SMT production line, full name surface assembly technology (Surface Mount Technology), is a modern electronic assembly technology. A new generation of electronic assembly technology developed from hybrid integrated circuit technology, characterized by the use of component surface mount technology and reflow soldering technology, has become a new generation of assembly technology in the manufacture of electronic products.
The basic composition of the SMT production line mainly includes the following parts:
Surface mount components. This is the SMT production line for mounting in the printed circuit board (PCB) on the electronic components, such as surface mounted components (SMD) and chips (Chip) components.
Circuit Substrate. This is the printed circuit board used to carry electronic components in an SMT production line.
Assembly design. This is the process used in an SMT production line to plan how electronic components will be mounted onto the circuit substrate.
Assembly Process. This is the specific step in the SMT production line used to perform the actual placement process, including printing solder paste, mounting components, reflow soldering, component testing and rework.
In addition, the main equipment of the SMT production line includes a printing machine , a placement machine , a reflow oven , a wave soldering machine , etc., which are responsible for executing the assembly process steps described above.The SMT production line may also include other auxiliary equipment such as dispensers , test equipment , cleaning equipment , drying equipment and material storage equipment , etc. These equipment support the normal operation of the production line and improve production efficiency.
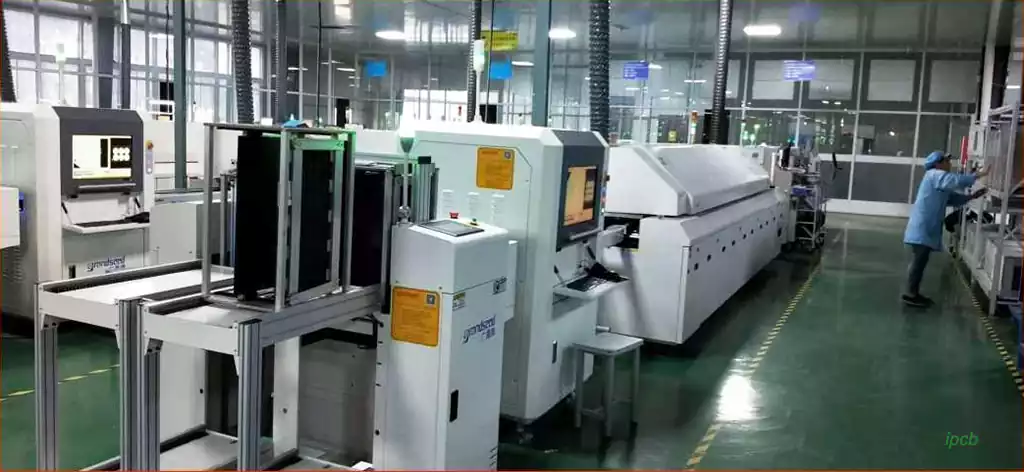

SMT placement process
SMT placement is the main part of the surface assembly process, which mainly includes four steps: stencil printing, placement, reflow soldering and testing.
Stencil Printing
Stencil printing is the first step of SMT placement, the main purpose is to apply solder paste evenly on the pads of the PCB board, in order to ensure the accuracy and quality of the placement. The key to stencil printing lies in the design and manufacture of the stencil, as well as the control of the printing process, which includes the control of printing pressure, printing speed, squeegee angle and other parameters.
SMD
SMD is the SMT components in accordance with certain rules and order on the pads of the circuit board, is the core link of the SMT placement process. Patch process should pay attention to the accuracy and stability, in order to avoid the paste put out of the wrong and missed paste situation.
Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering is the PCB board into the reflow soldering machine, through high-temperature heating will melt the solder and wet pads and component ends and pins, the formation of welded points of the process. The key to reflow soldering is the control of the heating and cooling process, as well as the selection and management of the solder.
Inspection
Inspection is the last step of SMT placement, mainly for the precision, quality, location, defects and other testing and judgment to ensure product quality and stability. Commonly used inspection methods include visual inspection, X-ray inspection and AOI inspection.
DIP plug-in process is to insert the components processed through the DIP process into the socket on the PCB board, which is one of the important process links in electronic manufacturing.DIP plug-in process includes assembly, welding, testing and debugging and other links.
SMT production line, as the core technology of modern electronic manufacturing, promotes the miniaturization and multifunctionalization of electronic products with its efficient and precise assembly process.