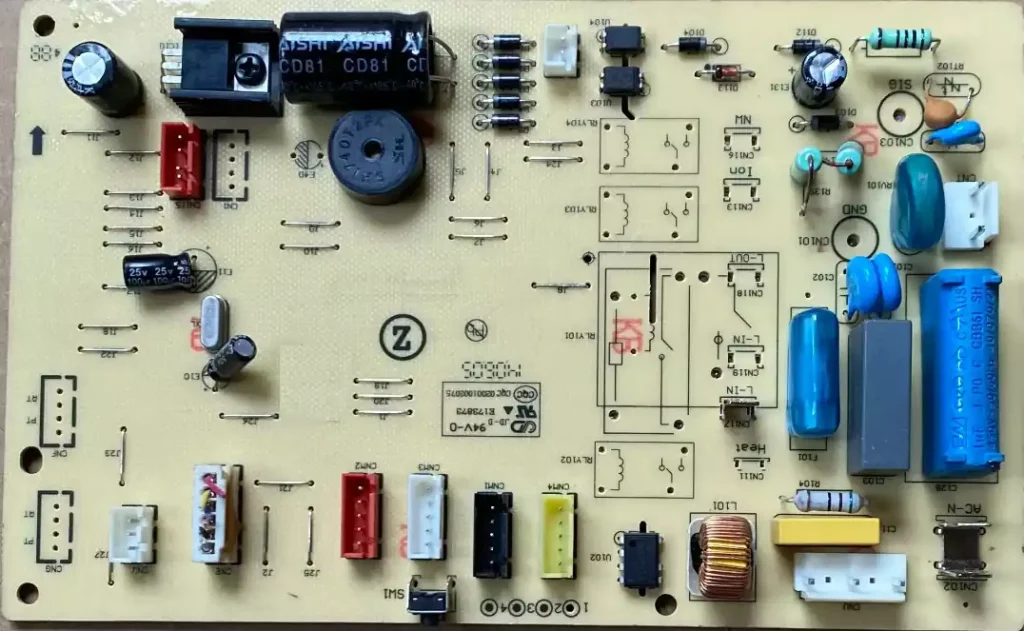
A main pcb assy, often referred to as a collection of various electronic components and connectors that make up a motherboard (also known as a motherboard, system board, or flat board). The motherboard is the core component in a computer or other electronic device, responsible for connecting and supporting other hardware devices.
Critical components of a main pcb assy
- Mouse and keyboard connectors
A computer motherboard must have two separate connectors that allow the user to connect an external mouse and keyboard. These connectors are responsible for sending commands and receiving responses from the computer. There are two keyboard and mouse connectors, PS/2 and USB. The Personal System/2 (PS/2) port is a miniature DIN plug containing six pins that connects a mouse or keyboard to an IBM-compatible computer. Other computers use the USB port to connect a mouse or keyboard. - Universal Serial Bus (USB)
USB is a computer interface that connects computers to other devices, such as cell phones.The USB port is an important part of the motherboard that allows users to connect external peripheral devices, such as printers, scanners, and pen drives, to the computer. In addition, it enables users to transfer data between the device and the computer. usb ports allow users to connect peripheral devices without rebooting the system. types of usb include usb-a, usb-b, usb-mini, micro usb, usb-c, and usb-3. - Central Processing Unit
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is often referred to as the brain of the computer. The CPU controls all the functions of the computer and comes in different form factors, each requiring a specific slot on the motherboard. A CPU can contain one or more cores. A single-core CPU can perform only one task at a time, while a multi-core CPU can perform multiple tasks at the same time. - RAM
The RAM slot connects random access memory (RAM) to the motherboard.RAM allows the computer to temporarily store files and programs that are being accessed by the CPU. A computer with more RAM capacity can hold and process larger files and programs, which improves performance. However, when the computer is turned off, the RAM contents are erased. Computers usually have two RAM slots. However, some computers have up to four RAM slots on the motherboard to increase the available memory. - Chipset
A computer’s chipset controls how the computer hardware and buses interact with the CPU and other electronic components. The chipset also determines the amount of memory the user can add to the motherboard and the type of connectors the motherboard can have.
The first chipset is the Northbridge chipset. The Northbridge manages the speed at which the CPU communicates with components. It also controls the processor, AGP video slot, and RAM.
The second chipset is the Southbridge chipset. The Southbridge chipset controls the communication between the rest of the components connected to the computer, including the processor and expansion ports such as the USB port and sound card.
- Cooling Fans
The heat generated by the flow of electricity between components can slow down a computer. If too much heat is left to build up uncontrollably, it can damage computer components.As a result,computers perform better when they are kept cool. Cooling fans increase airflow, which helps carry heat away from the computer. Some components,such as video adapters, have specialized cooling fans. - Adapter Cards and Expansion Slots
Adapter cards are integrated into the motherboard to enhance the functionality of the computer. Examples include sound and video adapters. Expansion slots allow users to install compatible adapters. Examples of expansion slots include Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) slots, AGP slots (where video cards can be inserted), PCI Express serial bus slots, and PCI expansion slots. - Storage Devices
Storage drives permanently store data or retrieve data from media disks. Storage devices can be installed in the computer as hard disk drives or in removable drives that can be connected to the computer through a USB port. Hard disk drives (HDDs) or solid-state drives (SSDs) are the primary storage drives for computers. Computers with SSDs perform tasks much faster and better than HDDs. Users can also use optical drives such as CD-ROMs to store information.
How motherboards are categorized
According to the CPU used on the motherboard
386 motherboards, 486 motherboards, Pentium (Pentium,that is, 586) motherboards, high-powered Pentium (Pentium Pro, that is, 686) motherboards. The same level of CPU is often further divided, such as Pentium motherboards,there is whether to support the multi-pentium (P55C, MMX requires motherboards built-in dual-voltage), whether to support the Cyrix 6×86, AMD 5k86 (are Pentium-level CPU, requiring the motherboard to have a better heat dissipation) and other differences.
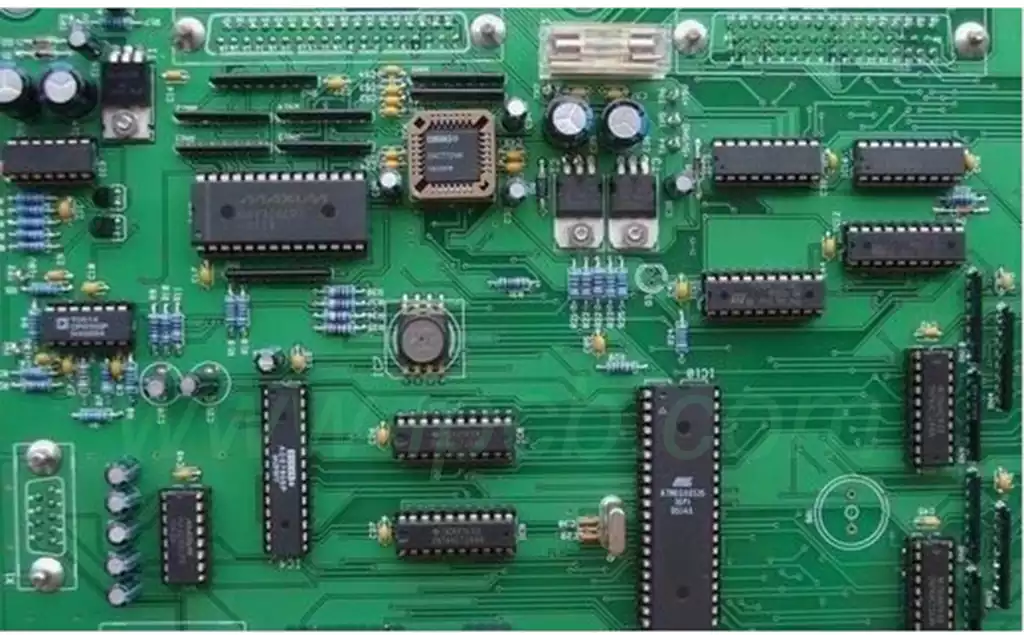
By the type of I/O bus on the motherboard
ISA (Industry Standard Architecture).
EISA (Extension Industry Standard Architecture) Extension Standard Architecture bus.
MCA (Micro Channel) microchannel bus. In addition, in order to solve the bottleneck problem of slow transmission speed between CPU and high-speed peripherals, two types of localized buses have emerged, which are:
VESA (Video Electronic Standards Association) local bus, abbreviated as VL bus.
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) local bus, abbreviated as PCI bus.486-class motherboards mostly use the VL bus, while Pentium motherboards mostly use the PCI bus. Currently, following the PCI has developed a more peripheral interface bus, they are: USB (Universal Serial Bus) Universal Serial Bus. IEEE1394 (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers 1394 standard) commonly known as FireWire (Fire Ware).
Main pcb assy components are all cornerstones of efficient computer operation, and together they build a computer’s powerful performance and functionality. With the continuous development of technology, the design of the motherboard will be more advanced, providing unlimited possibilities for the future application of computers.