The fr4 dielectric constant is a physical quantity that measures the degree of polarization of a dielectric material in the presence of an electric field. For copper-clad materials, the dielectric constant determines the speed of signal propagation in a circuit as well as the delay of the signal.The dielectric constant of Fr4 is usually in the range of 4.2-4.7, which indicates that it has good insulating properties and signal transmission capability.
Effects of Fr4 Dielectric Constant
Signal Transmission Speed: The speed of signal transmission is a key factor in PCB design, and the dielectric constant of Fr4 determines the speed at which a signal travels through a circuit. A lower dielectric constant means faster signal propagation, while a higher dielectric constant reduces the signal propagation speed. Designers need to select the appropriate Fr4 board for their needs to ensure stable and accurate signal transmission.
Delay and Crosstalk: Delay is the time required for a signal to travel while crosstalk is the phenomenon of a signal being interfered with by other signals during transmission. The dielectric constant of Fr4 affects the degree of delay and crosstalk. In high-speed circuits, where delay and crosstalk are particularly problematic, selecting Fr4 boards with the proper dielectric constant is critical to improving circuit performance.
Power Capacity: The dielectric constant of Fr4 also determines its power capacity at high voltages and frequencies. Higher dielectric constants provide better insulation properties, thus increasing the power capacity of the circuit. However, too high a dielectric constant can lead to reduced signal transmission speeds and increased delays. Therefore, the relationship between dielectric constant and power capacity needs to be considered when selecting Fr4 boards.
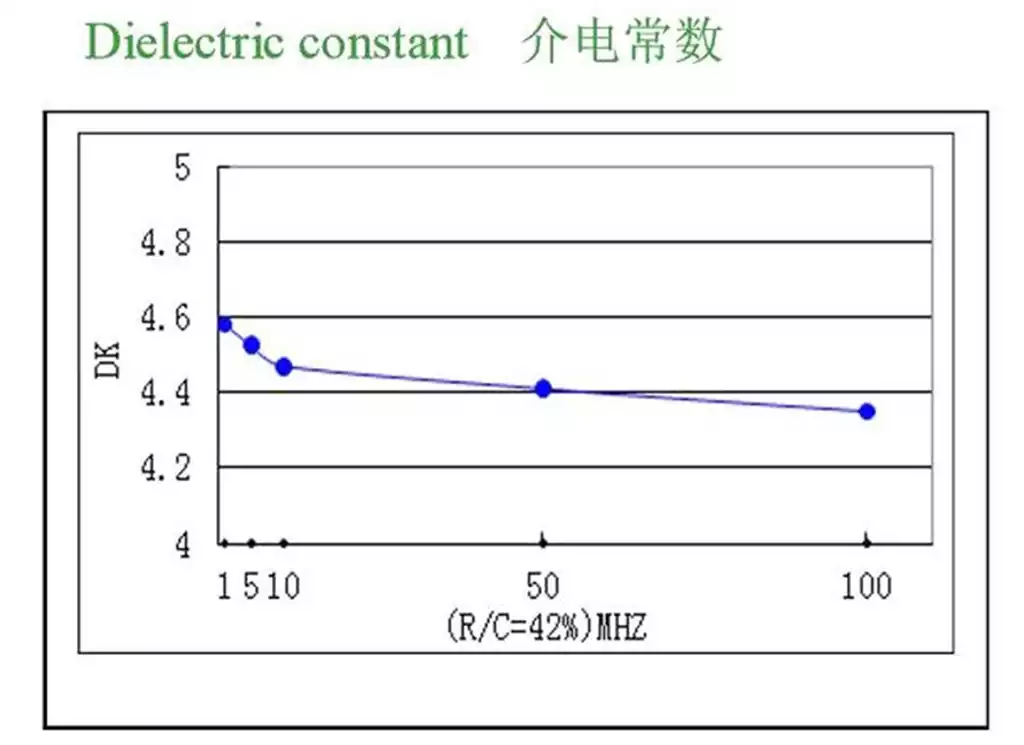
FR-4 sheet is made of epoxy resin + glass cloth pressed into a double-sided copper-clad PCB sheet, generally used FR4 copper-clad sheet, relative to the air’s dielectric constant is 4.2-4.7. This dielectric constant will change with the temperature, in the temperature range of 0-70 degrees, the maximum range of change can reach 20%. A change in dielectric constant will result in a 10% change in line delay, the higher the temperature, the greater the delay. Dielectric constant will also change with the frequency of the signal, the higher the frequency the smaller the dielectric constant, the general design of the dielectric constant of the classic value of 4.4. dielectric constant with the frequency change as shown in Figure:
Dk control (dielectric constant control), compared to high-frequency materials has a stable Dk, but FR-4 behaves erratically. For low-frequency applications, not being able to control Dk well is not much of a problem, but there are sometimes exceptions. Even low-frequency circuits sometimes require impedance control, and a stable Dk is good for high yields on impedance-controlled boards.
Very low Df control characteristics for low-frequency applications are usually not a problem either. If an electronics engineer wants to use FR-4 in an application where the loss factor is a consideration for this product, the following are some of the factors to consider
Limitations of High Frequency Applications
As operating frequencies increase, especially into the high frequency bands above GHz, the dielectric loss of FR4 begins to significantly affect signal integrity, resulting in increased signal attenuation, phase noise, and possibly circuit stability. Therefore, when designing high-frequency RF circuits (e.g., 5G communications, satellite communication systems, etc.), engineers often consider using high-performance materials with lower dielectric constants and lower dielectric losses, such as PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), Rogers series sheets, etc., which provide better control of signal propagation speeds and reduced energy losses.
How to choose the right Fr4 board
According to application requirements: Different applications have different requirements for the dielectric constant of Fr4 boards. For example, in high-speed digital circuits, a lower dielectric constant may be more appropriate to increase signaling speed. In high voltage and power applications, a higher dielectric constant provides better insulation and power capacity.
Material Performance Parameters: In addition to the dielectric constant, there are other material performance parameters to consider, such as heat resistance, mechanical strength, stability, etc. These parameters will affect the performance of the Fr4 sheet. These parameters will affect the service life and reliability of the Fr4 board, which in turn will affect the performance of the entire circuit.
Cost and availability: Fr4 materials from different manufacturers and brands may vary in price and availability. When selecting Fr4 boards, factors such as cost, performance and reliability should be considered to find the best material for your needs.
In summary, understanding the Fr4 dielectric constant is critical to the proper selection and use of this material. In PCB design, selecting Fr4 boards with the proper dielectric constant optimizes signal transmission, improves circuit performance, and ensures stable and reliable circuit operation.