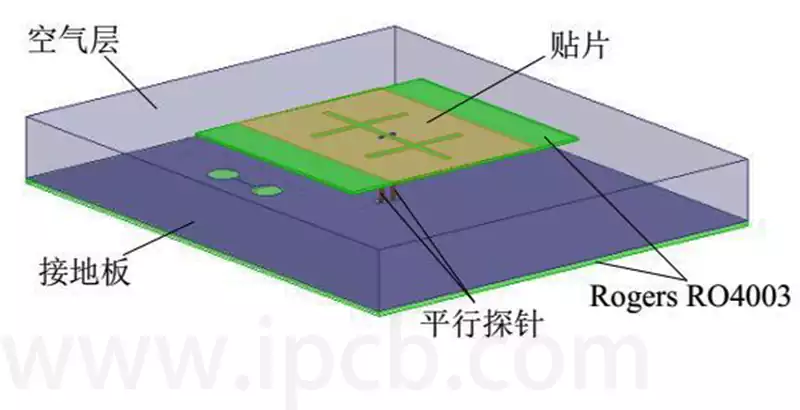
Common Microstrip Patch Antenna Structures
- Rectangular Microstrip Patch Antenna
The rectangular microstrip patch antenna is the most common type, which is simple and easy to fabricate. It usually consists of a dielectric substrate, a metal patch and a ground plate, and the metal patch is generally rectangular. This type of antenna has good radiation characteristics and moderate gain, and is widely used in wireless communication systems. - circular microstrip patch antenna
Circular microstrip patch antenna is a kind of deformed microstrip patch antenna, whose metal patch is circular or nearly circular. Compared with rectangular patch antenna, it has better radiation characteristics and higher gain, and at the same time, the structure is more compact, suitable for the antenna size has strict requirements of the scene. - Triangular Microstrip Patch Antenna
Triangular patch antenna is a kind of microstrip patch antenna with a special shape, whose metal patch is in the shape of equilateral triangle or isosceles triangle. This kind of antenna has higher gain and wider bandwidth, and at the same time the structure is simple and easy to fabricate, which is suitable for some specific wireless communication needs.
Advantages, Disadvantages and Applications of Microstrip Antennas
Compared with ordinary microwave antennas, microstrip antennas have the following advantages.
- low profile, small size, light weight, and
- with a planar structure, easy to missiles, satellites and other carriers surface conformal.
- Suitable for mass production of printed circuit technology.
- Can be integrated into a single module with active devices and circuits.
- Easy to obtain circular polarisation, easy to achieve dual-band, dual-polarisation and other multifunctional work.
Disadvantages of microstrip antennas are:
- Narrow frequency band;
- conductor and dielectric losses, will stimulate surface waves, resulting in reduced radiation efficiency
- Small power capacity, generally applicable to medium and low power occasions
- Performance is greatly affected by the substrate material. Microstrip antenna has been applied to a large number of radio equipment in the wide frequency domain of 100MHz-100GHz, especially in the aircraft and ground portable equipment.
Difference between microstrip antenna and patch antenna
Patch antenna is a form of microstrip antenna, but there are some differences between the two in the structure and working principle:
1.Structural differences
Microstrip antenna: usually consists of a radiating patch, a dielectric substrate, and a ground plate, and the patch is suspended on top of the dielectric substrate.
Patch antenna: the radiating element of patch antenna is directly attached to the dielectric substrate, usually there is no obvious suspension structure.
2.Feed mode
Microstrip antenna: the feed is usually connected to the radiating patch through the probe or microstrip line.
Patch antenna: the feed is more diverse, can be edge-fed, gap-fed or coplanar feed, etc.
3.Radiation efficiency microstrip antenna
Due to the existence of a certain gap between the radiation patch and the ground plate, there may be a certain air gap loss, affecting the radiation efficiency. Patch antenna:The radiating element of patch antenna is closely combined with dielectric substrate, which usually has higher radiation efficiency.
4.Bandwidth performance
Microstrip antenna:The bandwidth is relatively narrow, need to optimise the design to improve the bandwidth.
Patch antenna:A wide bandwidth can be achieved by designing various structures, such as adding radar ribs or using multilayer structures.
5.Applications
Microstrip Antenna:Suitable for applications with strict requirements on profile height, such as satellite communications and mobile communications. Patch antennas:Due to their structural versatility, they can be used in a wider range of applications, including radar, wireless LANs and personal communication systems.