Flex PCBA refers to printed circuit boards and their assembly technology made of flexible materials. This kind of circuit board is characterized by high wiring density, light weight and thin skin, and is constructed very reliably on the basis of flex, capable of bending, twisting and folding. It is suitable for special shapes and can meet a variety of complex space and shape requirements.
Compared with traditional rigid PCBA, flexible PCBA has the following significant features:
Flexibility:It can be bent, folded and even twisted, enabling it to adapt to a variety of complex space and shape requirements.
Lightweight: The use of flexible materials makes PCBA thinner and lighter, helping to reduce the overall weight of the device.
Reliability: Good durability and impact resistance, able to work stably in harsh environments.
Customizability:Can be custom designed according to specific needs to meet the individual needs of customers.
Automotive electronic PCBA board flexible circuit can be divided into four categories:
1. Bidirectional access to the flexible circuit, which is a single-sided flexible circuit, the purpose of manufacturing this circuit is to be able to access conductive materials from both sides of the flexible circuit boards.
2. Double-sided flexible circuits, is a kind of circuit with two conductive layers, two conductive layers are located in the circuit of the basic layer of the two sides; for your specific requirements, you can form the alignment pattern in the two sides of the substrate sheet, the two sides of the alignment can be realized through the copper-plated holes to connect to each other.
3. Multilayer flexible circuits, is the combination of several single-sided circuits with complex interconnections or double-sided circuits, in the multilayer design often need to use shielding technology and surface mount technology.
4. Rigid-flexible circuits, rigid printed circuit boards and flexible circuits, the advantages of both integrated, the circuit is usually through the rigid circuit and flexible circuit between the plated holes to achieve interconnection.
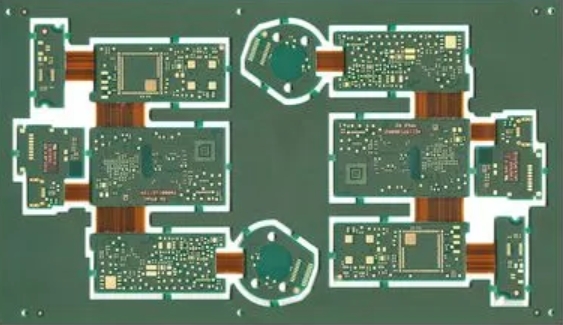
What is the difference between rigid PCB and flexible FPC?
Rigid PCBA is often referred to as a PCBA without emphasizing that it is a rigid PCB.There are a variety of different things that people will consider when thinking about circuit boards. These different discussions will determine which type of circuit board you purchase from the PCBA website.In a rigid PCB,the non-conductive substrate usually includes a glass fabric that reinforces the board and provides it with power and stiffness.Our discussion of rigid PCBAs centers more on their thermal resistance characteristics.
Although flexible flex circuit boards also have wires on a non-conductive substrate, such boards use a flexible substrate that includes polyimide (PI). The curved base allows the FPC to withstand vibration, dissipate heat and fold into different shapes. Because of their structural advantages, flexible circuits are increasingly used as an alternative to compact gadgets, including smart wearables, cell phones and cameras.
In addition to the underlying structure and stresses, the big differences between rigid PCBs and flexible circuits include.
1. Conductive Fabric: Since flexible circuits should bend, manufacturers can also use softer rolled annealed copper instead of conductive copper.
2. Manufacturing systems: Instead of using soldermask, flexible PCBA manufacturers use a system called a cover layer or overlay to protect the uncovered circuitry of the flexible PCB.
3. Typical Cost: Flexible circuits are typically more expensive than rigid circuits. However, because flexible circuit boards can be connected in tight spaces, engineers can reduce the size of their products, thereby saving overhead.
As an important innovation in the electronics manufacturing industry, flex PCBA technology is leading the industry’s new wave with its unique advantages and wide range of application prospects.