RF pcbs are core components in electronic devices, and their performance stability directly affects the overall operational effectiveness of the device. However, in complex electromagnetic environments, RF circuit boards are easily susceptible to various electromagnetic interferences, leading to performance degradation or even failure. Therefore, effective RF PCB shielding is particularly important.
Basic Principles of RF PCB Shielding
The basic principle of RF pcb shielding is to utilise the reflective, absorptive, and guiding properties of shielding materials to confine electromagnetic waves within a specific area, thereby protecting the circuit board. Factors such as the material, structure, and grounding method of the shielding material all influence the shielding effectiveness.
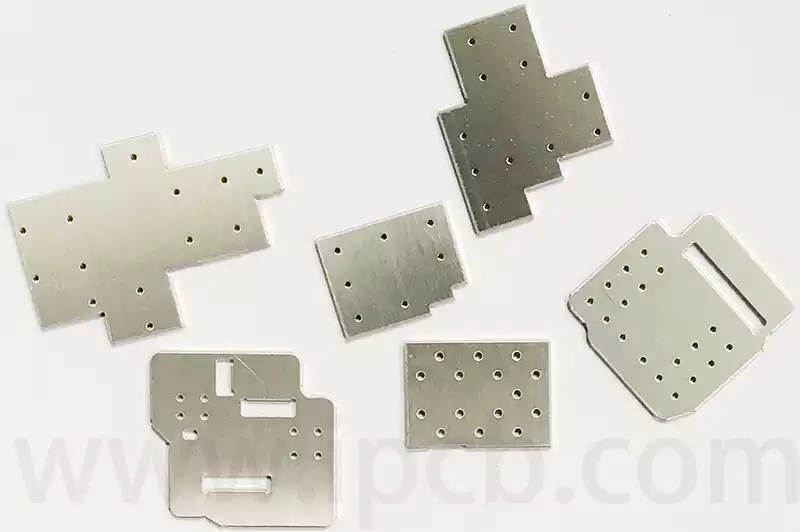

RF PCB Shielding Methods:
Metal Shielding Enclosures
Metal shielding enclosures are a commonly used RF pcb shielding measure. They effectively isolate external radio frequency signal interference by enclosing the equipment or components that require shielding within a metal enclosure. These enclosures are typically made of metallic materials such as copper, aluminium, nickel, and stainless steel, which possess excellent conductivity and reflectivity, enabling them to effectively reflect and absorb electromagnetic waves. For example, aluminium and copper are frequently used for electromagnetic shielding due to their excellent shielding performance. Nickel-copper alloy (nickel-copper alloy) is also commonly used for electromagnetic shielding because it contains nickel, which provides good electromagnetic shielding performance. Additionally, while nickel-based fillers have lower conductivity than silver and copper, they offer excellent corrosion resistance. In practical applications, the thickness of metal shielding enclosures typically ranges from 0.1 millimetres to 0.3 millimetres, with optimal selections made based on frequency range, shielding effectiveness, and application scenarios. For frequencies exceeding 1 MHz, most metals with a thickness of 0.5 millimetres or greater can provide good shielding effectiveness, and they perform exceptionally well at 100 MHz. Surface treatment of metal shielding covers is critical for enhancing corrosion resistance, surface hardness, and conductivity. Common surface treatment methods include hot-dip plating, electrochemical treatment, and anodising. For example, silver plating is suitable for circuit boards with EMI shielding, achieved by immersing copper PCBs in a silver ion bath.
Metal shielding plates
Metal shielding plates are a common type of radio frequency (RF) shielding material that can be directly applied to the surface of equipment or used for RF pcb shielding inside equipment. By installing metal shielding plates inside equipment or on circuit boards, RF signal leakage and interference can be effectively reduced, thereby enhancing the equipment’s interference resistance. When selecting metal shielding plates, factors such as material type, thickness, and surface treatment must be considered.
RF shielding coatings
RF shielding coatings are functional coatings that incorporate conductive particles into chemical solvents. They can be sprayed onto non-metallic materials such as engineering plastics, fibreglass, wood, and cement walls to shield electromagnetic waves. These coatings exhibit excellent RF shielding performance; for example, nickel-based composite coatings demonstrate high shielding performance against RF electromagnetic radiation in the environment. Anti-shielding conductive coatings used in 5G consumer electronics devices achieve excellent substrate adhesion, weather resistance, chemical resistance, and corrosion resistance through components such as epoxy-modified hydroxy acrylic resin, aliphatic isocyanate curing agents, silver-coated copper powder, and ultra-conductive silver paste. This coating can effectively block 99.9% of electromagnetic waves, with a shielding effectiveness of over 30 dB in the frequency range of 80 MHz to 6 GHz. When selecting RF shielding coatings, factors such as shielding performance, durability (e.g., abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance, temperature resistance, and moisture resistance), and application scope should be considered.
RF shielding curtains
RF shielding curtains are passive shielding devices commonly used in RF laboratories and medical equipment rooms. These curtains are made from special fabrics infused with conductive materials, which effectively block or attenuate electromagnetic waves by absorbing, reflecting, or dissipating electromagnetic radiation, thereby creating a Faraday cage effect. Shielding curtains provided by companies like Shieldex can effectively shield electromagnetic waves, ensuring reliable protection against signal interference. In military operations centres, shielding curtains and shielding tents are used as solutions to protect equipment and data from electromagnetic interference.
Grounding Shielding
Grounding shielding is an essential component of radio frequency (RF) shielding. Its principle involves connecting the outer casing, shielding covers, or other components of equipment or circuits to a grounding wire, thereby diverting external RF signals into the grounding wire and reducing signal interference. The shielding layer typically requires grounding to isolate electromagnetic noise sources from sensitive equipment and block the propagation path of noise sources. A well-designed grounding system ensures that interference currents flow smoothly into the ground, effectively suppressing electromagnetic interference and enhancing the equipment’s interference resistance and signal transmission stability. For example, a metal housing forming a shielding enclosure, when connected to ground, reduces interference from external electromagnetic radiation on electronic circuits and prevents excessive static charge accumulation that could cause equipment instability. In design, a low-impedance, large-area grounding plane should be established to provide a return path for interference currents and reduce common-mode noise. Additionally, care must be taken to avoid ground loops and multiple grounding points, preferably using single-point grounding or a reasonable zoned grounding strategy.
RF Shielding Rubber
RF shielding rubber is a material with high conductivity, electromagnetic shielding, and moisture-proof sealing properties, typically filled with conductive metal particles. This material is commonly used to manufacture RF shielding gaskets and other components. By using RF shielding rubber at device interfaces and connection points, external RF signal interference can be effectively isolated, thereby enhancing the device’s interference resistance and stability. For example, in satellite receivers, by machining grooves on the contact surfaces between metal structural components and printed circuit boards and embedding conductive rubber rings, the isolation between RF channels can be significantly improved while reducing the machining precision requirements for metal shielding enclosures. Conductive rubber shielding gaskets can be applied to chassis, cabinet gap shielding, and shielded rooms and shielded containers.
RF PCB shielding is a key technology for ensuring the stable and efficient operation of electronic devices in complex electromagnetic environments. With the continuous development of wireless communication and electronic integration, the importance of electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) design has become increasingly prominent. Selecting appropriate shielding materials, designing reasonable shielding structures, and establishing a comprehensive grounding system are the cornerstones of effective RF pcb shielding. In the future, with the continuous emergence of new materials and technologies, RF shielding technology will continue to innovate, providing electronic devices with more reliable electromagnetic protection to address the increasingly stringent challenges of electromagnetic compatibility.