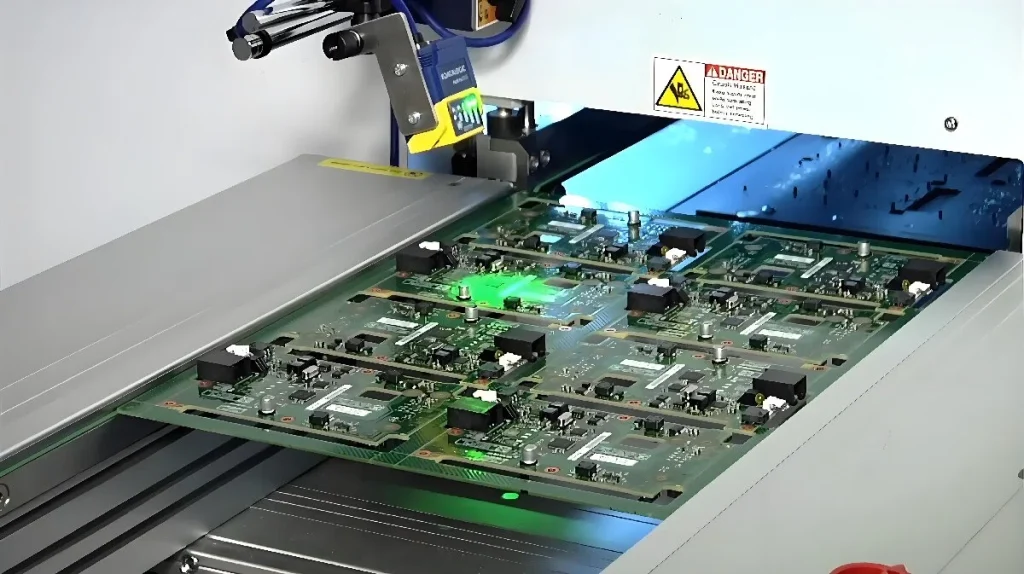
PCBA test fixtures, also known as ‘test fixtures, play a crucial role in the PCBA manufacturing process. They are primarily used to conduct comprehensive testing on PCBs that have undergone SMT placement and DIP insertion processes. These tests primarily include ICT testing and FCT testing, which utilise test points to verify the electrical conductivity of the circuit board and determine whether the entire PCB has been properly soldered. PCBA test fixtures are indispensable tools that enable these testing processes to proceed smoothly.
Working Principle of PCBA Test Fixtures
- Signal Connection
PCBA test fixtures connect test instruments to the PCB circuit board being tested through various interfaces and cables. Through accurate signal transmission, test instruments can communicate with the PCB circuit board and obtain test signals and feedback signals. - Signal Distribution and Expansion Components such as switches and connectors within the test fixture enable signal distribution and expansion. Through proper design, different test points can be connected to the test instruments, thereby enabling testing of various sections of the circuit board.
- Electrical Characteristic Testing
Electrical characteristic testing is a critical component of PCBA testing. By connecting to the PCB circuit board, the test fixture can measure parameters such as voltage and current to determine whether the electrical performance of the circuit board meets standards under normal operating conditions. - Functional Testing
Functional testing is a critical component of the pcba test fixture. By controlling components on the PCB circuit board and obtaining feedback signals, the fixture can simulate real-world usage environments to comprehensively test the circuit board’s functions and determine whether its performance meets requirements. - Fault Localisation and Debugging When abnormal situations occur during testing, the pcba test fixture can assist engineers in quickly localising faults and debugging. By providing detailed test results, derived data, and abnormal alarm information, it can quickly identify the fault location and provide strong support for problem resolution.
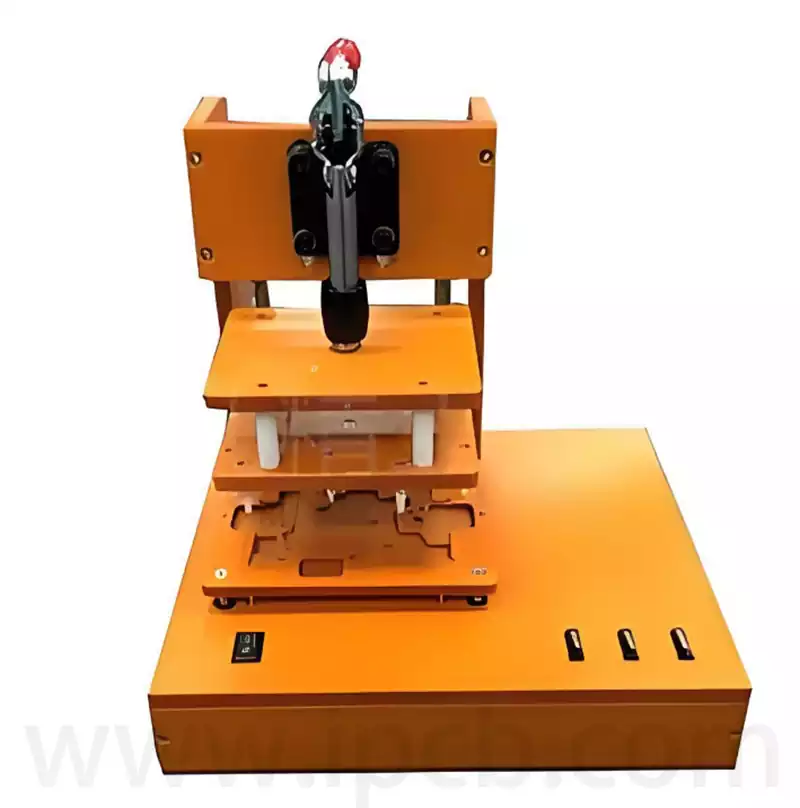

Common PCBA Test Fixtures and Their Characteristics:
ICT Test Fixture
ICT (In-Circuit Test) fixtures are primarily used to detect open circuits, short circuits, and component faults in PCBA circuits. Testing is performed by probes contacting test points on the PCB, requiring the use of specialised fixtures. Design must ensure accurate probe positioning and effective contact with test points, while optimising test point layout to minimise interference, thereby enhancing testing accuracy and efficiency.
FCT Test Fixtures
FCT (Functional Test) fixtures simulate the actual functionality of the entire PCBA, using IC program loading to detect issues in hardware and software. Typically equipped with production-required fixtures and test stands, they enable load connection and simulation of user input/output. Design considerations prioritise the stability and controllability of the test environment, as well as precise alignment between the fixture and the PCBA board.
Aging Test Fixture
Aging test fixtures simulate the aging process of products in actual usage environments by continuously powering the PCBA and electronic products over extended periods to observe any failures. Design considerations include ensuring stable and safe power supply, as well as strict control and monitoring of environmental factors such as temperature and humidity.
AOI Test Fixtures
AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) test fixtures identify defects by capturing PCB images and comparing them with design drawings. Although they do not directly participate in electrical testing, they require strict control of lighting and stability in the testing environment to ensure the clarity and accuracy of captured images.
Other Special Test Fixtures
In addition to the common types mentioned above, there are special test fixtures designed for specific requirements. For example, fatigue test fixtures are used for prolonged high-frequency operations to assess PCBA durability; harsh environment test fixtures simulate extreme conditions such as temperature, humidity, drops, water splashes, and vibrations to test PCBA reliability. When designing such fixtures, safety under extreme test conditions and controllability of the testing process must be prioritised.
The production of PCBA test fixtures is a highly customised process, with the following specific steps:
Data collection: PCBA factories must provide the fixture manufacturer with Gerber files of the PCBA board, material requirements, PCBA samples, and fixture requirement documents. If no samples are available, production can still be completed using only the Gerber files.
Fixture design: Based on the collected data, the fixture manufacturing factory designs the fixture. During the design process, factors such as fixture structure, positioning methods, and interface layout must be considered.
Material preparation: Materials such as acrylic or bakelite, plastic, metal probes, displays, wires, and simple PCB circuit boards are used for manufacturing.
Manufacturing: Based on the design drawings, the manufacturing process involves material cutting, drilling, and assembly.
Debugging and verification: After production, the test fixture is debugged and verified to ensure it meets testing requirements and has high accuracy and stability.
PCBA test fixtures, as critical equipment, ensure that circuit boards meet design requirements in terms of performance from manufacturing to assembly. Through precise connections and diverse testing, they effectively enhance product reliability and production efficiency. With technological advancements, test fixtures will continue to be optimised to safeguard electronic manufacturing quality.