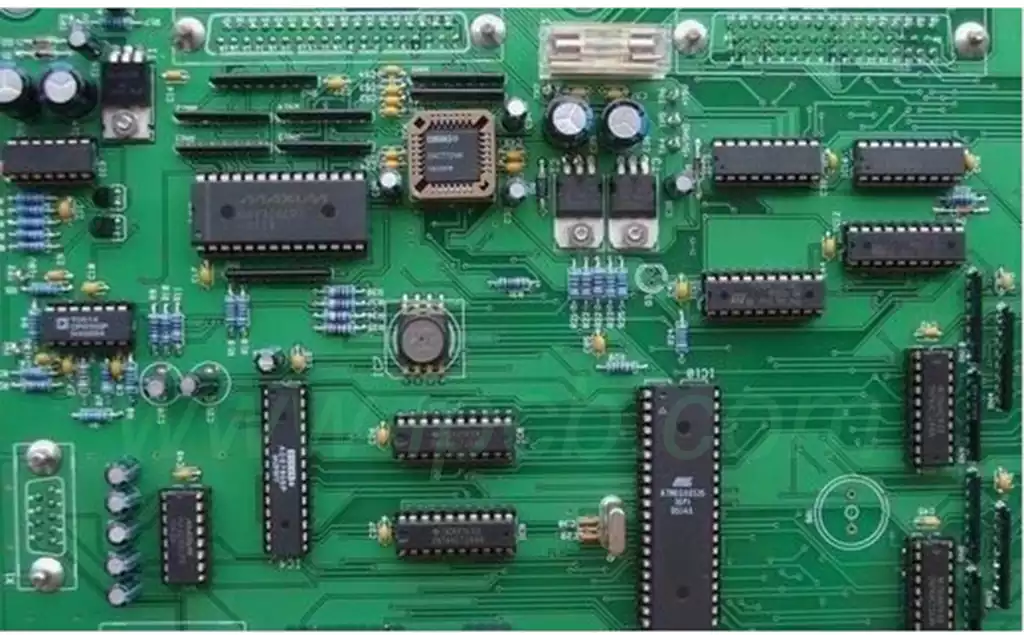
In the electronics manufacturing industry, soldering is a critical process, and the electronics soldering temperature is a key factor affecting the quality and effectiveness of soldering. The selection and control of soldering temperature is not only directly related to the firmness and stability of the soldering point, but also affects the performance and reliability of the entire electronic product.
The optimal temperature and time for electronic soldering: 250 ± 5 º C, the minimum soldering temperature of 240 º C. Too low a temperature is easy to form a cold solder joints. A temperature higher than 260ºC is likely to deteriorate the quality of the solder joint.
Completion of the wetting and diffusion of the two processes need 2 ~ 3S, 1S only complete the wetting and diffusion of the two processes of 35%. General IC, transistor welding time is less than 3S, other components welding time is 4 ~ 5S.
If the reflow soldering temperature is too high, its potential adverse effects in a number of ways:
Welding quality is impaired: too high a reflow temperature will lead to overactive solder, which in turn causes irregularities in the shape of the solder joints, the formation of bad welding, which in turn affects the stability of the electrical connection, and may even lead to damage to the circuit board.
Impaired component performance: For heat-sensitive components such as LEDs and thermistors, high temperatures can cause direct damage. In addition, high temperatures accelerate the aging of components and shorten their service life.
Concentration of stress: High temperatures cause thermal expansion and contraction of materials, which can easily lead to stress concentrations at solder joints or circuit boards, and these stresses can lead to fatigue ruptures and failure of solder joints or circuit boards under repeated temperature changes.
Increased oxidation: high-temperature environment will accelerate the oxidation process of the metal, once the solder joints or other metal components on the surface of the formation of an oxide layer, its conductive properties will be significantly reduced.
Reduced thermal stability: high-temperature environments may alter the thermal stability of materials, resulting in unstable performance of circuit boards or components during temperature changes.
Increased energy consumption: In order to maintain a high-temperature environment, more energy must be consumed, which not only increases production costs, but also a certain burden on the environment.
Increased Operational Risk: High temperature environments pose a threat to operator safety, so additional safety measures must be taken to ensure the safety of the operation process.
Solder wire electronic components when soldering, notes on temperature:
(1) The soldering temperature is required to be carried out at a relatively low temperature to ensure that the pcb components are not damaged by thermal shock. If the melting point of the solder is between 180-220°C, the soldering temperature is usually about 50°C higher than the actual melting temperature of the solder, and the actual soldering temperature is in the 220-250°C range. According to IPC-SM-782, usually chip components are only retained for 10s in a 260°C environment, while some thermal smt components have even lower heat-resistant temperatures. In addition, the PCB will also form thermal stress after high temperature, so the melting point of the solder should not be too high.
(2) molten solder must have good mobility on the surface of the metal being soldered, which is conducive to the uniform distribution of solder, and to lay the foundation for wetting.
(3) The solidification time should be short, conducive to the solder joint molding, easy to operate.
(4) After welding, the appearance of the solder joint should be good, easy to check.
(5) Good electrical conductivity, and sufficient mechanical strength.
(6) good corrosion resistance, electronic products should be able to work in a certain high or low temperature, smoke and other harsh environments, especially military, aerospace, communications and large computers, etc., for this reason, the solder must have good corrosion resistance.
(7) solder raw materials should be a wide range of sources, that is, the composition of the solder metal minerals should be abundant, the price should be low, in order to ensure stable supply.
Different soldering projects require different soldering temperatures to ensure the firmness and reliability of the solder joints. Specifically, the following are several common welding projects and their appropriate temperature range:
1. Electronic soldering: Electronic soldering is a common soldering project, which requires a temperature of about 250 degrees to ensure the firmness and aesthetics of the solder joints.
2. Metal welding: metal welding requires a higher temperature, generally between 280 degrees and 300 degrees.
3. Plastic welding: Plastic welding requires a lower temperature, generally around 220 degrees.
It should be noted that different solder has a different melting point, so in the choice of soldering temperature, but also according to the actual use of the type of solder to make appropriate adjustments.
Electronics soldering temperature is a key factor affecting the soldering quality and performance of electronic products.We need to select the appropriate soldering temperature according to the specific soldering object and solder material, and realize the effective control of soldering temperature through advanced soldering equipment and skillful operation techniques.