Circuit elements play a vital role in the development of electronic technology. They are the basic components of circuits, and the normal operation of various electronic devices is inseparable from them. From the simplest resistors and capacitors to complex integrated circuits, each circuit element plays a unique role in a specific application scenario.

Classification of circuit components
Circuit elements can be classified according to different standards. For example, according to their functions, they can be divided into passive components and active components. Passive components include resistors, capacitors, inductors, etc., which do not require additional power to work. Active components, such as transistors and diodes, require power drive. In addition, they can be further classified according to materials, packaging forms, application fields, etc.
1.Resistors
Resistors are one of the most basic circuit elements. Their function is to limit the flow of current and adjust the voltage and current in the circuit according to design requirements. The unit of resistance is ohm (Ω), and its main parameters include resistance, power, accuracy and temperature coefficient. Common resistors include fixed resistors, variable resistors, thermistors and photoresistors. The resistance of fixed resistors is constant, while the resistance of variable resistors can be adjusted. For example, the volume control knob is realized by variable resistors. The resistance of thermistors changes with temperature and is widely used in the field of temperature sensing, while the resistance of photoresistors changes with light intensity and is very common in automatic lighting systems.
2.Capacitors
The functions of capacitors in circuits mainly include energy storage, filtering, coupling, and oscillation. The unit of capacitance is farad (F), usually microfarad (μF) or nanofarad (nF) as the unit of measurement. The basic structure of a capacitor consists of two conductor plates with a layer of insulating medium sandwiched between them. Common types of capacitors include ceramic capacitors, electrolytic capacitors, and film capacitors. Ceramic capacitors have high stability and are suitable for high-frequency circuits, while electrolytic capacitors have large capacity and are suitable for power supply filtering.
3.Inductors
Inductors are circuit elements that can store magnetic energy. Their main functions are to hinder sudden changes in current, filter, and generate magnetic fields in oscillating circuits. The unit of inductance is Henry (H). Inductors play an important role in switching power supplies, radio frequency circuits, and electromagnetic compatibility design. For example, in power supply circuits, inductors can be combined with capacitors to form a filter circuit to smooth voltage fluctuations.
4.Semiconductor devices
Semiconductor devices are the core of modern electronic technology. They include diodes, transistors and integrated circuits. Diodes are components with unidirectional conductivity and are widely used in rectification, signal modulation and protection circuits. Transistors can amplify signals or be used as switches. They are often used in amplification circuits and logic circuits of various electronic devices. Integrated circuits integrate multiple electronic components on a silicon chip to achieve complex electronic functions. Microprocessors, memory and analog chips are typical applications of integrated circuits.
Application of circuit elements in electronic devices
Circuit elements perform different tasks in different types of electronic devices. For example, in household appliances, resistors are used for current limitation, capacitors are used for power filtering, diodes are used for rectification circuits, and integrated circuits control the overall operation of the device. In mobile communication devices, inductors, capacitors and transistors in radio frequency circuits work together to achieve signal amplification and modulation functions. Memory chips, processors, input and output interfaces in computer systems are also composed of different circuit elements.
In the field of automotive electronics, circuit elements are used for engine control, in-vehicle entertainment systems, automatic driving assistance systems, etc. Especially for new energy vehicles, battery management systems, motor control modules, on-board chargers, etc. are inseparable from high-performance circuit components.
Development trend of circuit components
With the continuous advancement of electronic technology, the development trend of circuit components presents the following characteristics:
Miniaturization and high integration
Electronic products have higher and higher requirements for space and power consumption, so the size of circuit components continues to shrink, while the functions are becoming stronger and stronger. For example, a large number of micro components are integrated on the motherboard of modern smartphones, making the devices thinner and lighter.
High efficiency and low power consumption
Green energy and sustainable development are important directions for the current development of science and technology. The research and development and application of low-power components can effectively reduce the energy consumption of equipment and improve battery life. Especially in IoT devices, the demand for low-power circuit components is very strong.
Intelligence and programmability
Traditional electronic components are mainly fixed functions, while modern intelligent circuit components can change their functions through software programming. For example, programmable logic devices (FPGAs) and system-on-chip (SoCs) can flexibly adjust their functions and improve the adaptability of the system.
Application of new materials
The emergence of new materials such as graphene and carbon nanotubes has provided new possibilities for the development of circuit components. For example, the high conductivity and transparency of graphene make it have broad application prospects in flexible electronic devices and high-frequency circuits.
Selection and reliability of circuit components
In the electronic design process, it is crucial to select suitable circuit components. Designers need to comprehensively consider the parameters, working environment, reliability and cost of the components. For example, in high-frequency circuits, low-loss capacitors and inductors need to be selected; in power circuits, high-voltage and high-temperature resistant devices need to be selected. In addition, the reliability of circuit components directly affects the life of the product. Therefore, in the fields of industry, medical care, and aerospace, the reliability of components is extremely high. In order to ensure reliability, engineers usually conduct rigorous tests, including temperature cycle tests, vibration tests, and wet heat tests.
Manufacturing process of circuit components
The performance of circuit components depends not only on their design parameters, but also on the manufacturing process. Different types of circuit components use different methods in the manufacturing process to ensure that they meet specific electrical characteristics and reliability requirements.
Manufacturing of resistors
Resistors are usually manufactured using thin film or thick film processes. Thin film resistors are made by depositing an extremely thin layer of metal oxide or carbon film on a ceramic substrate, with high precision and stability. Thick film resistors, on the other hand, use screen printing technology to print the resistor paste on the substrate, and then form the final resistor layer through high-temperature sintering. For high-power resistors, a winding process is usually used, that is, winding the resistor wire on a ceramic or glass fiber tube to improve heat resistance and power carrying capacity.
Manufacturing of capacitors
The manufacturing of capacitors involves the selection of dielectric materials and the deposition process of electrodes. For example, ceramic capacitors are made of multiple layers of ceramic dielectrics, which are sintered at high temperatures to form stable capacitance characteristics. Electrolytic capacitors use metal foil as electrodes and form an oxide layer on the anode foil through an electrochemical process to provide high-capacity charge storage capacity. In addition, organic thin film capacitors have also been widely used in recent years, with high reliability and low loss.
Manufacturing of semiconductor devices
The manufacturing of semiconductor devices is the most complex, requiring multiple process steps such as lithography, etching, diffusion, ion implantation, and thin film deposition. For example, the manufacturing of transistors and integrated circuits requires etching tiny circuit structures on high-purity silicon wafers and using chemical vapor deposition (CVD) technology to form metal interconnect layers. Advanced manufacturing processes continue to push semiconductor devices toward higher integration and lower power consumption, such as the current 7nm, 5nm, and even 3nm process technologies, which greatly improve chip performance.
Fault analysis and testing of circuit components
During the production and use of electronic products, circuit components may fail for various reasons. Therefore, engineers need to identify and troubleshoot faults through testing and analysis to ensure the normal operation of the circuit.
Common circuit component failures
Resistor failure: Mainly manifested as resistance drift, open circuit or short circuit. This may be due to material aging caused by long-term high temperature operation, current overload or high ambient humidity.
Capacitor failure: Mainly includes leakage, short circuit and capacity attenuation. After long-term use, the internal electrolyte of electrolytic capacitors may dry up, resulting in a decrease in capacitance or failure.
Inductor failure: Coil open circuit, short circuit or change in inductance are the most common problems, usually caused by mechanical damage, poor welding or electromagnetic interference.
Semiconductor device failure: Diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits are susceptible to damage from overvoltage, overcurrent, or electrostatic discharge (ESD), resulting in performance degradation or complete failure.
Testing methods for circuit components
Multimeter testing: Engineers usually use a multimeter to measure the basic parameters of resistance, capacitance, and inductance. For example, the measurement of resistance value can be completed directly through the ohm range of the multimeter, while the measurement of capacitance value requires the use of a capacitance test function or an LCR tester.
Oscilloscope testing: Oscilloscopes are used to observe the signal waveforms in the circuit, which can help analyze whether the circuit components are working properly. For example, by observing the waveform of the power supply filter capacitor, it can be determined whether it has leakage or failure.
X-ray detection: For components with complex packaging (such as BGA chips), X-rays can be used to check whether the internal solder joints are broken or poorly soldered.
Thermal imaging detection: Using an infrared thermal imager, abnormally hot components on the circuit board can be quickly found, thereby locating possible fault points. For example, when the temperature of a certain area on the circuit board rises abnormally, it may mean that there is a short circuit or overload problem there.
Environmental protection and recycling of circuit components
With the widespread use of electronic devices, the impact of discarded electronic products on the environment is becoming increasingly serious. Therefore, how to treat and recycle circuit components in an environmentally friendly manner has become an issue that the electronics industry must pay attention to.
Development of environmentally friendly circuit components
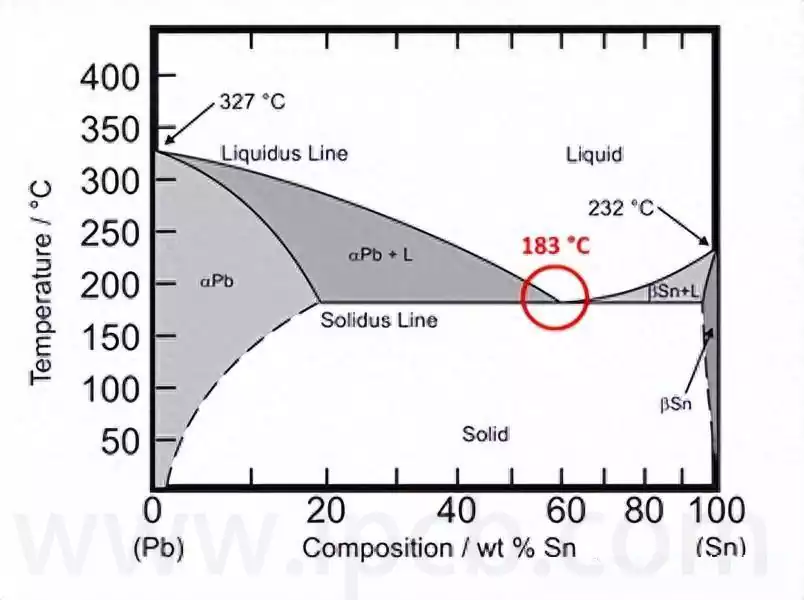
Traditional electronic components contain harmful substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, which pose potential hazards to the environment and human health. To this end, many countries and regions around the world have successively introduced environmental protection regulations, such as the EU’s Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive (RoHS), which requires that electronic products must not contain specific hazardous substances. This has prompted manufacturers to develop environmentally friendly circuit components, such as lead-free soldering materials, low-halogen circuit boards, and degradable plastic packaging.
Recycling and treatment of electronic waste
Disassembly and classification: When recycling electronic equipment, it is first necessary to disassemble the circuit board and classify the circuit components. For example, chips, capacitors, inductors, etc. with high precious metal content can be refined into metals such as gold, silver, and copper, while plastic shells and metal frames can be separated for secondary use.
Chemical treatment: Some waste electronic components can be chemically extracted with precious metals, such as using cyanide to recover gold from waste circuit boards.
Physical recycling: For circuit components that can still work properly, they can be put back on the market after testing, cleaning and repackaging. For example, many electronic manufacturers have set up electronic product recycling programs to reuse components in old equipment.
Sustainable development trends
In the future, the electronics industry will pay more attention to environmental protection and recyclability when designing circuit components. For example, using biodegradable materials to manufacture electronic components, or designing electronic products that are easier to disassemble and recycle. At the same time, the development of artificial intelligence and automation technology will also improve the recycling efficiency of electronic waste and reduce the impact on the environment.
Summary
Circuit components are the cornerstone of modern electronic technology, and their performance and quality directly affect the stability and reliability of electronic equipment. From basic resistors, capacitors, inductors to complex semiconductor devices, each component plays a key role in electronic circuits.
With the advancement of science and technology, the manufacturing process of circuit components continues to improve, the testing methods are becoming more and more perfect, and environmental protection and recycling have also become the focus of industry attention. In the future, as electronic products develop towards high integration, low power consumption and intelligence, circuit components will continue to evolve, providing more advanced and reliable technical support for all walks of life.