Insulate metal substrates are made using a unique insulating material that presses the copper foil of the circuit board to the metal substrate. The metal substrate is specially treated to increase adhesion and resilience, which allows the board to withstand the mechanical and thermal stresses of many applications. The insulating material is a special blend of ceramic-filled polymers with high thermal conductivity, insulation and elasticity. SMD circuit boards prepared with this blend meet the electrical and thermal performance requirements of power supply designers. Single-sided IMS allows SMD components to be surface-mounted on that side of the circuit layer, while the back side is fixed to a heat sink or motherboard for heat transfer. The processing of the wiring for this type of IMS is similar to that of FR4 wiring, except that the final board is shaped differently. This difference is due to the metal substrate of the IMS, which does not lend itself to the traditional moulding methods used in the PCB industry. It uses an advanced punch-cut moulding and a new V-groove technology.
The unique properties of the insulating layer are its thermal and electrical properties. To provide low thermal resistance, it must be thin (a few mils) and have high thermal conductivity. The polymer should have a high dielectric strength of about 2kV/mil. Most of these materials have a UL recognised operating temperature of 130°C or higher. Materials with more than one layer are also available to meet the need for shielding or additional electrical connections. As machining processes have evolved, various shapes of sheet metal have come into use .
Application areas for insulate metal substrate include:
Power conversion: insulate metal substrate can have a wide range of thermal properties, are compatible with mechanical reinforcements and are very reliable.
LEDs: The use of insulate metal substrate ensures the lowest possible operating temperature for LEDs at maximum brightness, colour and lifetime.
Motor drives: The dielectric selection of insulate metal substrate provides the required electrical insulation to meet operating parameters and safety agency test requirements.
Solid state delay:Insulate metal substrate can provide very high heat dissipation coefficients and can be used as a substrate to provide very stable mechanical support.
Automotive:insulate metal substrates are used in the automotive industry where long term reliability needs to be guaranteed at high operating temperatures and where the requirement for efficient use of space has to be met.
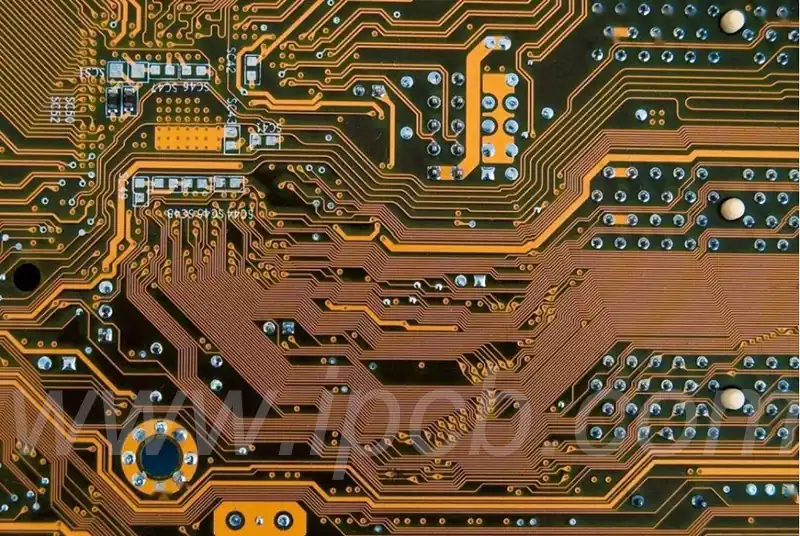

Thermal management processes in insulate metal substrate
The board has excellent thermal resilience because its thermal conductivity is very good for PCB IMS.
IMS PCBs also have thermal management features. This PCB uses metal as the base layer. Metals are good heat conductors and they are responsible for the high or low thermal resistance of the IMS PCB. The thermal conductivity of thermoelectric materials can be used for precise measurements during heat exchange.
Similarly, checking the thermal conductivity of components will help in understanding their thermal management and heat dissipation. Manufacturers must also provide the right material at a location to prevent heat loss. thermal conductivity in IMS boards helps with thermal management.
Different Types of insulate metal substrate
The following are the differences in IMS-based PCBs observed in industrial applications and manufacturing uses
Aluminium Metal Substrate PCBs
This metal is one of the widely used metal substrate materials. Aluminium has medium thermal conductivity and electrical properties and is much cheaper than copper.
Copper Metal Substrate PCBs
Copper is a material used as a substrate and is used in only a few applications due to its good thermal and electrical conductivity. Compared to aluminium and stainless steel, copper has desirable material qualities.
Copper’s tendency to corrode is its big drawback. And the material cost: copper substrate PCBs can be quite expensive.
Stainless steel metal substrate PCBs
Stainless steel is used as a base material in many applications, especially those requiring high mechanical strength. Compared to aluminium and copper, stainless steel has poorer electrical and thermal properties, although it is the cheaper option. It is much cheaper than aluminium and copper.
There are four different types of IMS PCBs, depending on the printed circuit board layer and component mounting position
Dual-layer single component mount side IMS PCBs
More complex circuits can be assembled due to the presence of two thick copper layers in this type. The presence of an FR4 layer between the two copper layers may reduce the excellent thermal conductivity.
Thermal vias are used because they have excellent thermal conductivity. Heat is conducted from the top to the bottom substrate through these thermal vias that contact the bottom surface of the SMD component.
Dual Component Placement Side Insulate metal substrates
The design has two soldermask layers, each of which can have components mounted on it. The metal substrate is located in the centre of the structure. Heat and current transfer is achieved through the vias. To insulate the carrier vias, a resin-like substance is placed around the heat vias.
Single-sided metal-core IMS PCB
Only one side of this particular IMS PCB variant is available for connecting components. One layer consists of thick copper, while the bottom side consists of a metal substrate that doubles as a heat sink for the device.
LED PCBs and Solid State Relay (SSR) PCBs are examples of typical circuit configurations using this type.
The mechanical properties of these PCBs have been improved. Because the metal substrate sits in the middle, its thermal performance is not as good as other types, but they do accommodate more complex circuits.
Insulate metal substrates have become an indispensable and critical component of modern electronic devices due to their superior thermal management capabilities and wide application adaptability. As technology continues to advance, IMS PCBs will demonstrate their unique value in more areas and continue to drive innovation and development in the electronics industry.