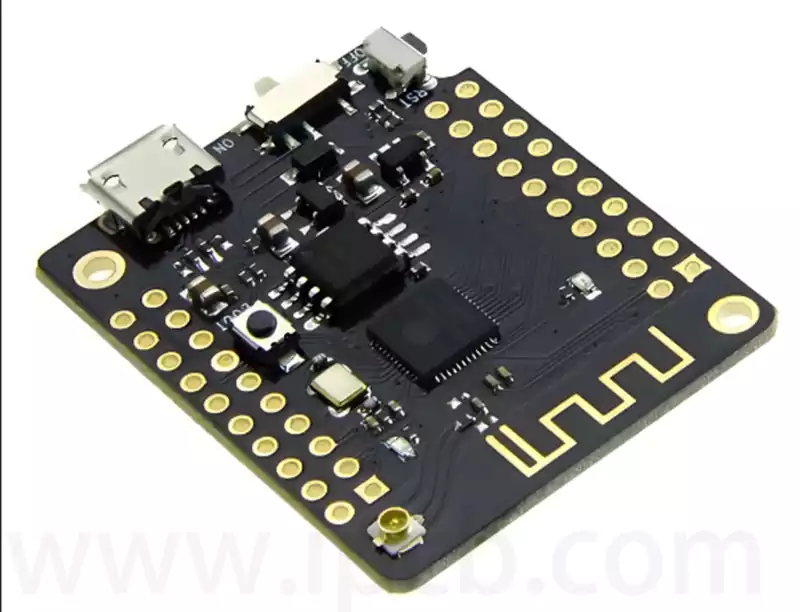
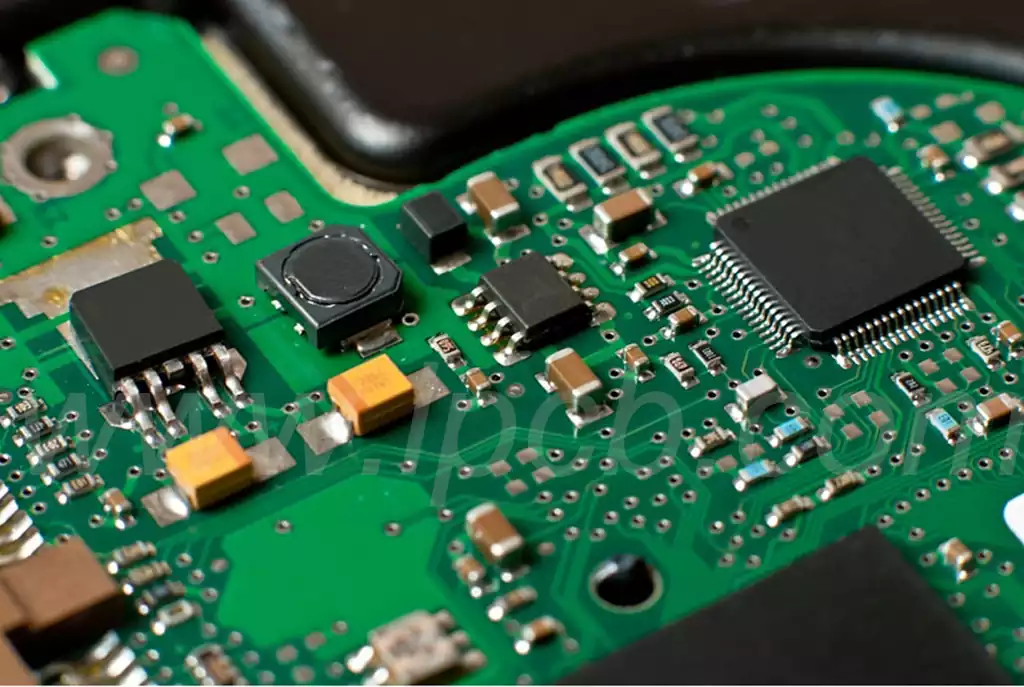
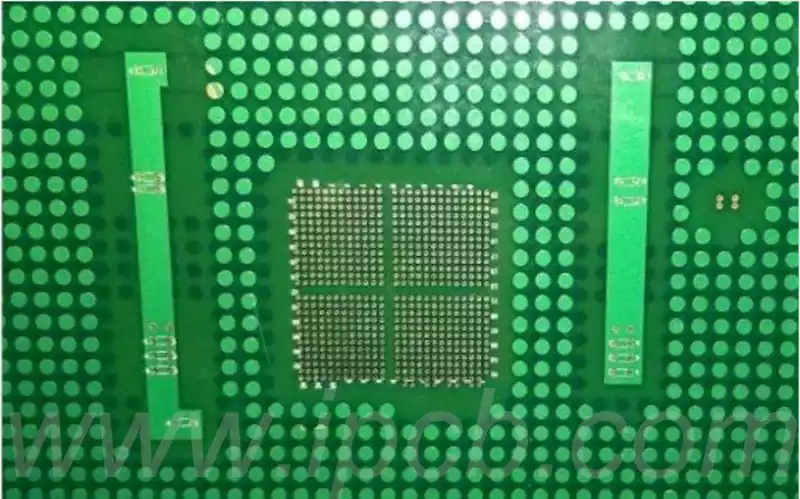
IC carrier board that is, ic packaging substrate, is a class of circuit boards used to carry the chip, belongs to a branch of the PCB, with high density, high precision, high performance, miniaturization and thin and light features, can provide support for the chip, heat dissipation and protection, but also for the chip and PCB motherboard to provide electrical connections and physical support.
Classification
According to different materials, it can be divided into rigid package substrate (rigid), flexible package substrate and ceramic package substrate, of which rigid package substrate is most widely used.
Rigid encapsulation substrate can be divided into BT encapsulation substrate, ABF encapsulation substrate and MIS encapsulation substrate according to the main raw materials, of which BT encapsulation substrate and ABF encapsulation substrate are the most widely used.
According to the IC package substrate and bare chip connection side of the encapsulation process is different, can be divided into lead bonding (WB) package substrate and flip-chip (FC) package substrate.
According to the substrate and PCB connection side of the different packaging processes, ic chip packaging substrate can be divided into ball grid array package (BGA), pin grid array package (PGA), grid array package (LGA), chip size package (CSP), board on chip package (BOC) and so on.
According to the different application areas, the package substrate can be divided into memory chip package substrate, logic chip package substrate, sensor chip package substrate and communication chip package substrate.
IC carrier board is the key component of chip packaging, which is the carrier for connecting and transmitting signals between the bare chip (DIE) and the printed circuit board.
In the field of IC packaging, carrier board is undoubtedly the largest cost source, occupying more than 30% of the total cost of packaging. This cost structure not only covers the packaging board itself, but also involves packaging materials, equipment depreciation and testing and other aspects. Among them, the IC substrate is the core position, its cost in the integrated circuit packaging accounted for more than 30%, highlighting its importance.
The manufacturing of IC substrates involves a variety of key raw materials. First of all, copper foil, as one of its main raw materials, is similar to the electrolytic copper foil used in PCBs, but with more stringent requirements. Ultra-thin and homogeneous copper foils, with thicknesses as low as 1.5 μm and generally in the range of 2-18 μm, are more difficult to process and more expensive than the copper foil used in traditional circuit board.
In addition, the substrate, as another important component of the package substrate, is of various types, including rigid substrates, flexible film substrates and LTCC co-fired ceramic substrates. Each type of substrate has its own unique application areas and development potential. Rigid substrates and flexible substrates have large development space, while the development of co-fired ceramic substrates is relatively slow.
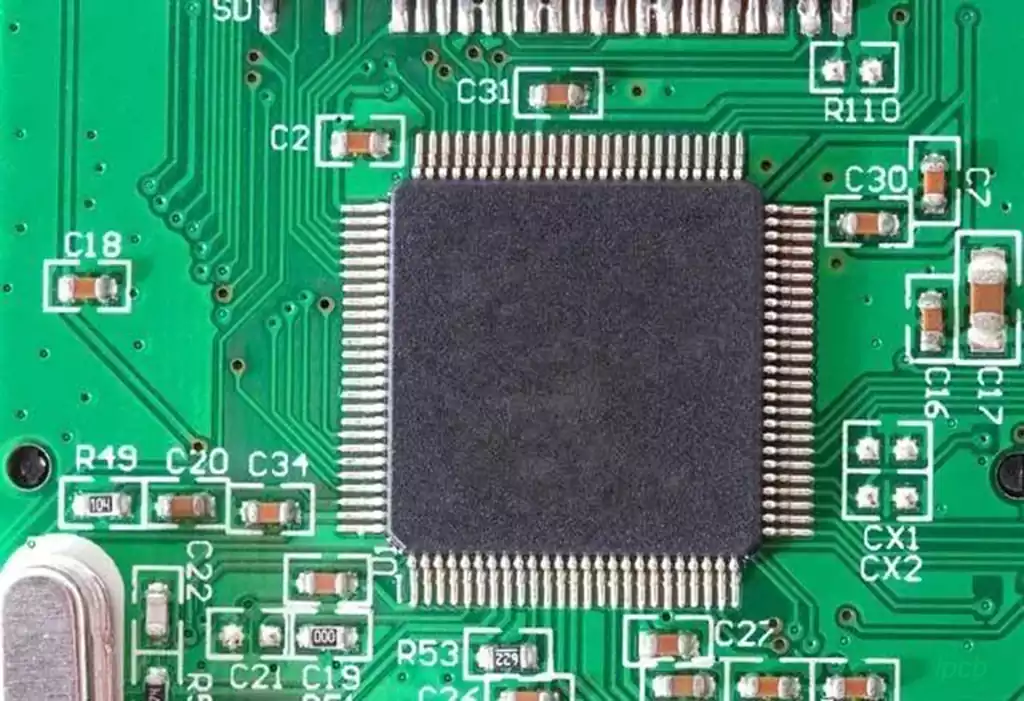
When selecting an IC substrate, factors such as dimensional stability, high-frequency characteristics, heat resistance and thermal conductivity need to be considered. According to different packaging needs, the materials of the substrate are different, such as BT materials, ABF materials and MIS materials, etc., which have their own advantages and disadvantages and are suitable for different application scenarios.
For flexible packaging substrates, PI (polyimide) and PE (polyester) resins are widely used due to their excellent performance. These materials not only have good heat resistance and electrical properties, but also have high flexibility and processability, making flexible IC carrier boards have a broad application prospect in consumer electronics, automotive electronics and other fields.
However, it is worth noting that the core material substrate of IC substrate mostly relies on the supply of foreign enterprises. Take the most commonly used BT materials and ABF materials as an example, the world’s major IC substrate manufacturers are mostly Japanese and South Korean companies, which to a certain extent limits the development of the domestic IC packaging substrate industry.