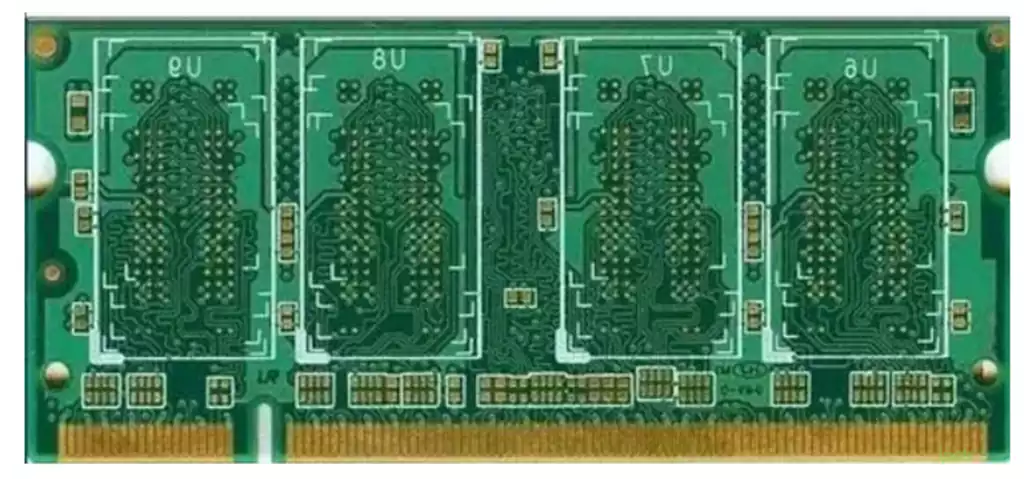
PCB coating, refers to the conductive layer of the circuit board, through a certain process method, covered with a layer of metal or other materials of the film. This film not only plays a protective role in preventing the circuit from oxidation, corrosion and other external factors, but also to improve the conductivity and stability of the circuit board. With the development of science and technology, the coating technology is also progressing, from the early electroplating, chemical plating, the development of the current vacuum coating, sputtering coating and other high-end technology.
The process of printed circuit board coating is a complex and delicate process, the main steps include.
Board processing: first, according to the demand for large board material cut into the appropriate size of the board, and carry out the necessary processing, such as curium board, beer rounded corners, grinding edges and so on.
Drilling: Drill holes in the board to prepare for subsequent conduction and connection.
Copper deposition: A thin layer of copper is chemically deposited on the wall of the hole, a process called copper deposition, which is used to make the through-hole conductive between layers.
Pattern Plating: Plating a layer of copper of the required thickness on the exposed copper skin of the circuit pattern or on the walls of the vias, as well as other metal layers of the required thickness, such as gold, nickel or tin. This process is to ensure the conductivity and stability of the circuit board.
Desmear: The use of a NaOH solution to retire the anti-plating overlay film layer, leaving the non-circuit copper layer exposed.
Etching: Unwanted copper layers are chemically removed from the board to form the final circuit pattern.
Green Oil: A solder resist layer is applied to the circuit board to protect the circuit and prevent short circuits.
Hot Air Leveling: A hot air leveling process is used to make the surface of the circuit board flatter and improve solderability.
There are many factors affecting the quality of circuit board plating, and these factors involve all aspects of the plating process as well as related equipment, materials and environmental conditions:
Current density: In the plating process, current density is a key factor. The level of current density directly affects the deposition rate and thickness of the coating. If the current density is too high, it may result in a rough plated surface and affect the performance of the board.
Plating time: Plating time is also an important factor affecting the thickness of the plated layer. Too short a plating time, the plating layer may be too thin, affecting the conductive properties; while too long a plating time may lead to too thick a layer, increasing the cost and weight of the pcb board.
Temperature: The temperature of the plating solution also has a significant effect on the quality and speed of plating. Generally speaking, higher temperatures can accelerate the plating reaction and improve the deposition rate of the plating layer, but too high a temperature may lead to changes in the structure of the plating layer, affecting the performance.
Plating solution composition: The composition and concentration of the plating solution are critical to the quality and performance of the plated layer. If the concentration of the main salt, additives, etc. in the plating solution does not meet the requirements, it may lead to rough surface, defects or unstable performance of the plated layer.
Stirring: Stirring the plating solution can improve the current density and the uniformity of the plating solution, which is conducive to obtaining a uniform, dense plating layer.
Substrate surface condition: The substrate surface condition of the circuit board has a great influence on the coating quality. The presence of oil, oxides and other impurities on the substrate surface may lead to poor adhesion of the plated layer, blistering and other problems.
Equipment condition: the condition of the plating equipment is also an important factor affecting the quality of the coating. If the equipment is aging, malfunctioning or improperly maintained, it may lead to problems such as unstable current and temperature fluctuations, which may affect the quality of the plated layer.
Environmental conditions: Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and cleanliness can also have an impact on coating quality. For example, high humidity may lead to increased water in the plating solution, affecting the quality of the coating.
PCB coating technology is an indispensable part of the electronics industry. It provides a solid guarantee for the stable operation of electronic equipment with its unique charm and precision process.