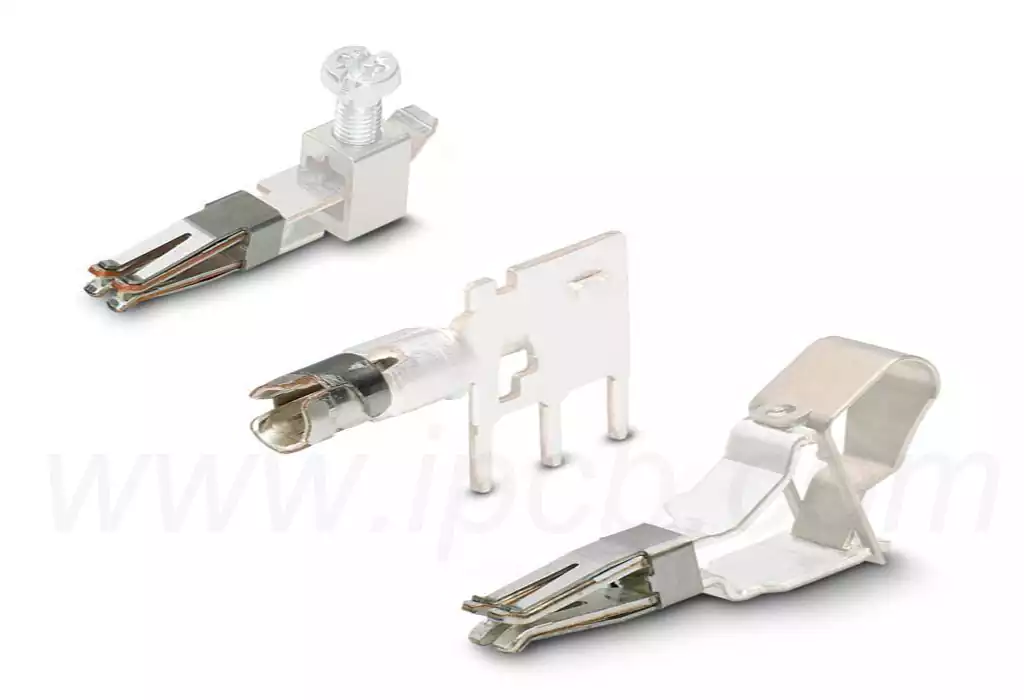
In the precision manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs), the surface finish of cleaning copper wire for soldering is critical. These wires are a core component of the soldering process, and their surface cleanliness directly affects the quality of the soldering and further determines the overall performance and reliability of the final circuit board. Therefore, ensuring that the copper wires are thoroughly cleaned prior to soldering is a key component in guaranteeing high quality soldering and excellent circuit performance.
Impact of Improper Cleaning on the Long-Term Performance of PCB:
Corrosion Risk
Improper cleaning copper wire for soldering of PCB can lead to flux residues that contain ionic compounds that corrode the board surface, increasing the risk of failure. Especially in humid environments, the corrosive nature of the residues can be exacerbated, leading to long-term performance degradation.
Electrochemical Migration
Uncleaned PCBs may be subject to electrochemical corrosion and chemical migration under the influence of temperature and humidity. This may not only affect the strength of solder joints, but may also cause short circuits that can lead to failure of the entire board. If halides are hidden underneath components, this can be disastrous due to improper localized cleaning.
Short circuits and failures
Contaminants on the surface of the PCB can lead to dendrite growth, a phenomenon that is particularly noticeable in high humidity environments. The growth of dendrites can cause unwanted connections between circuits, leading to short circuits. This occurrence can directly affect the normal operation of the equipment and shorten its life.
Performance degradation
Chronic poor cleaning copper wire for soldering can also lead to performance degradation of the PCB substrate. For example, uncleaned components on the board may affect the efficiency of signal transmission, leading to signal distortion, increased noise, and so on. This type of problem is particularly acute in high-frequency applications, where cleanliness is critical to signal integrity.
Maintenance and Cost
Improper cleaning also increases the cost of PCB maintenance. For PCBs that are already damaged, the cost of repair or replacement is often higher than the initial cost of cleaning. Therefore, maintaining PCB cleanliness is critical to reducing long-term operating costs.
Cleaning copper wire for soldering plays an indispensable role in PCB soldering, providing a solid foundation for improving soldering quality, securing electrical connections and extending the life of equipment:
Improved soldering quality
Cleaning copper wire for soldering significantly improves the soldering quality of circuit boards. During the soldering process, oxides and other contaminants on the surface of clening copper wire for soldering can affect the wettability of the solder, resulting in weak solder joints or false soldering. Therefore, thorough cleaning of copper wire surfaces ensures good solder flow during soldering, resulting in strong solder joints.
Ensure good electrical connection
Ensuring a good electrical connection is crucial in PCB soldering. If the surface of the copper wire is dirty or oxidized, it may prevent current from passing through, leading to problems such as signal attenuation or short circuits. After cleaning, the electrical conductivity of the copper wire is improved, helping to ensure the reliability and stability of the electrical connection.
Extends the life of electronic components
By removing contaminants and oxidized layers from the surface of copper wires used for soldering, you can reduce the risk of equipment failure in subsequent use. Contaminated solder joints tend to lead to unstable current flow, which in turn affects the efficiency of the entire electronic assembly. Regular cleaning extends the service life of electronic components and reduces repair and replacement costs.
Facilitates post-soldering maintenance
Cleaning copper wire for soldering is not only important before soldering, but also after. With proper cleaning measures, the quality of soldering is maintained by preventing the re-formation of oxides. Good post-soldering maintenance also improves the overall performance and reliability of the equipment and ensures that the product meets the expected performance specifications.
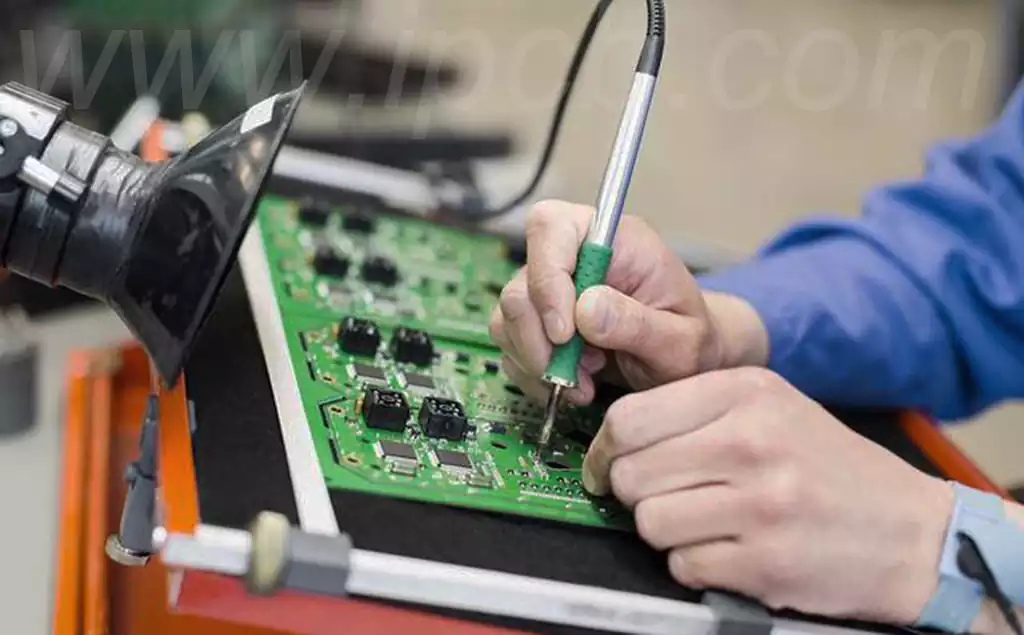

Common methods for cleaning copper wire for soldering
Physical Cleaning Methods
Physical cleaning is one of the most common methods for soldering copper wire.Fine sandpaper, cloth or metal brush can be used to gently rub the copper wire to remove surface oxides and other impurities. This method is simple and effective, but care needs to be taken to avoid physical damage to the copper wire and maintain its integrity.
Chemical Cleaner Use
Chemical cleaning is another effective cleaning method.The use of specialized solder cleaners can effectively remove oxides and flux residue. These cleaners often contain strong chemicals that quickly break down contaminants attached to the surface of copper wire. When using them,follow the product instructions to ensure safe operation.
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning
To maintain soldering quality, it is important to clean copper wire for soldering on a regular basis.Cleaning before and after each use is recommended to prevent the accumulation of oxides and impurities. Regular cleaning not only improves soldering efficiency, but also extends the life of the copper wire.Keeping the working environment as clean as possible will help minimize the occurrence of contamination.
Use of flux
The proper use of flux during the soldering process can also reduce oxidation on the surface of copper wire. Flux can effectively improve the quality of soldered joints by making it easier for the solder to wet and adhere. Before soldering, make sure that the clean copper wire surface is coated with an appropriate amount of flux to achieve better soldering results.
Testing the performance of PCB board after cleaning:
Visual Inspection
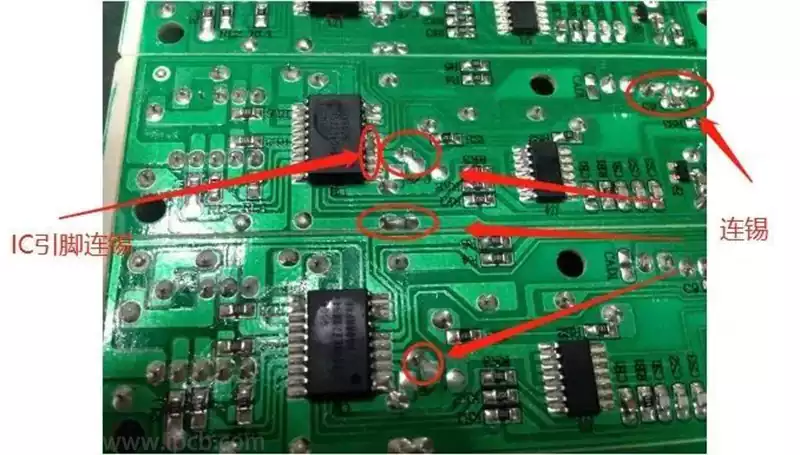
Visual inspection is a very intuitive method of evaluating the effectiveness of cleaning. By looking at the PCB surface through a body-view microscope or electron microscope, the appearance of the cleaned circuit board can be directly examined to confirm whether there are any visible residues or contaminants. This method is simple and easy to use, but has limited ability to detect tiny particles and contaminants hidden on the underside of components, so it often needs to be used in combination with other inspection methods.
Cleanliness Test
Cleanliness testing is an important means of evaluating the effectiveness of PCB cleaning. Commonly used test methods include ionic contaminant test and surface insulation resistance test. Ionic contaminant test by measuring the PCB surface residual ion concentration to assess the cleanliness, usually using the standard is ≤ 0.2 (NaCl) micrograms per square centimeter. The Surface Insulation Resistance Test, on the other hand, is able to assess whether cleaning is still effective in preventing electrical failures by measuring the level of insulation resistance between PCB conductors.
Electrical Performance Test
Electrical performance testing evaluates the functionality of PCBs through actual operating conditions. During the test, the signal transmission capability and power stability of the PCB can be measured under different environmental conditions. By comparing the changes in electrical performance before and after cleaning, it is possible to determine whether the cleaning is effective and whether it has negatively affected the overall performance of the PCB.
Residue Analysis
Residue analysis is also an important method to monitor the effectiveness of PCB cleaning. By analyzing the chemical composition of the residue on the surface of the PCB, you can determine whether the cleaning effect of the cleaning agent is ideal. Common analysis methods include weighing and optical analysis to confirm the presence of different types of residues and their potential impact on the product.
Flux Residue Detection
Flux residue in the cleaned PCB is a key factor in evaluating cleaning effectiveness. According to IPC standards, there must be clear residue detection thresholds for PCBs with different types of fluxes to ensure subsequent soldering and product reliability. Regular testing of flux residue concentration allows for better control of PCB cleaning quality.
The cleaning copper wire for soldering plays an extremely important role in the manufacture of printed circuit boards (PCBs). A good cleaning process not only improves soldering quality and ensures the stability of the electrical connection, but also extends the service life of electronic components and reduces maintenance costs. The long-term performance of PCBs can be significantly improved through an effective combination of physical and chemical cleaning methods, as well as regular maintenance and cleaning.