With the rapid development of the electronics industry, the demand for printed circuit boards is also growing. In this efficient and precise market environment, “fast-turn printed circuit boards” has become a manufacturing model that has attracted much attention.
This article will conduct an in-depth analysis of quick turn printed circuit boards from the aspects of technical overview, production process, application fields and future development trends to help relevant practitioners better understand and apply this technology.

Overview of qucik turn printed circuit boards
As the name suggests, fast-turn printed circuit boards refer to the production of printed circuit boards completed in a shorter production cycle. This rapid manufacturing model is designed to meet the market’s demand for rapid iteration of electronic products, especially in the case of new product development, prototype verification and emergency orders.
The key features of this manufacturing method include:
Short delivery cycle: From design submission to product delivery, the production cycle of fast-turn printed circuit boards can usually be controlled within a few hours to a few days.
High flexibility: Able to quickly respond to customers’ diverse needs and adapt to small batch and multi-variety orders.
Cost control optimization: Although the cost of a single production is high, the overall development cost is reduced due to time saving.
Production process of fast-turn printed circuit boards
In order to achieve fast delivery, the production process of fast-turn printed circuit boards needs to be efficient and accurate. The following is a typical production process:
Data processing
The design files (such as Gerber files) submitted by customers are the basis of production. Engineers need to check the files to ensure that the design meets production capabilities and complete necessary optimizations and adjustments.
Material preparation
Select suitable substrate materials such as FR4, high-frequency materials or flexible materials according to design requirements. The choice of materials directly affects the performance and applicable scenarios of the circuit board.
Graphic transfer
The circuit pattern is transferred to the substrate through photolithography or direct imaging technology. Fast-turn printed circuit boards usually use more automated equipment to improve efficiency.
Etching and cleaning
After the pattern transfer is completed, the circuit board is etched to remove excess copper foil. This process requires precise control of etching time and solution concentration to ensure the accuracy of the circuit.
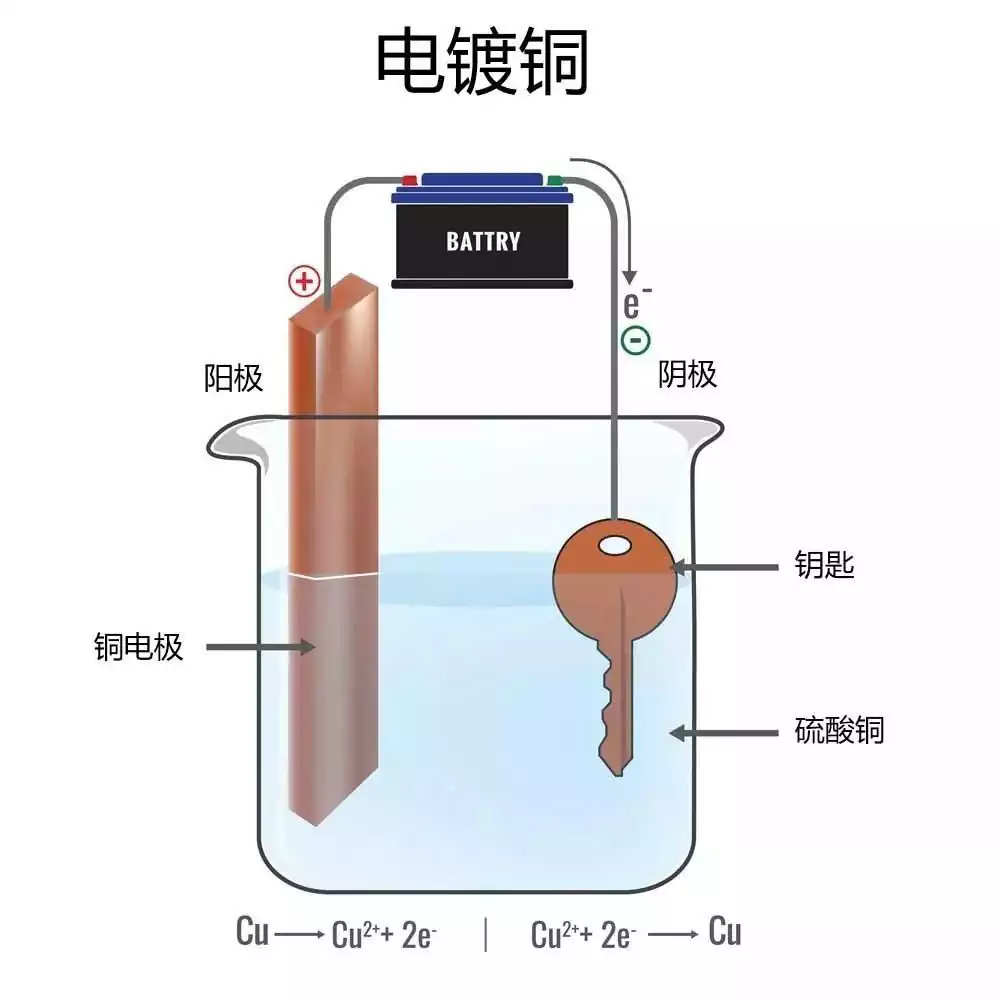
Drilling and electroplating
Mechanical drilling or laser drilling is performed according to design requirements, and then the vias are electroplated to ensure that they have good conductivity. This link has a greater impact on the production efficiency of fast-turn printed circuit boards, and high-speed drilling equipment is usually used.
Surface treatment
To improve soldering performance and prevent oxidation, the surface of the circuit board needs to be treated. Common methods include HASL (hot air leveling), OSP (organic protective film) and ENIG (electroless nickel gold plating).
Testing and inspection
After production, the circuit board needs to be electrically tested and visually inspected to ensure that its performance meets the design requirements.
Application areas of quick turn printed circuit boards
Due to the characteristics of fast response and flexible production, quick-turn printed circuit boards have been widely used in many fields:
New product development
In the process of electronic product development, prototype verification is a key link. Quick-turn printed circuit boards can provide R&D teams with fast, high-quality prototypes and shorten the time to market.
Military and aerospace
In the military and aerospace fields, the demand for product customization is high, and production often needs to be completed in an emergency. Quick-turn printed circuit boards provide a reliable solution for such tasks.
Medical equipment
The circuit boards in medical devices need to meet the requirements of high precision and high reliability. The high-efficiency production of quick-turn printed circuit boards can meet these special needs.
Consumer electronics
Smartphones, tablets and other consumer electronics products are updated and replaced at a very fast speed, and fast-turn printed circuit board technology plays an important role in small-batch trial production.
Advantages of fast-turn printed circuit boards
Compared with traditional production methods, the advantages of fast-turn printed circuit boards are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Time advantage
By optimizing the production process and adopting highly automated equipment, fast-turn printed circuit boards can significantly shorten production time and meet customers’ urgent needs.
Flexibility
The fast-turn production model can cope with small batches and diversified order requirements, and is particularly suitable for prototype design and customized orders for small and medium-sized enterprises.
High reliability
Although the production cycle is short, fast-turn printed circuit boards do not compromise on quality control and can ensure product reliability through rigorous testing and inspection.
Technical challenges and solutions
Although fast-turn printed circuit board technology has many advantages, it also faces some challenges in practical applications:
Cost issues
Quick-turn production usually requires highly automated equipment and highly qualified technicians, and the initial investment cost is high. Through large-scale production and technological innovation, costs can be gradually reduced.
Process control
Efficient production requires precise control of each process link, and any mistake in any step may affect the quality of the final product. The introduction of real-time monitoring and intelligent management systems will help improve process stability.
Material selection
In order to meet the needs of different application scenarios, fast-turn printed circuit boards need to use a variety of materials. Optimizing the material supply chain and increasing R&D investment will help solve this problem.
Technical details
Direct imaging technology (LDI)
Laser direct imaging technology can reduce the mask preparation time in the photolithography step and improve the accuracy of graphic transfer. This technology is of great significance in the production of fast-turn printed circuit boards.
High-speed automatic drilling
The use of the latest automatic drilling equipment can not only shorten the processing time, but also improve the consistency and accuracy of the aperture to meet the needs of high-density circuit boards.
Automatic optical inspection (AOI)
In the quality control link, AOI equipment can quickly identify defects on the circuit board to ensure the reliability of the finished product.
Optimization of surface treatment
For different application scenarios, optimizing the surface treatment process (such as using micro-etching technology) can improve weldability and electrical performance, and further enhance the service life of the circuit board.
Future development trend of fast-turn printed circuit boards
Intelligent production
In the future, fast-turn printed circuit boards will rely more on intelligent technology. By using artificial intelligence algorithms to optimize production scheduling and using big data analysis to improve equipment operation efficiency, delivery cycles can be further shortened and product quality can be improved.
Integration of high-density interconnect technology (HDI)
With the miniaturization and high-performance requirements of electronic devices, HDI technology will be more widely used in fast-turn printed circuit board production. Multilayer board design and high-precision blind hole technology will become key research and development directions.
Sustainable development
With increasing environmental pressure, the production of fast-turn printed circuit boards will pay more attention to green environmental protection. From reducing the use of chemicals to developing degradable materials, the industry will gradually achieve sustainability.
New material research and development
Future fast-turn printed circuit boards will use more high-frequency and high-speed advanced materials to meet the needs of cutting-edge fields such as 5G communications, artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things. This will require the development of materials that are more suitable for fast-turn mode, such as substrates with low dielectric constants and high thermal conductivity.
Global collaborative production
With the diversification of market demand, cross-regional collaborative production models will become a trend. By establishing distributed production bases and using cloud platforms to achieve real-time sharing of design and production data, customer needs can be met more efficiently.
Quality Management in Fast Turn PCBs
In the production of fast turn PCBs, although speed is the primary goal, quality is still a key factor that cannot be ignored. Here are some specific quality management methods:
Multi-layer inspection process
In the data processing stage, it is necessary to introduce automated design rule checking (DRC) tools to ensure that the customer’s design files are error-free. In addition, during the production process, each key step (such as etching, electroplating, and welding) needs to be inspected in stages to reduce the defect rate.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
Automated optical inspection equipment (AOI) is indispensable in the production of fast turn PCBs. These devices can quickly identify defects on the circuit board, such as open circuits, short circuits, or poor welding, thereby reducing the number of rework.
Functional testing and durability testing
In addition to electrical functional testing, fast turn PCBs should also be subjected to high temperature and high humidity environment testing, mechanical shock testing, etc. to ensure that they can adapt to various complex application environments.
Closed-loop management of customer feedback
After production is completed, collect actual application feedback from customers to improve the production process. This closed-loop management helps to improve customer satisfaction and product competitiveness.
Exploration of fast-turn printed circuit boards in special applications
With the diversification of technological needs, fast-turn printed circuit boards are gradually being applied to some special fields:
Automotive electronics field
In the fields of autonomous driving and new energy vehicles, fast-turn printed circuit boards are used for core components such as sensors and control modules. Since these fields require high reliability, fast-turn printed circuit boards need to meet more stringent quality standards.
5G communication equipment
The application of fast-turn printed circuit boards in high-frequency and high-speed signal transmission is very extensive. For example, for high-speed circuit modules used in base station antennas, these boards need to support higher signal frequencies while delivering prototypes in a short time to meet R&D needs.
Internet of Things (IoT) devices
For IoT devices such as smart homes and industrial monitoring, fast-turn printed circuit boards can quickly respond to new product iteration needs. For example, when a customer needs to test a new communication module, the fast-turn PCB can quickly complete the design verification and put it into use.
Green development of fast-turn printed circuit board production
The future fast-turn printed circuit board production will also pay more attention to environmental protection, which includes the following directions:
The use of low VOC (volatile organic compound) materials
By using environmentally friendly materials, the impact on the environment during the production process is reduced while meeting the requirements of international environmental regulations.
Resource recycling
In production, by sorting and recycling waste materials, the waste of raw materials can be greatly reduced. This is not only beneficial to environmental protection, but also reduces the operating costs of enterprises.
Energy-saving production technology
By using efficient equipment, such as low-energy photolithography machines, efficient etching equipment, etc., energy consumption can be further reduced and a greener production process can be achieved.
Industrial cooperation and technology sharing
In the future, the fast-turn printed circuit board industry will rely more on cooperation between industrial chains.
Cross-industry collaboration
For example, cooperate with material suppliers to develop new high-performance materials suitable for fast-turn printed circuit boards, and cooperate with equipment manufacturers to develop more efficient production equipment. These collaborations can greatly improve production efficiency and product performance.
Data sharing platform
Establishing a cross-enterprise data sharing platform can achieve comprehensive optimization from customer needs to production processes. For example, customers’ design files can be directly uploaded to the intelligent system of the production enterprise to achieve seamless production.
Open technical standards
By formulating unified industry standards, ensure consistency in production processes and product quality between different enterprises. This not only helps to improve industry efficiency, but also enhances customer confidence in the industry.
Summary
As an important technology in the electronics manufacturing industry, quick-turn printed circuit boards provide efficient solutions for new product development, small-batch production and emergency orders. Although there are still certain challenges in technology and cost, its application prospects will be broader through continuous innovation and optimization. For electronic manufacturing companies, in-depth understanding and mastery of quick-turn printed circuit board technology can not only enhance market competitiveness, but also bring more potential to the development of the industry.