Printed circuit board material composition refers to the relationship between the combination of various materials in the PCB board.
Generally speaking, PCB boards can be divided into a variety of structures, respectively, single-sided boards, double-sided boards, multilayer boards, high-level boards and so on.
1. Single-sided PCB
Substrate materials to paper phenol (phenol) copper laminate (paper phenol when the bottom, on the copper foil) paper epoxy resin (Epoxy) copper laminate mainly.Mainly used in radios, DVD players, washing machines and other home appliances, as well as printers, vending machines, circuit machines, electronic components and other commercial machines, the advantage of low prices.
2. Double-sided PCB
Substrate materials to Glass-poxy copper laminate, GlassComposite (glass composite) copper laminate, paper Epoxy copper laminate-based. Most of them are used in personal computers, electronic musical instruments, multifunctional telephones, automotive electronics, electronic peripherals, electronic toys and so on. As for the Glass benzene resin copper laminate, Glass polymer copper laminate due to excellent high-frequency characteristics, mostly used in communications equipment, satellite broadcasting equipment, set of mobile communications equipment, of course, the cost is also high.
3.Multilayer PCB
Substrate material is mainly Glass-Epoxy or benzene resin. Uses are mainly personal computers, Me (MedicalElectronics, Medical Electronics) machines, measuring devices, and so on.(MedicalElectronics, medical electronics) machines, measuring machines, semiconductor testing machines, NC (NumericControl, numerical control) machines, electronic switches, communication machines, memory circuit boards, IC cards, etc., but also glass synthesized copper tensile laminates when the multilayer PCB materials, mainly focusing on its processing Excellent characteristics.
4.High-level PCB
The substrate is mainly made of Glass Styrene Resin or Glass-Epoxy as a multilayer PCB substrate material. This type of PCB application is more special, most of the mainframe computers, high-speed computers, communications equipment, etc., mainly because it has high-frequency characteristics, high-temperature characteristics of excellent.
What are the main substrate materials for printed circuit boards?
1. Printed circuit board materials – FR4
FR4 is a flame-resistant material grade code, is a glass fiber reinforced epoxy resin composite material represents the meaning of the resin material after the combustion state must be able to self-extinguish a material specification, it is not a material name, but a material grade, so the general circuit boards used in the FR-4 grade materials have a very wide range of types, but also the most widely used PCB substrate materials. One of the most widely used PCB substrate materials.
FR4 has the following advantages: Good electrical properties: its excellent insulation properties, can effectively isolate the signal in the circuit, reduce interference and leakage phenomenon. Relatively low cost: due to the abundance of raw materials and mature production processes, the price is relatively affordable, suitable for mass production and wide range of applications.Stable mechanical properties: with a certain degree of strength and toughness, able to withstand the mechanical stress of the assembly and use process.However, FR4 also has some limitations: General thermal conductivity: in high-power electronic equipment, it may not be able to effectively dissipate heat in a timely manner. Limited high-frequency performance: For high-frequency signal transmission, signal attenuation and distortion may occur. FR4 is widely used in a variety of electronic equipment, such as computer motherboards, consumer electronics, industrial control equipment, etc., especially in the cost and performance requirements of a more balanced low-end products dominate.
2. Printed circuit board materials – high Tg boards
Usually TG ≥ 170 ℃ PCB printed circuit board, called high TG printed circuit board. High TG PCB board Refers to polymer substrates with a high glass transition temperature (Tg), usually Tg values above 150 ℃. Compared with ordinary FR-4 boards, high TG boards have
Compared with ordinary FR-4 boards, high TG boards have outstanding heat and moisture resistance, chemical resistance and better dimensional stability, making them suitable for use in high-temperature environments. High TG refers to high heat resistance. Computer as a representative of the electronic products, towards high functionality, high multilayer development, printed circuit board materials, high Tg board has a higher heat resistance as an important guarantee.
3. Printed Circuit Board Materials – Teflon Boards
Teflon in a broad sense,Also known as “Teflon”, “Teflon”, “Teflon”, “Teflon”, etc., all are phonetic translations of “Teflon”. “Teflon” is a synthetic polymer material that uses fluorine to replace all the hydrogen atoms in polyethylene, which is characterized by anti-adhesion, heat resistance, moisture resistance, abrasion resistance, resistance to acids and alkalis, and resistance to various organic solvents (almost insoluble in all solvents).Teflon in the narrow sense.Also known as poly tetra fluoroethylene (Poly tetra fluoroethylene, abbreviated as PTFE), is a polymer material with excellent heat resistance, corrosion resistance and insulation properties. Teflon is made from the fluorinated monomer tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) through a polymerization reaction.Teflon boards have a very low thermal conductivity of up to 0.0250. They have excellent performance in high temperature and high frequency environments. Teflon as a printed circuit board material because of the high price, the use of relatively small.
4. Printed circuit board materials – ceramic board
Ceramic board is extremely weather resistant, whether sunlight, rain, or moisture on the surface and substrate have no effect. Resistance to ultraviolet radiation and color stability fully meet the international gray level 4-5. Similarly, large or rapid temperature changes do not affect the characteristics and appearance of the material. The reasonable combination of flexural strength and elasticity gives ceramic panels high impact strength. The dense material surface makes dust less likely to adhere, making it easier to clean. Ceramic plates have excellent fire resistance properties; they do not melt, drip or explode and remain stable for long periods of time.
Ceramic plates are easy to maintain, and neither the surface nor the cut edges need to be painted or given a protective top coat.The emergence of ceramic substrate products, opened up a new development in the heat dissipation application industry, due to the ceramic substrate heat dissipation characteristics, coupled with the ceramic substrate with high heat dissipation, low thermal resistance, long life, voltage resistance and other advantages, with the improvement of production technology, equipment, product price to accelerate the rationalization, and then expand the LED industry applications, such as home appliances indicators, automotive lamps, street lamps and outdoor large-scale billboards and so on.
The successful development of ceramic substrate for indoor lighting and outdoor lighting products to provide better service, so that the LED industry’s future market area is broader. Ceramic board as a printed circuit board material, although its dielectric constant and stability are very good, but the production process is complicated and the price is higher.
5. Printed circuit board materials – aluminum substrate
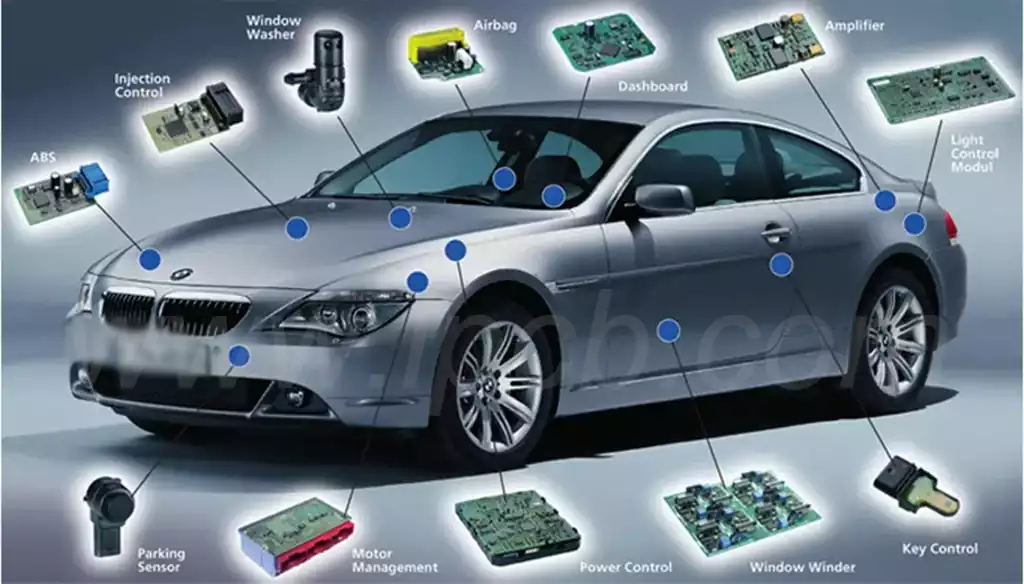
Aluminum-based PCBs are one of the most common types that provide efficient heat dissipation and cooling of electronic components, thereby improving the overall performance of the product.Aluminum substrates are suitable for circuit boards that generate large amounts of heat, such as input and output amplifiers and balanced amplifiers for audio equipment; CPU boards floppy disk drives and power supply units for computers; electronic regulators, ignition, and power supply controllers for automobiles; and LED lights for lighting fixtures, such as high-power LED lights. It has excellent heat dissipation performance and reliability, making it the best choice for high power electronic components and devices.
Advantages; Environmental protection, aluminum is non-toxic and recyclable.Excellent heat dissipation: High temperatures can cause serious damage to electronic equipment. Therefore using materials that favor heat dissipation is the right choice. Aluminum effectively transfers heat away from heat-generating or critical components, minimizing any potentially harmful effects on the circuit board.
Durability: Aluminum provides strength, toughness and durability that fiberglass substrates cannot. Aluminum is a harder material that reduces the risk of accidental damage during production, handling and everyday use. Aluminum enhances the strength and flexibility of the product without adding extra weight.
6. Other PCB Substrate Materials
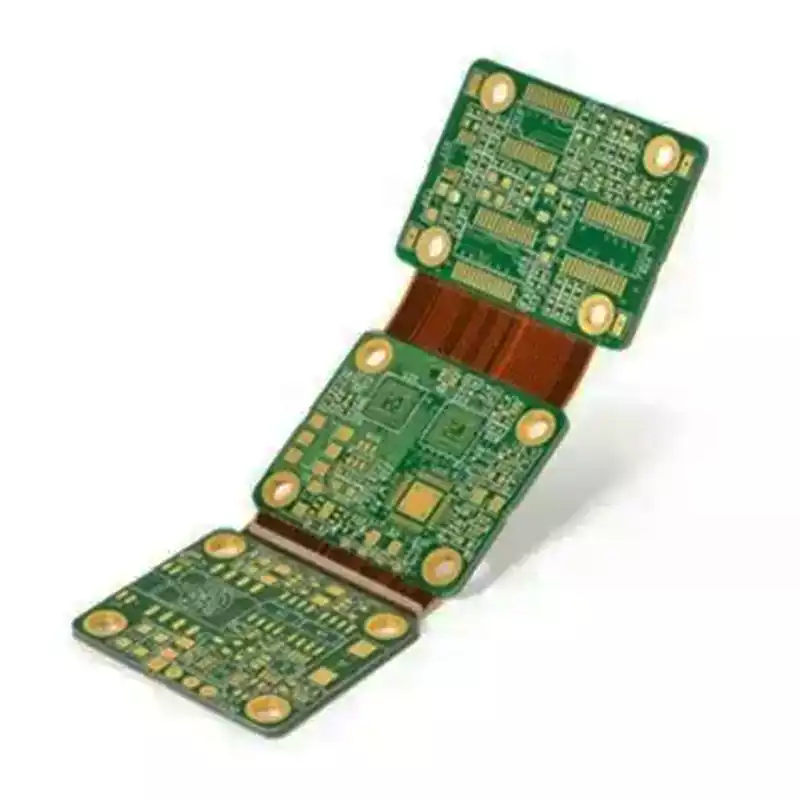
Other PCB materials include aluminum and copper substrates. Circuits will be formed on the substrate, there are also flexible PCB (FlexibIPrintCircuitBoard), the circuit is formed in the polymer, polyester and other materials based on the formation of single-layer, double-layer, to multi-layer board can be. This flexible circuit board is mainly used for the movable parts of cameras, OA machines, etc., as well as the connection between the above rigid PCBs or the effective combination of connection between rigid PCBs and flexible PCBs.As for the combination of connections, the shapes are diversified due to the high flexibility.
Pcb board commonly used materials made of mainly: substrate, copper foil, PP, photosensitive materials, anti-solder paint and negative, etc..
1. The first material of printed circuit board is the substrate:
In addition to some with special purposes will use ceramic materials as a substrate, usually with organic insulating materials as a substrate. We know that pcb has a rigid and flexible points, the corresponding organic insulation materials can be divided into thermosetting resins and thermoplastic polyester. Commonly used thermosetting resins are phenolic resins and epoxy resins; commonly used thermoplastic polyurethane polyimide and polytetrafluoroethylene and so on.
2. Printed circuit board second material copper foil:
At present, most of the metal foils coated on the pcb are made of copper foil by calendering or electrolytic methods. Copper foil thickness is oz (ounce) for the unit, oz itself is a unit of quality, usually copper foil thickness with the quality as “thickness” expressed value, the thickness of copper foil is usually “oz”, 1oz copper thickness definition: one ounce of copper uniformly spread to a square foot area, then the copper foil thickness, the copper foil thickness, the copper foil thickness, the copper foil thickness, the copper foil thickness. Definition of 1oz copper thickness: When one ounce of copper is spread evenly over a square foot of area, the thickness of the copper foil is called 1oz copper thickness, which is exactly 1.37mil (about 1.4mil) thick. Standard thicknesses of copper foil are 12μm (1/3oz), 18μm (Hoz), 35μm (1oz) and 70μm (2oz). The main thicknesses are: 1/3OZ, 1/2OZ, 1OZ Core board (Core): Chinese name can be called core board, copper-clad board, substrate, used to do the inner layer of graphic or double-sided boards, which is composed of copper foil + insulation layer + copper thin, the middle insulation layer is already cured resin and glass cloth composition; Core can also be made of two copper foils + PP through high temperature and high pressure compression. It has certain hardness and thickness, and is double wrapped with copper. Requirements of copper foil: Purity: Electrolytic copper foil should be higher than 99.8%, calendered copper foil should be higher than 99.9%.
The main thicknesses are: 1/3OZ, 1/2OZ, 1OZ, 2OZ, 3OZ, 4OZ. The specific choice depends on the size of the load current and etching precision. Copper foil has an impact on the quality of the product, specifically in the product surface dents and pits, peeling strength and so on.
3. Printed circuit board third material PP:
Prepreg is the English abbreviation for Pre-impregnate, the Chinese name is semi-cured sheet, is a resin and carrier synthesis of a sheet bonding material. pp is composed of resin and glass fiber cloth, glass cloth is some inorganic material after high-temperature fusion cooled into a non-crystalline state of the hard objects, and then by the warp, weft yarns interwoven longitudinally and horizontally formed by the reinforcement material.According to the type of glass cloth can be divided into 106, 1080, 3313, 2116, 7628 and so on. Resin is a thermosetting material that can undergo polymer polymerization reaction and can be used as an adhesive between copper foil and reinforcement (fiberglass cloth) . And the process principle of platen is to utilize the conversion process of semi-cured sheet from B-stage to C-stage to bond each circuit layer into one.
The state of the conversion process of the semi-cured sheet in this process .Stage A: Liquid resin that can flow completely at room temperature, which is the state of the fiberglass cloth impregnation, liquid epoxy resin is also known as Van Lixu (Varnish).Stage B: The epoxy resin is partially cross-linked in a semi-cured state, and can be restored to a liquid state under heated conditions (part of the polymerization reaction, which becomes a solid film, is a semi-cured sheet pp).Stage C: resin all crosslinked for the C stage, in the heating, pressurization will be softened, but can no longer become liquid, which is a multilayer board after pressing the semi-cured sheet into the final state (in the pressure plate process, semi-cured sheet after high temperature melting into a liquid, and then polymer polymerization reaction occurs).
Resin according to the crosslinking status can be divided into: A-order (completely uncured); B-order (semi-cured); C-order (fully cured) three categories, the production of all the B-order state of P / P, is indispensable interlayer adhesive.
4. The fourth material for printed circuit boards is photographic material:
Light-sensitive dry film referred to as dry film, the main component is a specific spectral sensitivity and photochemical reaction of the resin material. Practical dry film has three layers, the light-sensitive layer is sandwiched between the upper and lower layers of plastic film to play a protective role. There are two types of dry film, photopolymerized and photodegradable, according to the chemical properties of the photosensitive substance. Photopolymerized dry films harden under light irradiation of a specific spectrum, turning from a water-soluble substance into a water-insoluble one, while photodecomposability is just the opposite. They are generally categorized into photoresist and photographic film, and in the words of industry insiders, wet film and dry film. Wet film coating on copper-clad laminates in a certain wavelength of light will undergo a chemical change, thereby changing the solubility in the developer (solvent).
Wet film is divided into photodecomposition type (positive) and photopolymerization type (negative) difference, photopolymerization type resist in the unexposed can be dissolved in the developer, and after the exposure of the polymer into the polymer can not be dissolved in the developer; photodecomposition type resist is just the opposite of the photogeneration of a polymer that can be dissolved in the developer. Dry film also has a positive and negative, that is, the difference between photodecomposition and photopolymerization, they are very sensitive to ultraviolet light. In the future, dry film is likely to replace the wet film, because the film can provide high-precision lines and etching.
5. The fifth material of the printed circuit boardhttps://ipcb.co/printed-circuit-board/ solder resist (ink):
Printed ink is generally used to mark the PCB number, green paint, black paint, etc. It can also act as a protective layer of the PCB board to enhance the waterproof, corrosion resistance and insulation of the PCB board. It is a solder resist, common to liquid solder does not have an affinity for liquid photopolymer, in a specific light situation will change and harden. There are many different colors of ink, the most common solder resist color is green.
6. Printed circuit boards, the sixth material negative (film):
Negative here is similar to the photographic negative, is the use of light-sensitive materials to record the image of the material. Customers will be designed to the circuit board factory, the circuit board by the CAM center of the workstation will be the output of the circuit board, but not through the common printer, but the light painting machine. The role of the negative in the circuit board factory is pivotal, and all that is to be done to the substrate utilizing the principle of image transfer must first be turned into a negative.
In short, the printed circuit board is a very complex process, it is necessary to go through nine hundred and ninety-one difficulties to be able to put a draft map, presented as a real circuit board, and a variety of materials for printed circuit boards, in the purchase of the composite board must be selected material