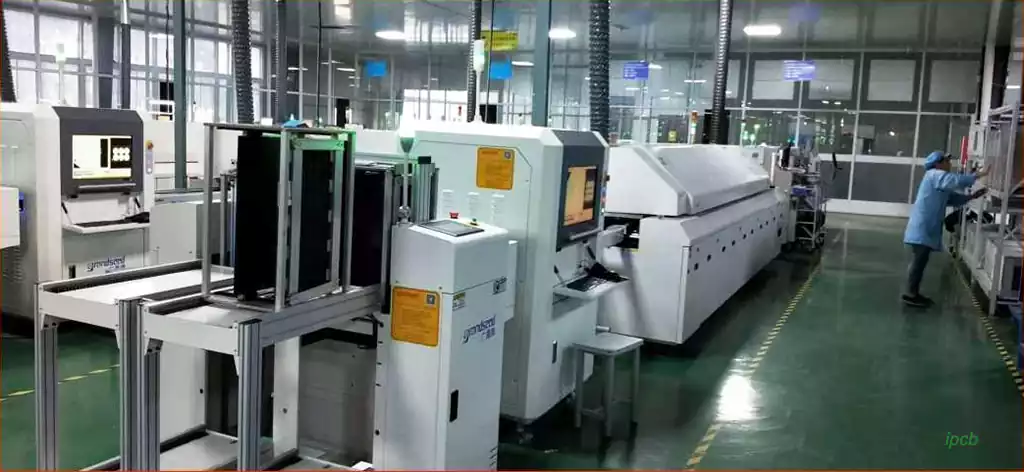
PCB reflow soldering hot plate is a process that involves re-melting a paste solder that has been pre-coated on a printed circuit board pad to make a mechanical and electrical connection between the solder ends or pins of a surface-mounted component and a printed board pad.
PCB reflow hot plates, as a method of soldering components to PCB boards, are widely used in surface mount equipment. Through the action of hot air flow on the solder joints, the flux in the specific high-temperature airflow conditions of the physical reaction, to complete the SMD mounting device welding process. It is named “reflow hot plate” because in the welding machine, the gas (such as nitrogen) circulates to generate high temperature to realize the purpose of welding.
PCB reflow hot plate usually contains four main working areas: heating area, holding area, welding area and cooling area.
1) When the PCB board enters the heating zone, the solvents and gases in the solder paste gradually evaporate. At the same time, the flux in the solder paste begins to wet the pads, component ends and pins. The solder paste softens and collapses, covering the pads and forming a barrier to the pads, component pins and oxygen.
2) Subsequently, the PCB enters the holding area. This stage fully preheats the PCB and components to prevent the PCB from suddenly entering the high-temperature soldering area, thus avoiding damage to the PCB and components.
3) When the PCB enters the soldering zone, the temperature rises rapidly, causing the solder paste to reach a molten state. The liquid solder wets, spreads and mixes with the pads, component ends and pins of the PCB to form a firm solder joint.
4) Finally, the PCB enters the cooling zone, making the solder joints quickly cured, completing the entire reflow soldering process.
PCB reflow hot plate technology has significant advantages:
The process makes the temperature control more accurate, to prevent oxidation in the soldering process, and help control manufacturing costs.
The reflow hot plate is equipped with internal heating circuitry that heats nitrogen to a high enough temperature and blows it onto the circuit board where the components have been connected, so that the solder on both sides of the components melts and combines with the main board.
Instead of immersing the printed circuit board in molten solder when soldering with reflow technology, the soldering task is realized by local heating. As a result, the soldered components are subjected to less thermal shock and are less likely to be damaged by overheating.
Since the soldering technology only requires the application of solder and localized heating at the soldering site to complete the soldering, soldering defects such as bridging are avoided.
In reflow soldering technology, the solder is disposable and does not need to be reused. Therefore, the solder is pure and free of impurities, ensuring the quality of the solder joints.
The working principle of PCB reflow hotplates is based on heating the solder paste coated pads and pre-assembled electronic components on the circuit board, so that the solder paste melts and connects with the circuit board pads and electronic component pins.
Reflow hot plates are usually heated by hot air or infrared radiation using high-temperature heating pipes. Before the soldering process begins, the solder paste is applied to the circuit board pads and electronic component pins using specialized equipment (e.g., printing presses). When the circuit boards and electronic components are placed in the reflow soldering equipment, the heating system preheats them and gradually warms them up to a constant temperature.
When the soldering temperature reaches the specified soldering temperature, it is held for a certain period of time to ensure that the soldering is complete. At the end of the soldering time, the board can be removed from the reflow soldering equipment for subsequent testing, inspection and other process steps.
The process flow of a reflow hot plate consists of the following four main steps:
Solder Paste Printing: A solder paste containing solder particles is applied to the circuit board component pads.
SMD Mounting: The circuit board coated with solder paste is fed into the automatic SMD machine to realize the automatic mounting of SMD components on the circuit board.
Reflow Hot Plate Soldering: The circuit board with components installed is heated to a certain temperature, so that the solder paste melts, and the solder paste in the circuit board’s soldering plate combines with the component pins under the pads at high temperature to complete the soldering.
Inspection and Testing: After the soldering is completed, electrical performance tests and reliability tests are performed to ensure that the product meets established quality standards.
PCB reflow soldering hot plate technology can complete the connection of circuit board and surface mount component solder joints in a short period of time, improving the safety of solder joints and reducing the risk of poor soldering.