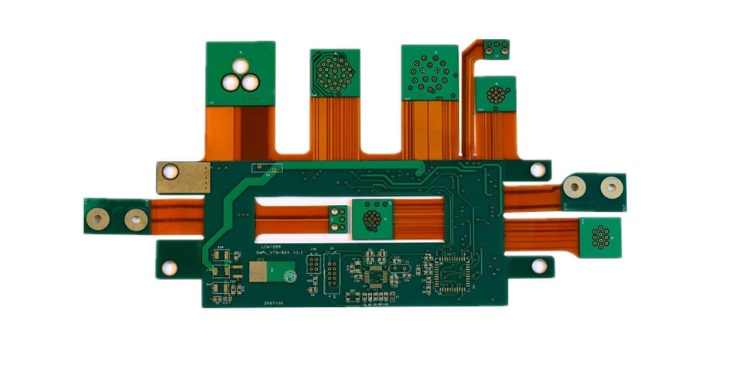
Flexible board, is the so-called flexible circuit board, in fact, also belongs to a kind of printed circuit boards, but with the traditional printed circuit boards and has a great difference, so it will be called flexible board, full name of the flexible circuit board.
Flexible board generally use PI as a substrate, is a flexible material, can be bent and flexed arbitrarily.Flexible board is usually used in the need to repeat the flex and some small parts of the link, but now it is not only so, the current smartphone is trying to bend to prevent, which requires the use of FPC flexible board this key technology.
PCB is the so-called printed circuit board, usually will be called PCB hard board, is the electronic components in the support body, is very important electronic components. PCB hard board usually use FR4 as a substrate, also called FR4 circuit board, can not be bent, flexing.
PCB hard board is usually used in some places that do not need to bend and have more hard strength, such as computer motherboards, mobile phone motherboards and so on. In fact, flexible board is not only the circuit board can be flexed, but it is also connected to the three-dimensional line structure of the important design, this structure with other electronic product design, you can build a variety of different applications, therefore, from this point of view, FPC and PCB is very different. Flexible board of course, you can use the terminals to connect the line connection, but you can also use the soft hard board to avoid these Connection mechanism, a single FPC can use the layout of the configuration of many hard board and will be connected. This approach reduces connector and terminal interference, which can improve signal quality and product reliability. For PCB, unless the way to make three-dimensional form of the line with film glue, the circuit board in general conditions are flat. Therefore, to make full use of three-dimensional space, flexible board is a good solution. In terms of hardboards, the common space extension programme is to use the slot plus the interface card, but FPC as long as the adapter design can make a similar structure, and in the direction of the design is also more flexible. Using a piece of connecting FPC, two pieces of rigid board can be connected into a set of parallel line system, can also be folded into any angle to adapt to different product shape design.
Flexible boards are more expensive than rigid boards for this reason:
Material cost analysis
Flexible boards are made of more expensive materials than rigid boards. Flexible PCBs usually use materials with high moisture absorption and high temperature resistance, such as polyimide (PI), which are relatively expensive. In addition, the conductive layer of the flexible PCB is usually made of precious metal materials such as gold and silver, which are more expensive than ordinary conductive materials such as copper.
Processing complexity impact
Flexible board production and processing process is relatively cumbersome, requiring multiple processes, including film preparation, film lamination, circuit patterning, lithography, etching, etc.. Each process requires a high degree of precision and expertise, increasing production costs.
At the same time, there is a high failure rate in the production of flexible boards, because the film material is easily affected by environmental factors during processing, and it is difficult to control the film preparation process, resulting in a high rate of scrap, which further increases the cost.
Large investment in equipment
Flexible board production requires special production equipment, including film preparation equipment, film lamination equipment, photolithography equipment. These devices are expensive and have high investment costs. At the same time, due to the high process requirements of flexible PCB, the maintenance and repair of equipment also requires a higher level of technology and economic investment, increasing production costs.
High technical requirements
Flexible PCB production process requires a high level of technology. For example, the preparation of conductive materials requires control of their thickness and quality, the film lamination process requires precise temperature and pressure control, and the photolithography process requires high-precision patterning. These requirements require employees with high technical skills, increasing training and management costs.
There are significant differences between flexible boards and PCB rigid boards in terms of materials, processing, equipment investment and technical requirements, etc. Flexible boards, with their unique flexibility and three-dimensional line design capabilities, show unrivalled advantages in applications that require repetitive flexing and complex spatial layouts. However, these advantages also bring higher production costs, mainly in expensive materials, complex processing, high equipment investment and strict technical requirements. Nevertheless, with the development of electronic products to thin and light, bendable direction, the importance of flexible board will become more and more prominent, its application in the future of electronic manufacturing is promising.