What is reflow soldering? It is a process in which solder paste (a viscous mixture of powdered solder and flux) is used to temporarily connect one or thousands of tiny electrical components to their contact pads, and then the entire assembly is subjected to controlled heat. The solder paste reflows in a molten state to form a permanent solder joint. Heating can be accomplished by passing the assembly through a reflow oven, under an infrared lamp, or (unconventionally) by soldering individual solder joints with a desoldering hot air pen.
Reflow soldering, a key process in surface mount technology, is primarily used to solder surface mount components to circuit boards. The process is quite complex and can be categorized into two main types: single-sided placement and double-sided placement.
In the single-sided mounting process, one side of the board first needs to be pre-coated with solder paste. Subsequently, the components are pasted onto the board. After placement, the component is securely soldered to the board by reflow soldering. Finally, an electrical test is performed to ensure the quality of the soldering.
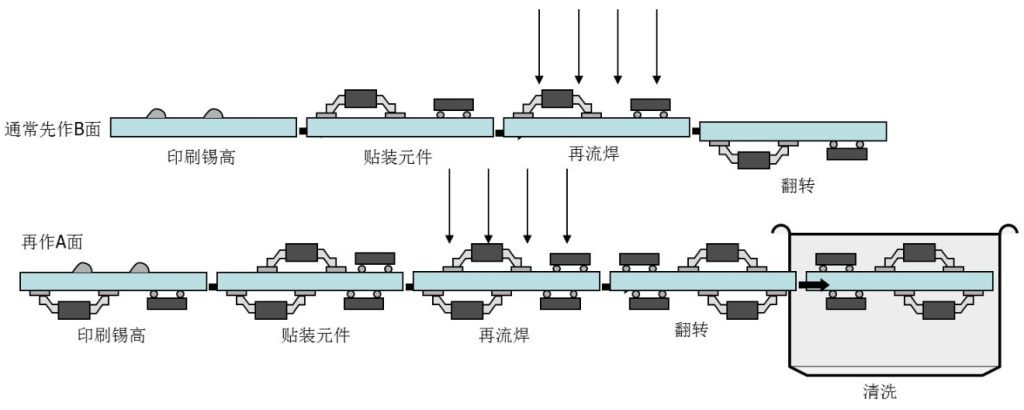
The process for double-sided placement is more complex. First, the A-side of the board is pre-pasted, patched, and then reflowed to complete the soldering. Next, the same process is performed on the B side: pre-paste, patch, and then reflow again to complete the soldering. Finally, the same electrical tests are performed to ensure the quality of the soldering.
The heart of the reflow process is the control of the temperature profile of the rise, the maximum temperature and the fall. To obtain excellent soldering quality, we must set a reasonable reflow soldering temperature profile and regularly do real-time testing of the temperature profile. At the same time, the soldering process needs to pay attention to some key process requirements, such as according to the direction of the PCB design when the soldering, to prevent conveyor belt vibration, check the first printed circuit board soldering effect.
In the production process, there are several factors that may affect the reflow soldering process results:
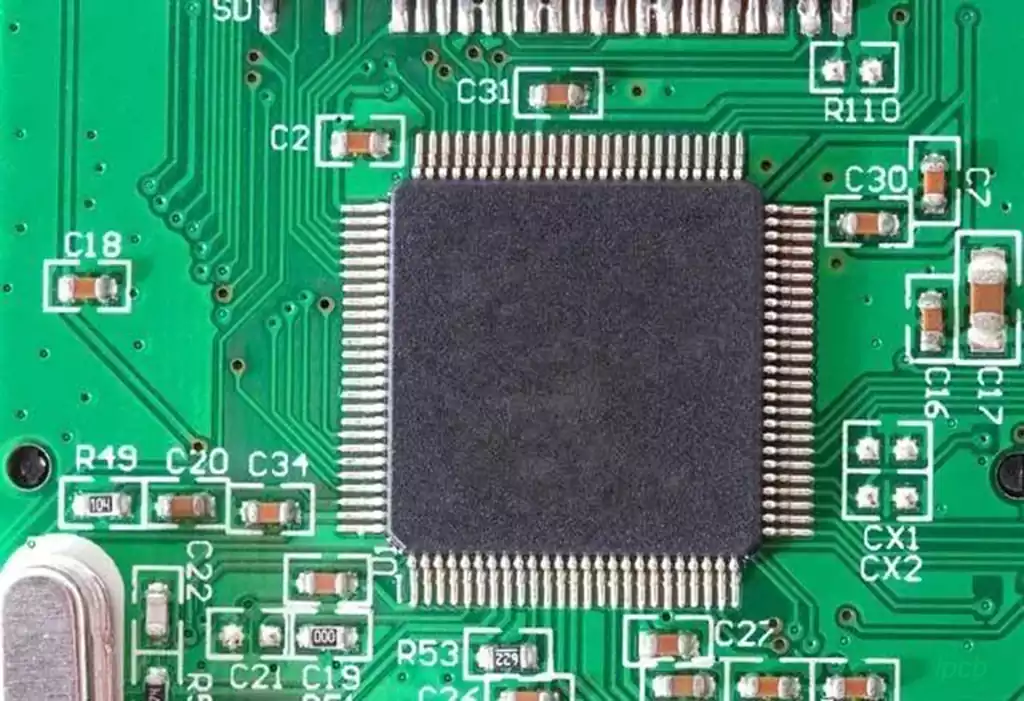
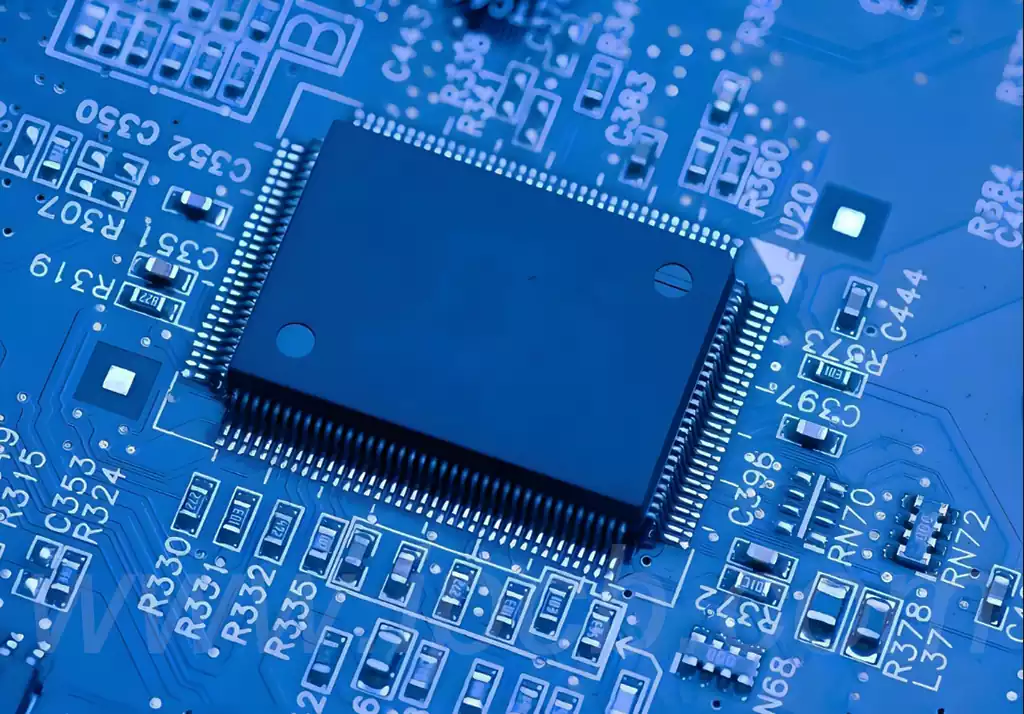
The type of components and heat capacity: PLCC, QFP and other components due to the heat capacity, soldering large area components may be more difficult than small components.
The impact of the heat dissipation system: reflow soldering furnace in the conveyor belt in the week after week to transfer the product for reflow soldering at the same time, but also become a heat dissipation system. In addition, the temperature of each temperature zone in the oven and differences in heat dissipation conditions at the edges and in the center may also affect soldering results.
Influence of product loading: Adjustment of the reflow temperature profile needs to take into account good repeatability at no load, load and different load factors. Load factor is defined as: LF = L / (L + S); where L = the length of the assembled substrate, S = the spacing of the assembled substrate. The larger the load factor, the more difficult it is for the reflow process to get repeatable results.
Eeflow soldering is the core technology of the SMT process. Through the overall heating of a one-time soldering of all electronic components on the PCB, electronic factory SMT production line quality control accounted for the absolute weight of the work in the end is to obtain excellent soldering quality. Setting a good temperature profile is the key to managing the furnace, but also an important step to ensure excellent soldering quality.