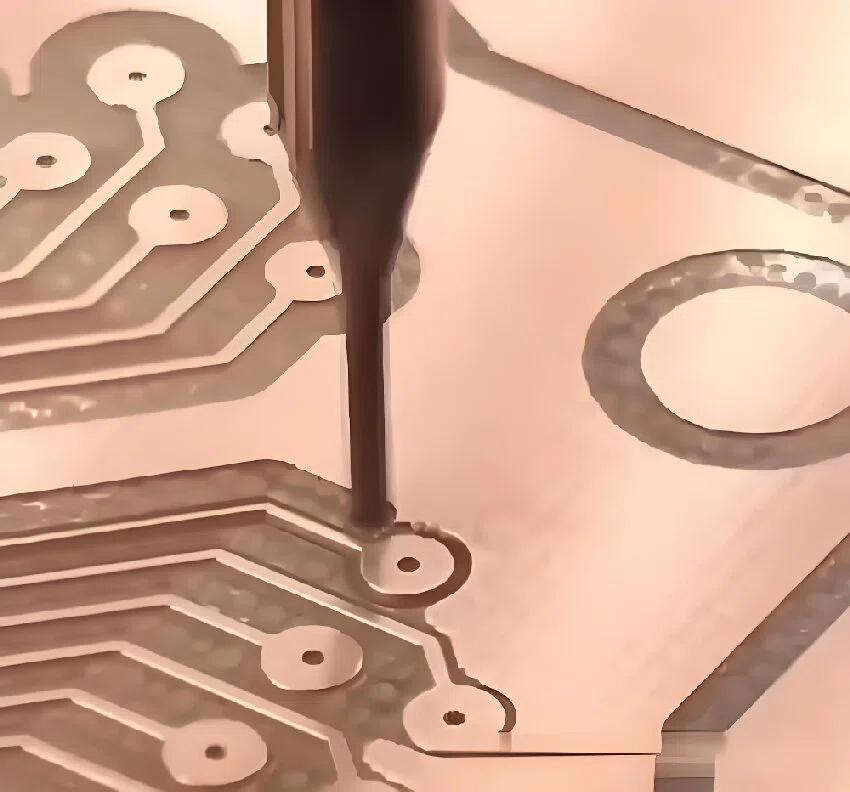
FPCB, also known as Flexible Printed Circuit Board, is a flexible circuit board. Because FPC flexible board can be freely bent, coiled, folded and other advantages, greatly reducing the size of electronic products, applicable to electronic products to high-density, miniaturization, high-reliability direction of the development of the need for FPC in aerospace, military, mobile communications, laptop computers, computer peripherals, PDAs, digital cameras, and other fields or products have been widely used.
Characteristics of Flexible Printed Circuit Board
Reduce the size of the applied products, save space, reduce the weight significantly, increase the role and reduce the cost.
Highly flexible, can be three-dimensional wiring, according to the space limitations to change the shape.
Can be folded without affecting the signal transmission function, anti-static interference.
Resistant to high and low temperatures, flame resistant.
Chemically stable, high stability and reliability.
Provide more design solutions for related products, reduce assembly time and errors, and improve the service life of related products.
The role of fpcb
The functions of flexible boards can be categorized into four types, which are lead-in, printed circuit, connector, and multi-functional integrated system.
Leaded circuits: Connections between rigid printed circuit boards, stereo circuits, movable circuits, and high-density circuits.
Printed circuits: high-density thin stereo circuits
Connectors: Low-cost connections between rigid boards
Multi-function integration system: Integration of rigid board leads and connectors
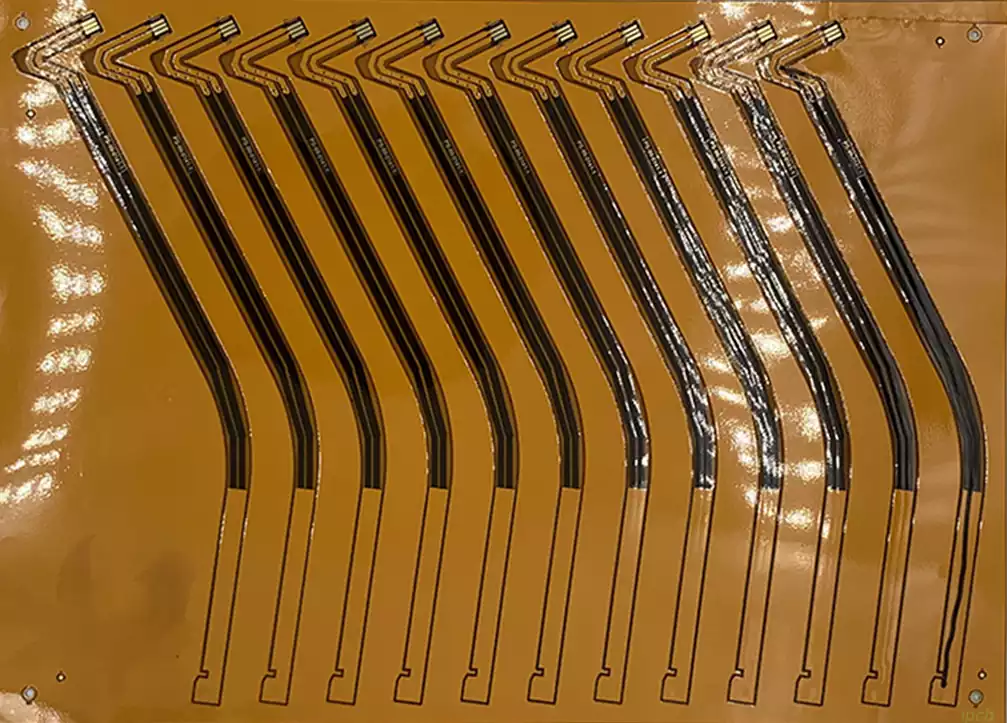

Compared to traditional rigid boards, FPCB has better bendability and flexibility, allowing them to adapt to more complex device forms and design requirements. This unique performance makes it widely used in smartphones, wearables, medical devices, and other fields.
In the field of smartphones, with its thin, light and flexible characteristics, it provides a solution for the connection of internal components of cell phones. Traditional rigid circuit boards are difficult to meet the demand of modern smartphones for thinness and portability due to their large size and poor bendability. FPCBs, on the other hand, can easily realize the flexible connection of the internal components of cell phones, providing more possibilities for the design of cell phones.
In the field of wearable devices, this kind of circuit board also shows great advantages. Wearable devices need to be close to the user, which requires the circuit board must have a high degree of flexibility.
In addition to smartphones and wearable devices, they also play an important role in the field of medical devices. Some medical devices need to be implanted inside the human body, which requires a high degree of flexibility and biocompatibility of the circuit board.
The production process for FPCB is a complex and delicate one, involving several key steps:
Material selection: First, a suitable flexible substrate, such as polyimide (PI), needs to be selected. These materials have good flexibility, high temperature resistance and electrical insulation properties. In addition, it is also necessary to select appropriate conductive materials and protective films, etc.
Design and Graphics: According to the product demand and circuit requirements, the designer will utilize professional circuit design software to draw graphics, including circuit wiring, pad locations, dimensions, etc.
Plate making: A photolithography mask plate is made according to the designed circuit graphics. This mask plate will be used in the subsequent circuit fabrication process.
Circuit Fabrication: A photosensitive solder resist is coated on a flexible substrate, and then the circuit pattern is transferred to the substrate through exposure and development processes. Next, unwanted parts are removed by chemical etching or laser engraving to form the circuit line.
Conductive layer treatment: A layer of highly conductive metal, such as copper or silver, is applied to the circuit line to improve the conductivity and corrosion resistance of the circuit.
Insulation Covering: Covering the circuit lines with a layer of insulating material to protect the circuits and prevent short circuits.
Punching and Connecting: Drilling holes in the insulation to connect the circuit wiring to external connectors. This usually involves techniques such as brazing, gluing or patching.
Surface treatment: Surface treatment of circuit lines, such as the application of protective coatings, soldering treatment, etc., in order to enhance their durability and reliability.
Quality Inspection: Stringent quality inspection is performed on the produced boards, including conduction test, impedance test, appearance inspection, etc., to ensure that they meet the product requirements and quality standards.
Cutting and assembly: According to the product requirements, FPCBs are cut into the required size and assembled with other pcb components such as chips, resistors, capacitors,etc.
As the future star of flexible electronics, FPCB is leading the new trend of electronic manufacturing industry with its unique performance and wide range of applications.