In the production process of electronic products, circuit card assembly testing is a crucial step, which is directly related to the performance and reliability of the product. Circuit card, as a carrier connecting various electronic components, the quality of its assembly directly affects the function of the whole system to achieve. Therefore, a reasonable assembly process and strict testing standards are important to ensure product quality.
Types of circuit card assembly testing
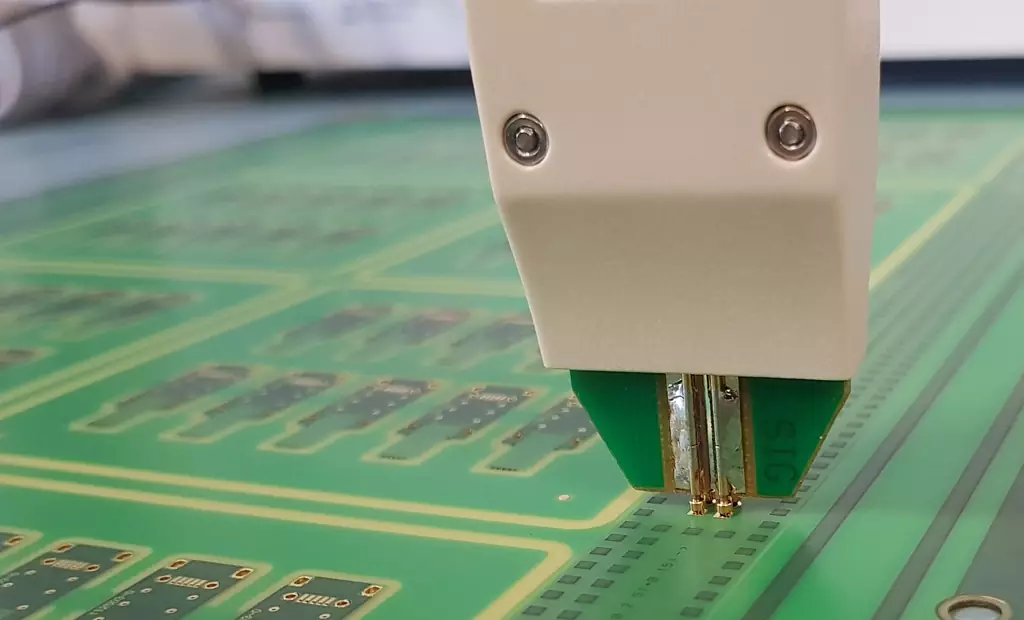
Flying probe test
The flying probe test is a method of circuit card assembly testing, which uses a probe that can be quickly displaced to examine the various contacts on the circuit card. No fixturing is required, but the overall test takes a long time due to the limited number of probes that can be moved. Flying probe testing is commonly used in small-scale production, but attempts are being made to improve and speed up the efficiency of flying probe testing by expanding the number of probes, reducing the number of necessary inspection steps, and streamlining the movement path of the probes.
In-Circuit Testing
In-circuit testing is another method of circuit card assembly testing that relies on fixtures equipped with probes to make contact with circuit nodes and monitor their electrical performance. The number of probes on the fixture matches the number of test points on the PCB. In-circuit testing is known for its rapid detection and diagnostic capabilities. ICT (in-circuit test technology) is highly efficient in identifying manufacturing defects such as component errors, mis-orientation of chips, as well as breaks and shorts. Sequences of test procedures can be easily obtained from the Gerber file of the circuit card design. However, ICT has some drawbacks, mainly the high cost of the required probe equipment as well as the automation system. In addition, because ICT relies on automation, design modifications become more complex and may even require replacing the entire test fixture, which undoubtedly adds additional cost.
Circuit card assembly testing is usually divided into the following segments:
Component Preparation:
Ensure that the quantity, specification and quality of all components meet the standards, and make the necessary inventory and inspection.
Assembly process monitoring:
During the assembly process,maintain monitoring of key factors such as soldering quality, component location, etc. to ensure compliance with the design drawings.
Functional Testing:
After assembly,test the function of the circuit by applying input signals to confirm that the output meets the design expectations.
Electrical Characteristics Test:
Use multimeters,oscilloscopes and other instruments to measure voltage, current and other electrical parameters to ensure that the electrical properties of the circuit card are normal.
Environmental testing:
Tests are conducted under different temperature and humidity conditions to verify the endurance and reliability of the circuit card.
Recording & Analysing:
Detailed records and analyses of test results are made to provide data support for subsequent quality improvement.

The Circuit Card Assembly (CCA) or Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) process is a challenging process that requires a high degree of attention to the arrangement and handling of electronic components. These electrical components are essential to the operation of the circuit board. Depending on the characteristics of the equipment or product to which the board is applied, a wide variety of components may be required. Therefore, it is essential to have a thorough understanding of the various components used in circuit card assembly. Circuit boards are made up of various components such as diodes, capacitors, inductors, transistors, and resistors.
Diode
A diode is a semiconductor device with two ports that allow current to flow smoothly in only one specific direction, while restricting current flow in the opposite direction. It is therefore the electrical equivalent of a one-way valve. This characteristic is often used in the conversion of alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). Diodes can be made from vacuum tubes or semiconductor materials (i.e., semiconductor diodes). However, most diodes are now made using silicon, a semiconductor material, as the primary manufacturing ingredient.
Capacitors
Capacitor plays an important role in the construction of various electronic circuits. It is a passive, two-terminal electrical component that accumulates energy electrostatically in the presence of an electric field. Its function is similar to that of a rechargeable battery in that it is able to store electrical energy and release it when needed. However, unlike a battery, a capacitor is able to complete the charging and discharging process in a very short period of time (less than a second). In electrical circuits, capacitors can perform a variety of functions, such as blocking direct current and allowing alternating current to pass through, or regulating the output of a power supply. In addition, capacitors are used to stabilise voltage and power flow in power transmission systems.
Inductors
An inductor is a passive, two-terminal electronic component that stores energy in a magnetic field as current flows through it (also known as a reactor) and can return that energy to the circuit when needed. Direct current (DC) is able to pass smoothly through the inductor, while alternating current (AC) is hindered. It was shown that when two inductors were placed in close proximity to each other but not in contact, the magnetic field generated by the first inductor would have an effect on the second inductor. This important discovery eventually gave rise to the first transformer. In addition, inductors, in combination with capacitors, could be used to build the tuned circuits that play a key role in radio and television receivers.
Transistors
The transistor is one of the components that revolutionised the field of electronics and is an essential part of electronic circuits. These tiny semiconductor devices with three terminals have been in production for over fifty years. They are widely used as switching and amplifying components. Transistors are able to ‘activate’ or ‘deactivate’ devices without physical movement, and can therefore be regarded as relays without mechanical moving parts. Due to their versatility, transistors play a vital role in the circuit card assembly (CCA) process. They are compact, have a relatively long service life, and can operate stably at low supply voltages without additional filament current. Bipolar transistors (BJTs) and field effect transistors (FETs) are the two basic types of transistors.
Resistors
A resistor is a passive electrical component with two terminals whose primary function is to impede the flow of current. It is probably one of the most basic components in a circuit. It is also one of the most frequently used components, considering that resistors are the basic elements that make up almost all circuits. It is common practice to identify the specifications of a resistor through colour coding. Resistors play a role in circuits by regulating the voltage of each connected component and the current flowing through them. Without resistors to perform this regulation, other components may not be able to withstand the excessive voltage and overload the system.
Circuit card assembly testing is the core link in the manufacturing of electronic products, to ensure the quality of circuit card, and then guarantee the overall product performance and reliability. With the continuous progress of technology, testing methods will be more efficient, laying a solid foundation for the development of electronic products.