Pins have various functions, and the most common ones are power pins, ground pins, input pins, and output pins. The power pin provides the power supply voltage required by the chip, and the ground pin is used for grounding to ensure the stability and reliability of the circuit. The input pin receives the signal input from the external circuit, while the output pin outputs the signal processed inside the chip to the external circuit. Power pin: Its function is to introduce DC working power to the integrated circuit, which is divided into two types: single power supply and dual power supply.
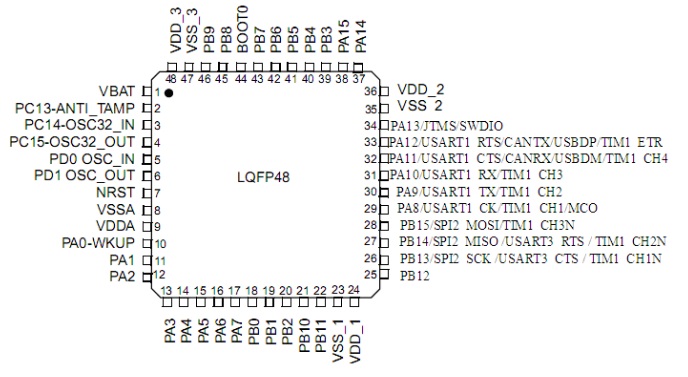
The pins of the chip refer to the metal pins on the chip, which play the role of connecting the chip to the external circuit. Each pin has a specific function and purpose. Through the pins, the chip can communicate and interact with other electronic components. The function of the pin is to transmit the electronic signal inside the chip to the external circuit, or to input the signal of the external circuit into the chip. They act as a bridge between the chip and the outside world, playing a key role in signal transmission and data exchange.
First, it can be identified by characters. Single power supply uses a single positive DC voltage as the working voltage. The integrated circuit has a power pin, and the “VCC” character is often marked next to the pin in the circuit diagram. Dual power supply generally uses symmetrical positive and negative DC voltages as working voltages. Integrated circuits have two power pins, and the circuit diagram often marks “+VCC” and “-VSS” characters next to the positive and negative pins respectively.
Ground pin: The function is to connect the ground wire inside the integrated circuit with the ground wire of the external circuit. Integrated circuits generally have a ground pin, and the “GND” character is marked next to the pin in the circuit diagram. The obvious feature of the ground pin external circuit is: directly connected to the ground wire in the circuit diagram, or there will be a ground symbol directly.
Signal input pin: The function is to introduce the input signal into the integrated circuit. Integrated circuits with one signal input pin are generally marked with the “IN” character next to the pin. If there are two input pins, the same phase and the opposite phase, the “+” and “-” characters are marked next to the pins.
Signal output pin: The function is to lead out the output signal of the integrated circuit, and the “OUT” character is generally marked next to the output pin in the circuit diagram. The external circuit characteristics of its output pins are: connected to the input end of the subsequent circuit through coupling elements such as capacitors, resistors, transformers, or directly driving loads such as speakers, light-emitting diodes, and indicator heads
The number and arrangement of pins depends on the design and functional requirements of the chip. Different chips may have different numbers of pins, ranging from a few to hundreds. There are also many ways to arrange pins, such as direct plug-in, surface mount, and ball grid array.
The integrated circuit pin is the connection point between the internal circuit of the integrated circuit and the peripheral circuit. Only when the external components or circuits are connected to the pins as required can the integrated circuit work. The integrated circuit often contains one or more unit circuits, and these unit circuits are connected to the external circuit through pins. The integrated circuit pins have three functions: first, the external components on these pins are part of the internal circuit of the integrated circuit. Only with the cooperation of external components can the integrated circuit form a complete circuit; second, through these pins, the working power supply is provided to the integrated circuit; third, through these pins, the input signal is provided to the integrated circuit, and the output signal processed by the integrated circuit is led out.
The role of ground wire
The main role of ground wire is that when an electrical appliance fails, the power supply may break down (or: destroy) certain components, making the outer shell of the appliance charged. Grounding the outer shell of the appliance can make the leakage protection device
- Signal “ground”;
Signal “ground” is also called reference “ground”, which is the reference point of zero potential and the common section of the circuit signal loop, with the graphic symbol “⊥”.
1) DC ground: DC circuit “ground”, zero potential reference point.
2) AC ground: zero line of AC power. It should be distinguished from the ground wire.
3) Power ground: zero potential reference point of high current network devices and power amplifier devices.
4) Analog ground: zero potential reference point of amplifiers, sample-and-hold devices, A/D converters and comparators.
5) Digital ground: also called logic ground, which is the zero potential reference point of digital circuits.
6) “Hot ground”: The switching power supply does not need to use a transformer. The “ground” of its switching circuit is related to the mains power grid, the so-called “hot ground”, which is charged, and the graphic symbol is: “”.
7) “Cold ground”: Since the high-frequency transformer of the switching power supply isolates the input and output ends; and since its feedback circuit often uses photoelectric coupling, it can both transmit feedback signals and isolate the “ground” of both sides; the ground at the output end is called “cold ground”, which is not charged. The graphic symbol is “⊥”.
- Protective “ground”;
Protective “ground” is a wiring method set up to protect personnel safety. One end of the protective “ground” line is connected to the electrical appliance, and the other end is reliably connected to the earth.
- “Ground” in audio.
1) Shielded wire grounding: In order to prevent interference, the metal casing of the audio system is connected to the signal “ground” with a wire, which is called shielded grounding.
2) Audio-specific “ground”: In order to prevent interference, professional audio, in addition to the shielded “ground”, must also be connected to the audio-specific “ground”. This grounding device should be specially buried and connected to the corresponding grounding terminal of the isolation transformer and shielded voltage regulator as a dedicated audio grounding point in the sound control room.
What are the GND pin, 3.3V pin and 5V pin used for?
The GND pin is the ground pin of the chip, which is used to provide a potential reference for the circuit.
The 3.3V pin is the 3.3V power pin of the chip, which is used to provide 3.3V power to the chip. Some peripheral devices such as chip modules or sensors can also obtain power supply through this pin. The 5V pin is the 5V power pin of the chip, which is also used to provide power supply to the chip. However, please note that not all chips support 5V voltage. You need to choose the appropriate power supply voltage according to the chip specification.
Why are the 3.3V pin and GND pin of STM32F103C8T6 connected?
If the 3.3V pin and GND pin of STM32F103C8T6 are connected, it may be because of one of the following reasons:
- Short circuit: There may be a short circuit connection between the pins, resulting in a direct connection between the 3.3V pin and the GND pin.
- Wrong connection: The 3.3V pin may be mistakenly connected to the GND pin during the connection process, or the GND pin may be mistakenly connected to the 3.3V pin.
- Damaged components: It is possible that the STM32F103C8T6 chip or other related components are damaged, resulting in the loss of isolation between the 3.3V pin and the GND pin.
In any case, if the 3.3V pin and the GND pin are connected, it is recommended to check whether the circuit connection is correct and ensure that there is no short circuit or wrong connection. If it is confirmed that there is no problem but the conduction phenomenon still exists, the chip or other related components may need to be replaced. Please note that for circuit connection and troubleshooting issues, it is recommended to consult professional engineers.
Different types and functions of grounding have different grounding methods for different circuits. The following are the common grounding methods in electronic power equipment:
- Safety grounding
Safety grounding is to connect the casing of high-voltage equipment to the earth. First, to prevent the accumulation of charge on the casing, generate electrostatic discharge and endanger the safety of equipment and personnel. For example, the grounding of computer cases and the tail of oil tankers dragging on the ground are to release the accumulated charge and prevent accidents; second, when the insulation of the equipment is damaged and the casing is charged, the power supply protection action is prompted to cut off the power supply to protect the safety of the staff, such as the casing of refrigerators and rice cookers. Third, it can shield the huge electric field of the equipment and play a protective role, such as the guardrail of civil transformers.
- Lightning protection grounding
When power electronic equipment is struck by lightning, whether it is direct lightning or induction lightning, if there is no corresponding protection, the power electronic equipment will be greatly damaged or even scrapped. To prevent lightning strikes, we generally set lightning rods at high places (such as roofs and chimney tops) connected to the earth to prevent lightning strikes from endangering the safety of equipment and personnel. Both safety grounding and lightning protection grounding are to provide safe protection measures for electronic power equipment or personnel to protect the safety of equipment and personnel.
- Working grounding
Working grounding is a reference potential provided for the normal operation of the circuit. This reference potential is generally set to zero. The reference potential can be set to a certain point, a certain section or a certain block in the circuit system. When the reference potential is not connected to the earth, it is regarded as a relative zero potential. However, this relative zero potential is unstable. It will change with the change of the external electromagnetic field, causing the parameters of the system to change, resulting in unstable operation of the circuit system. When the reference potential is connected to the earth, the reference potential is regarded as the zero potential of the earth, and will not change with the change of the external electromagnetic field. However, unreasonable working grounding will increase the interference of the circuit. For example, interference caused by incorrect grounding points and interference caused by the common end of electronic equipment not being properly connected. In order to effectively control the various interferences generated by the circuit during work so that it can meet the electromagnetic compatibility principle. When we design the circuit, according to the nature of the circuit, we can divide the working ground into different types, such as DC ground, AC ground, digital ground, analog ground, signal ground, power ground, power supply ground, etc. Different grounding should be set separately. Do not mix them together in one circuit. For example, digital ground and analog ground cannot share a ground wire, otherwise the two circuits will generate very strong interference and paralyze the circuit!
- Signal ground
The signal ground is the common reference ground wire of the zero potential of various physical quantity signal sources. Since the signal is generally weak and susceptible to interference, unreasonable grounding will cause interference in the circuit, so the requirements for the signal ground are high.
- Analog ground
The analog ground is the common reference ground wire of the zero potential of the analog circuit. There are small signal amplifier circuits, multi-stage amplifiers, rectifier circuits, voltage regulator circuits, etc. in the analog circuit. Improper grounding will cause interference and affect the normal operation of the circuit. The grounding in the analog circuit is of great significance to the entire circuit. It is one of the foundations for the normal operation of the entire circuit. Therefore, the role of reasonable grounding in the analog circuit on the entire circuit cannot be ignored.
- Digital ground
The digital ground is the common reference ground wire of the zero potential of the digital circuit. Since the digital circuit works in a pulse state, especially when the leading and trailing edges of the pulse are steep or the frequency is high, a large number of electromagnetic waves will interfere with the circuit. If the grounding is unreasonable, the interference will be aggravated, so the selection of the grounding point of the digital ground and the laying of the grounding wire should also be fully considered.
- Power ground
The power ground is the common reference ground wire of the zero potential of the power supply. Since the power supply often supplies power to each unit in the system at the same time, and the power supply properties and parameters required by each unit may be very different, it is necessary to ensure the stable and reliable operation of the power supply and the stable and reliable operation of other units. The power ground is generally the negative pole of the power supply.
- Power ground
The power ground is the common reference ground wire of the zero potential of the load circuit or power drive circuit. Since the current of the load circuit or power drive circuit is strong and the voltage is high, if the ground wire resistance is large, a significant voltage drop will be generated, resulting in greater interference, so the interference on the power ground wire is large. Therefore, the power ground must be set separately from other weak current grounds to ensure the stable and reliable operation of the entire system.
In short, the ground pin of the chip is the key interface connecting the chip with the external circuit. Through the pin, the chip can communicate and interact with other electronic components to achieve various functions and applications. Knowing and understanding the pins of a chip is crucial for electronic engineers and technicians, as they are the basis for realizing circuit connections and signal transmission.