Printed circuit board parts is the process of connecting electronic components to the wiring of a printed circuit board. The traces or conductive pathways engraved in the laminated copper sheets of the PCB are used within the non-conductive substrate to form the assembly. Connecting an electronic component to a printed circuit board is the end action before a fully operational electronic device can be used.
As one of the indispensable core components of modern electronic devices, printed circuit board parts provide electrical connections and mechanical support for electronic components. They not only ensure the normal operation of the equipment, but also directly affect the working effect and service life of the equipment. Therefore, the quality and stability of the components are crucial.
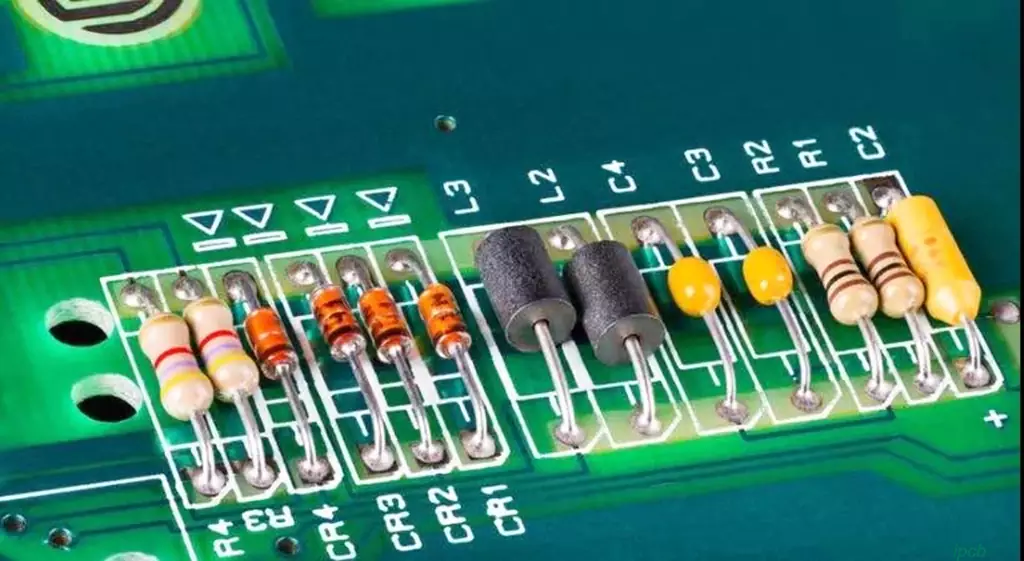
On a printed circuit board, various electronic components are combined together in the form of welding or plugging to form a complete circuit. The main components include:
Resistors: control the current and voltage, and regulate the operating state of the circuit.
Capacitors: store electrical energy and are used to smooth current and eliminate spikes in signals.
Inductors: store magnetic energy in circuits and are often used to filter and tune circuits.
Semiconductor devices: such as diodes, transistors and integrated circuits (ICs), responsible for signal processing and control.
Connectors: Realize the connection between circuit boards and external devices.
Buzzers, LEDs and displays: used for feedback and indication functions.
Role of printed circuit board parts
Capacitor Functions and Applications
Capacitor is the most widely used printed circuit board parts, second only to resistors. Its main function is to temporarily store electrical charge and release electrical energy when additional power is required in a circuit. Capacitors are widely used for filtering, coupling and decoupling, and are commonly used in power supply circuits, audio circuits and RF circuits.
Functions and Applications of Resistors
Resistors are important components that control the flow of current and are widely used in PCBs to help stop the flow of current by dissipating electrical energy as heat. They are commonly used in circuit configurations such as current limiting, voltage dividing, and feedback to ensure the proper functioning of electronic components, and are commonly found in almost all electronic devices.
Transformer Functions and Applications
PCB transformers are responsible for transferring energy from one power source to another and controlling the flow of current. This component is very important in power supply circuits to help adjust the voltage to the right level and is commonly used in home appliances and industrial equipment.
Functions and Applications of Transistors
A transistor is an important part of modern electronic components and is used as an amplifier and switch. It is able to regulate current and signals and is a key component in both analog and digital circuits, widely used in computers, cell phones, and audio equipment, among others.
Diode Functions and Applications
Diodes play an important control role in PCBs by ensuring that the current flows in one direction only and preventing it from flowing in the opposite direction. Common applications include rectification of power supplies, protection circuits and signal modulation, and are found in almost all electronic devices.
Functions and Applications of Integrated Circuits
Integrated circuits (ICs) contain multiple electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors, and are capable of providing multiple functions in a single miniaturized assembly.ICs are widely used in computers, cellular phones, and other complex electronic devices, reducing the complexity and size of circuit boards.
Functions and Applications of Switches and Potentiometers
Switches control the opening and closing of electric current and are widely used to control the function of electrical appliances by the user. Potentiometers, on the other hand, are used to regulate the magnitude of current and voltage, and are widely used for applications in devices such as volume control and brightness adjustment.
Functions and Applications of Sensors
Sensors are capable of sensing changes in the environment and responding accordingly. They play an important role in automation, medical monitoring, and environmental monitoring by converting physical signals into electrical signals for use in other circuit components.
Functions and Applications of PCB Cable Assemblies
PCB cable assemblies combine multiple wires together to simplify the process of assembling circuit boards and improve system reliability by providing centralized and secure connections. These assemblies are widely used in a variety of electronic devices to connect to other systems and improve the neatness and maintainability of the wiring.
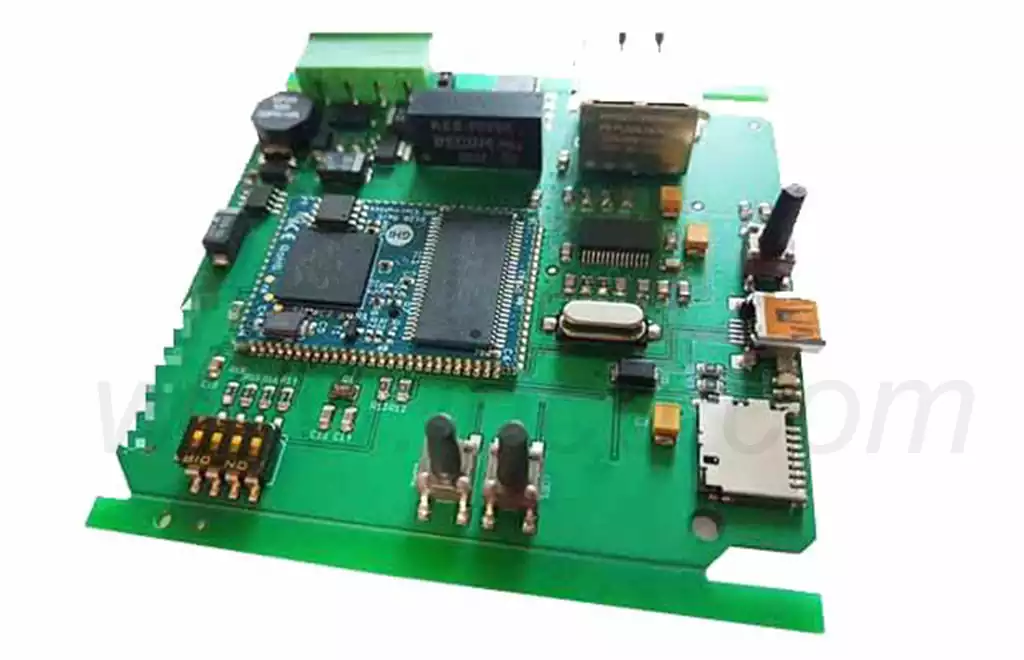

Printed circuit board parts play a vital role in circuit board assembly, not only providing mechanical support and electrical connections, but also ensuring the functionality and reliability of the entire electronic device.
- Mechanical Support
PCBA provides the structural foundation for the entire electronic device, allowing the various electronic components to be securely mounted on the circuit board. This support not only helps to prevent physical damage during daily use, but also helps to securely connect the electrical components to the power and signal lines, thus ensuring stable operation of the equipment.
2.Electrical Connection
PCBA enables the electrical connection of various electronic components by soldering them together to form a complete circuit network. This connection is critical, because it ensures the effectiveness of signal transmission and power supply, so that electronic equipment can operate in accordance with the design of the expected function. The proper configuration of the components and the quality of the soldering directly affect the performance of the circuit.
3.Performance Optimization
When designing printed circuit board components, proper planning and layout can help optimize signal transmission paths and reduce signal interference and loss. This is especially important for high-frequency applications where signal integrity is critical in high-speed data transmission. High-quality PCBA design can significantly improve the overall performance of electronic devices.
4.Cost Effectiveness
The use of printed circuit board parts reduces production costs and increases productivity. automated processes for PCBA assembly reduce the need for manual labor and can significantly increase the speed of assembly, thus meeting market demands faster. In addition, the integration of the entire supply chain allows companies to more effectively control material costs and shorten the delivery cycle.
5.Test and Inspection
In the PCBA assembly process, the printed circuit board parts also need to go through several rounds of testing and quality inspection to ensure its function and reliability. This inspection process helps to identify problems and make adjustments in a timely manner, reducing the risk of product failure after release. Testing not only checks the quality of soldering, but also verifies the electrical characteristics of the entire circuit to ensure that the final product meets the expected standards.
Key factors to consider when selecting printed circuit board parts:
Physical Characteristics of the Component
When selecting a component, it is important to first consider its physical characteristics, including the body contour of the device and the pins connected to the PCB. These characteristics not only affect the mounting and routing of the component, but may also affect the overall layout of the PCB as well as its electrical performance.
Functional Requirements
The functional requirements of the component are also critical. The role and function of each component in the circuit should be clearly defined during selection to ensure that the selected component meets the needs of the particular application. For example, selecting the right capacitors, resistors, or other components to achieve the desired electrical performance and effectiveness.
Environmental Adaptability
The environmental suitability of the component is also an important factor in the evaluation. For some applications, factors such as operating temperature, humidity, and vibration resistance may need to be taken into account to ensure that the selected component can function properly in harsh environments. Therefore, understanding the component’s environmental ratings and certifications is necessary.
Cost Considerations
Cost is an integral consideration when selecting components. Depending on the budgetary constraints of the project, selecting the right type and brand of module ensures that costs can be controlled while meeting performance and quality requirements. High-quality components may be more expensive, but their potential long-term benefits and reliability are often more worth the investment.
Compatibility and Standardization
The design process also needs to ensure that the selected components are compatible with other circuit elements. For example, ensuring that components such as plugs, sockets and connectors match the circuit design, as well as following relevant industry standards, avoids potential interference and faults.
Supply chain reliability
Finally, the supply chain reliability of the component is also an important consideration. Ensure that components are selected from reputable suppliers to ensure long-term supply stability. Especially in the case of high volume production, choosing a reliable source of supply can avoid production delays due to stock-outs.
Printed circuit board parts play a vital role in modern electronic equipment, not only to provide electrical connections and mechanical support, but also directly affect the performance and life of the equipment. Designers need to consider factors such as physical characteristics, functional requirements, environmental adaptability, cost, compatibility and supply chain reliability when selecting suitable PCB components to ensure the quality and stability of the final product.