Printed circuit board recycling refers to the process of treating and reusing discarded printed circuit boards (PCBs). Waste circuit boards contain a large amount of precious metals, such as copper, gold, silver, etc. Therefore, through professional recycling technology can effectively reduce the waste of resources and achieve the purpose of environmental protection.Printed circuit board recycling can not only reuse these metals, but also avoid environmental pollution caused by improper disposal.
Hazards of circuit boards
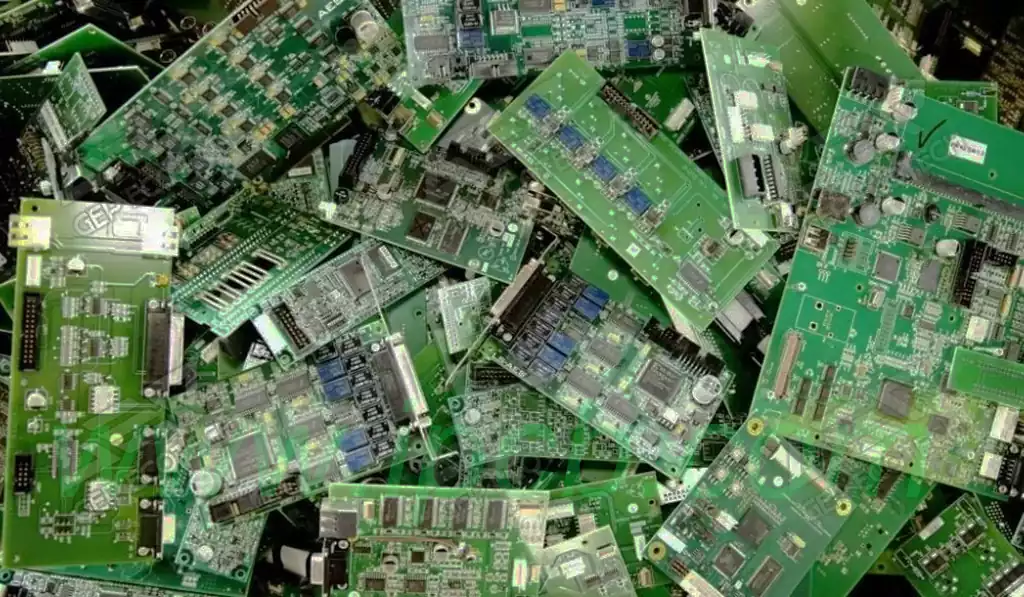
In the world, billions of circuit boards are shipped from circuit board manufacturers every day. In every day every day life, there are probably hundreds of millions of tons of waste circuit boards pile up. Once the circuit boards are piled up, over time they will be harmful to our ecosystem as well as to the health of human beings. No matter which circuit board will produce organic pollution to society. There are PCBA board above the electronic components will also give there is pollution, the most important pollution or metal pollution, especially tin, lead, cadmium and other heavy metals, directly endangering human health.
To be more professional, the waste printed circuit board is a mixture of glass fiber reinforced resin and a variety of metals, is a typical electronic waste, if not properly handled and disposed of, not only will result in a large loss of useful resources, but also contains a large number of cadmium and brominated flame retardants, such as teratogenic, mutagenic, carcinogenic substances, the environment and human health will be a serious hazard.
The printed circuit board recycling generally includes physical and chemical treatment processes. For example, circuit boards can be shredded through physical sorting and then separated using the physical properties of different materials to extract metallic and non-metallic components. Advanced chemical technologies can also be used to extract metals from circuit boards, thus achieving the goals of environmental protection and resource reuse.
How to recycle printed circuit boards
- Physical method
Physical method realizes the printed circuit board recycling through mechanical means and the difference of physical properties of PCBs.
1.1 Crushing
The goal of crushing is to try to separate the metal and organic matter within the waste circuit board to improve the separation efficiency. Studies have shown that when crushed to 0.6mm, the metal can be almost 100% separation effect, but the crushing method and the number of levels need to be selected according to the subsequent process.
1.2 Sorting
Sorting through the material density, particle size, electrical conductivity, magnetic conductivity and surface properties and other physical characteristics to achieve separation. Currently commonly used sorting techniques include wind shaker, flotation, cyclone separation, floatation and sinking, and eddy current sorting.
- Supercritical technology processing method
Supercritical fluid extraction technology is a method of purification and separation based on the effect of pressure and temperature on the solubility of supercritical fluids without changing the conditions of chemical composition. Compared with traditional extraction methods, supercritical CO2 extraction has the advantages of being environmentally friendly, easy to separate, low toxicity, almost no residue and can be operated at room temperature.
Research on supercritical fluids in the treatment of waste PCBs has focused on two directions: first, supercritical CO2 fluids can effectively extract the resin and brominated flame retardant components in printed circuit boards. When the resin bonding material is removed by supercritical CO2 fluid, the copper foil layer and the glass fiber layer can be separated more easily, thus achieving efficient recycling. Secondly, supercritical fluids are directly utilized to extract metals from scrap PCBs. It has been shown that the efficiency of metal extraction from model samples such as cellulose filter paper or sand using lithium fluorinated diethyl dithiocarbamate (LiFDDC) as the complexing agent is more than 90%.
Despite the many advantages of supercritical processing techniques, there are still some drawbacks, such as the high selectivity means that entrapping agents need to be added, which may have an impact on the environment; in addition, the extraction process requires high pressure and temperature, which puts high demands on the equipment and consumes more energy.
3.Chemical method
Chemical treatment technology is a process of extraction through the differences in chemical stability of different components in PCB.
3.1 Thermal treatment method
Thermal treatment method mainly through the high temperature way to make organic matter and metal separation, including incineration, vacuum cracking method and microwave treatment method.
3.1.1 Incineration method
Incineration method will be crushed to the specified particle size of electronic waste, placed in the incinerator for burning, decomposition of organic components and separation of gas and solid. The residue left after incineration contains bare metals or their oxides and glass fibers, which can be recycled by physical and chemical methods after crushing. However, this method produces large amounts of exhaust gases and toxic substances.
3.1.2 Cracking
Cracking, also known as dry distillation, involves placing the e-waste in an airtight container, controlling the temperature and pressure of the heating, and carrying out thermal cracking under anaerobic conditions to break down the organic matter into oil and gas and collect it by condensation for recycling. Unlike incineration treatment, vacuum cracking is carried out in an anaerobic environment, thus reducing the production of dioxins and furans, and the emission of exhaust gases is less, which has less impact on the environment.
3.1.3 Microwave Treatment Technology
The microwave recycling method first crushes the e-waste and then uses microwave heating to decompose the organic matter. Heating to about 1400 ℃, glass fibers and metal melting to form glassy substances, cooling gold, silver and other metals will precipitate in the form of small beads, the remaining glassy substances can be recycled as building materials. This method has the significant advantages of high efficiency, fast speed, high resource recovery rate and low energy consumption compared with the traditional heating technology.
3.2Hydrometallurgy
Wet metallurgy technology mainly utilizes the property of metal dissolving in nitric acid,sulfuric acid and aqua regia, etc. to separate and recover the metal from e-waste.As a more common e-waste treatment method, hydrometallurgy has obvious advantages over pyrometallurgy in terms of less exhaust gas emission,easy treatment of residues after metal extraction and high economic benefits.
- Biotechnology
Biotechnology utilizes the adsorption and oxidation of microorganisms on the surface of minerals to recover metals.Microbial adsorption can be carried out in two ways: one is the use of microbial metabolites to fix metal ions, and the other is the direct fixation of metal ions by microorganisms.The former is through the hydrogen sulfide produced by bacteria on the bacterial surface adsorption of metal ions to saturation after the formation of precipitation; the latter is the use of the oxidizing property of trivalent iron ions, so that the other metals in the precious metal alloy are oxidized to soluble matter,which facilitates the extraction of precious metals. Although the process of metal extraction by biotechnology is simple,low-cost and easy to operate,its leaching time is relatively long and the leaching rate is low, so it is not yet widely used.

Anti-deformation methods for printed circuit board recycling products:
- Add the thickness of the PCB circuit board. Can advocate trying to use more than 1.6mm thickness of the circuit board. Still have to use the thickness of the board, advocating the use of over-furnace fixtures to support and strengthen the board over the furnace when the amount of deformation. Although it is possible to test down.
- Use high Tg PCB material. High Tg means high rigidity, but the price will also follow the rise, there are trade-offs.
- Jinshan circuit board recycling in the circuit board filling Epoxy glue (potted). Can also think about the BGA or its corresponding circuit board around the reverse side of the potting, to strengthen its anti-stress capabilities.
- Add reinforcement around the BGA. If there is space, you can think like building a house, the same in the BGA around the iron frame with support to strengthen its resistance to stress.
Printed circuit boards recycling not only helps to reduce resource waste, but also brings significant economic benefits. Globally, the economic value of recycling circuit boards has been widely recognized, and many companies have started to invest in this business to gain considerable profits. Through scientific and reasonable recycling, not only can we maximize the use of resources, but also promote sustainable development.