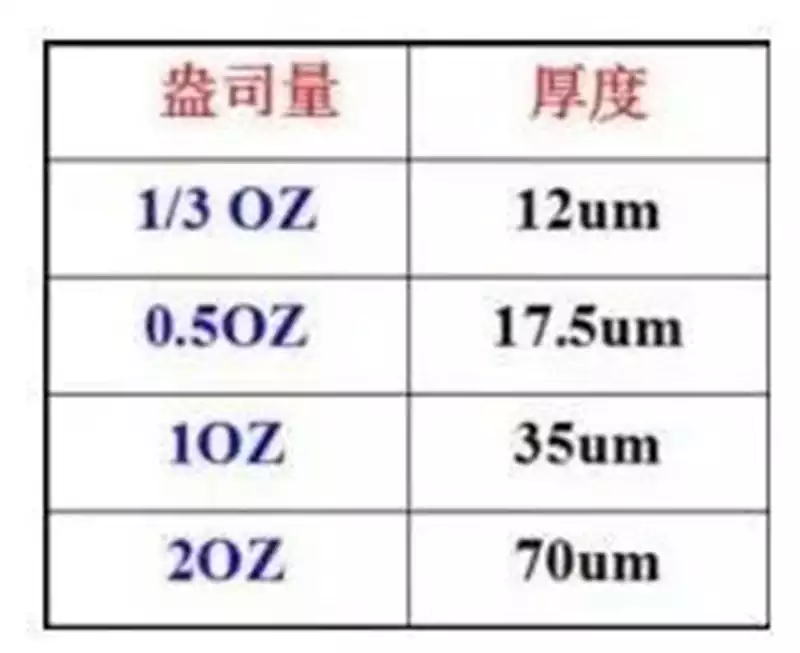
The Position and Value of AlN Aluminium Nitride in Advanced Electronics Manufacturing
As electronic products continue to evolve towards higher power, higher frequency, and higher integration, traditional substrate materials are gradually revealing their bottlenecks in terms of heat dissipation and reliability. Against this backdrop, AlN aluminum nitride, as a high-performance ceramic material, is beginning to occupy an increasingly important position in power electronics, semiconductor packaging, and high-end electronics manufacturing.
Compared to common organic substrates or alumina ceramics, AlN aluminum nitride’s most prominent advantage lies in its extremely high thermal conductivity. This characteristic allows it to efficiently conduct heat within a limited space, thereby significantly reducing device operating temperatures. For modern electronic systems with continuously increasing power densities, thermal management is no longer an additional issue but a core factor determining the long-term stable operation of products.
In practical applications, thermal problems often have systemic characteristics. The increased heat resulting from improved chip performance directly affects solder joint reliability, material aging rate, and overall structural stability. The introduction of AlN aluminum nitride allows engineers to redesign heat dissipation paths at the material level, rather than relying solely on external heat dissipation structures for remedies.
Beyond its thermal properties, AlN aluminum nitride also excels in electrical performance. Its excellent insulation characteristics enable stable operation in high-voltage, high-frequency applications. This characteristic gives it a natural advantage in power modules, RF devices, and high-reliability electronic systems.
From a manufacturing perspective, AlN aluminum nitride is not an “easy-to-use” material. Its processing difficulty, cost, and requirements for process control are significantly higher than traditional materials. This determines that it is not a general-purpose solution, but rather a high-end material choice for specific application scenarios.
Therefore, the value of AlN aluminum nitride does not lie in whether it can replace existing materials, but in whether it can solve core problems that other materials struggle to address. In applications with high power density, high heat flux density, and extremely high requirements for long-term stability, it is often one of the few feasible technical paths.
From an industry development trend perspective, with the continuous evolution of power semiconductors, new energy, and high-end industrial electronics, the requirements for material performance will only continue to increase. AlN aluminum nitride is gradually demonstrating its irreplaceable role in this trend, becoming an important but relatively specialized material choice in advanced electronic manufacturing systems.
AlN Aluminium Nitride Material Properties and Core Technological Advantages
To truly understand the value of AlN aluminum nitride in high-end electronics manufacturing, it’s essential to start with the material’s inherent physical and electrical properties. Unlike many “passive” substrates, AlN’s performance isn’t a single advantage, but rather a combination of highly synergistic material properties, which is the fundamental reason it excels in harsh application environments.
First and foremost, its most representative characteristic is its extremely high thermal conductivity. Among common ceramic materials, AlN’s thermal conductivity is significantly higher, giving it a unique position in thermal management design. For power devices, heat is not generated uniformly but is highly concentrated in localized areas. If heat cannot be quickly dissipated, localized temperature rises can rapidly lead to performance drift or even failure.
AlN aluminum nitride’s high thermal conductivity allows heat to diffuse rapidly along the substrate direction, reducing heat buildup. This “actively participating in heat dissipation” material characteristic provides more freedom in system design, freeing engineers from relying entirely on external heat sinks to compensate for the material’s inherent limitations.
Secondly, AlN maintains excellent electrical insulation properties while retaining high thermal conductivity. This is particularly crucial. Many high thermal conductivity materials have significant shortcomings in electrical insulation, while AlN aluminum nitride achieves a good balance between the two. This allows it to be used directly in high-voltage, high-power-density applications without the need for complex isolation structures.
In high-frequency and high-voltage applications, the dielectric properties of the material are equally important. AlN has a relatively stable dielectric constant and low dielectric loss, which helps reduce energy loss and maintain signal quality. This characteristic gives it a significant advantage in RF power modules and high-speed power conversion systems.
From a mechanical performance perspective, AlN aluminum nitride exhibits good structural stability. Its dimensional changes are relatively controllable under conditions of rapid temperature changes or prolonged high-temperature operation. This stability in thermal expansion characteristics helps reduce stress concentration problems caused by material mismatch, thereby improving overall structural reliability.
Furthermore, AlN has good thermal expansion matching with common semiconductor materials, which is particularly important in power module and packaging applications. A good fit can effectively reduce thermal stress at the welding interface and in the packaging structure, extending the product’s lifespan.
It’s important to emphasize that these advantages of AlN aluminum nitride are not “free.” Its high-performance characteristics place extremely high demands on raw material purity, sintering processes, and processing precision. Any minute process deviation can significantly impact the final performance. This explains why AlN-related products are typically concentrated in high-end applications and have not been widely adopted.
In summary, the core advantage of AlN aluminum nitride is not reflected in a single parameter, but in the comprehensive performance balance it achieves between thermal management, electrical insulation, and structural stability. This balance makes it one of the few choices in high-power, high-reliability electronic systems that truly possesses “material-level solution” capabilities.
Typical Applications of AlN Aluminium Nitride in Power Electronics and Packaging
In practical engineering applications, AlN aluminum nitride is not a “general-purpose material,” but a specialized material that has gradually established its position for high power density and high heat flux density scenarios. Its applications are often concentrated in fields with extremely high requirements for thermal management, electrical isolation, and long-term reliability, with power electronics and semiconductor packaging being the most representative areas.
In power electronic systems, thermal issues are often the core factor limiting performance improvement. As the size of power devices continues to shrink, the heat generated per unit area continues to increase, rapidly amplifying the shortcomings of traditional substrate materials in terms of heat dissipation capabilities. Against this backdrop, AlN aluminum nitride, with its high thermal conductivity, provides a more direct and efficient heat dissipation path for power modules.
Taking power modules as an example, heat is often concentrated and released from the bottom of the chip. If the substrate itself cannot quickly dissipate heat, even the most complex external heat dissipation structure cannot compensate for the fundamental deficiency. AlN substrates can form an efficient heat conduction channel between the chip and the heat dissipation system, alleviating the problem of heat accumulation at the material level. This is one of the important reasons why it is widely used in high-power modules.
In the field of semiconductor packaging, the value of AlN aluminum nitride is also reflected in the combination of “structural stability” and “thermal management capabilities.” Modern packaging forms are increasingly trending towards high integration, with multi-chip, stacked structures, and high-power devices coexisting becoming more and more common. These structures place extremely high demands on packaging materials, requiring not only excellent heat dissipation but also reliable electrical isolation.
AlN materials demonstrate a balance in these two aspects, making them a crucial option in high-end packaging solutions. Especially in applications requiring high power output and long-term reliability within limited space, AlN aluminum nitride can significantly reduce system thermal stress and improve overall package lifespan.
Furthermore, dielectric stability is equally critical in high-frequency power applications. As signal frequencies increase, the impact of material dielectric properties on system performance becomes more pronounced. AlN’s stable dielectric properties allow it to maintain low energy loss in high-frequency, high-power environments, providing greater design margins for related applications.
It is important to note that applying AlN aluminum nitride does not simply replace traditional materials to achieve performance improvements. Its introduction often necessitates simultaneous adjustments to structural design, manufacturing processes, and cost models. For example, during module design, engineers need to re-evaluate thermal path layouts; during manufacturing, they must ensure that material processing and metallization processes match its physical properties.
This is why successful applications of AlN often occur in projects with clear performance targets and thorough control over engineering details. It is not a “panacea” material, but rather a technological choice that can significantly improve system performance under specific boundary conditions.
From an industry trend perspective, with the continued development of new energy, electric transportation, and high-end industrial electronics, the requirements for power density and reliability will only continue to increase. In these fields, the application space for AlN aluminum nitride is gradually expanding, and its role is shifting from a “high-end option” to a “critical basic material.”
Manufacturing Challenges and Key Process Control Points of AlN Aluminium Nitride Substrates
Although AlN aluminum nitride exhibits significant performance advantages, its real barrier lies not in the “excellence of the material itself,” but in whether it can be stably and controllably processed and manufactured. It is these manufacturing challenges that have kept AlN substrates concentrated in high-end applications for a long time, preventing their widespread adoption like traditional substrates.
First, the purity of raw materials has a decisive impact on the performance of AlN substrates. AlN is extremely sensitive to impurities; even minute changes in oxygen content can significantly affect its thermal conductivity and electrical properties. If purity control is not rigorous during the raw material preparation stage, even with advanced subsequent processes, it will be difficult to achieve the design expectations. This high requirement for raw materials naturally creates a high technological barrier in the AlN supply chain.
The forming and sintering stages are equally complex. The sintering process for AlN aluminum nitride requires extremely strict control over temperature, atmosphere, and time windows. Any deviation in these parameters can lead to abnormal grain structure, affecting thermal conductivity and mechanical strength. In contrast, traditional ceramic materials have higher process tolerance, which is one of the important reasons for the high manufacturing cost of AlN.
The processing stage is another major challenge in AlN substrate manufacturing. AlN has high hardness and brittleness, making it prone to microcracks or latent defects during processing. If processing parameters are not properly controlled, these defects may gradually expand during subsequent thermal cycling or long-term operation, ultimately affecting product reliability. Therefore, controlling processes such as cutting, grinding, and surface treatment requires higher-level equipment and process experience.
Metallization is also a key factor influencing the success or failure of AlN substrate applications. To achieve electrical connections and heat dissipation pathways, the AlN surface typically requires metallization. However, due to its high chemical stability, controlling the bonding strength between the metal layer and the substrate is not easy. If the interface bonding is unreliable, delamination or failure may occur under thermal cycling conditions.
Furthermore, AlN aluminum nitride is also sensitive to environmental control during manufacturing. Humidity, contaminants, and process residues can all affect the final performance. This makes AlN substrate manufacturing more reliant on a comprehensive process management system, rather than optimizing a single step.
From an engineering perspective, AlN manufacturing is not simply about “being able to make it,” but rather about “being able to stably replicate it over a long period.” For end applications, single success is insufficient; batch-to-batch consistency and long-term reliability are crucial. This is why AlN substrates often require more rigorous validation cycles before being introduced into critical systems.
In summary, the manufacturing challenges of AlN aluminum nitride are another aspect of its high-performance value. The high manufacturing difficulty and stringent process requirements ensure stable and predictable performance even in extreme application environments. For systems that truly need to address thermal management and reliability issues, this “high barrier to entry” is not an obstacle, but a necessary technological guarantee.
Summary
Why AlN is Becoming a Key Choice for High-End Electronic Heat Dissipation Substrates
As electronic products continue to evolve towards higher power, higher frequency, and miniaturization, traditional PCBs and conventional ceramic substrates are gradually showing bottlenecks in terms of heat dissipation performance and reliability. Aluminum nitride (AlN) materials, with their ultra-high thermal conductivity, good electrical insulation, and thermal expansion coefficient matching silicon devices, are becoming a highly promising solution for high-end electronic applications.
Compared to alumina (Al₂O₃), AlN has significant advantages in thermal management, making it particularly suitable for power modules, IGBTs, SiC/GaN devices, automotive electronics, 5G communications, and new energy fields. It not only effectively reduces device operating temperature but also significantly improves system stability and lifespan.
Of course, AlN is not a “panacea.” Its complex manufacturing process, high cost, and stringent process control requirements make it more suitable for applications with extremely high performance demands. However, as material technology matures and the industry expands, the application threshold for AlN substrates is gradually decreasing.
Overall, AlN is not a replacement for traditional FR4 or ordinary ceramics, but rather a “key supplement” in high-performance electronic systems. With heat dissipation becoming a core challenge in system design, aluminum nitride is gradually moving from a “high-end niche material” to broader and more mature engineering applications.