What is a PCBA? PCBA meaning PCB Assembly, which means Printed Circuit Board Assembly, that is to say, the electronic components are fixed on the PCB by welding or plugging to form a complete electronic product. PCB is the basis of PCBA, An insulated substrate used for electrical connection between electronic components, through the pre-designed line graphics and holes, so the connection between components becomes simple and convenient. The characteristics of PCBA mainly include high efficiency and reliability, lightweight, small size, easy maintenance and upgrading, etc. PCBA is widely used in various electronic products, such as cell phones, TVs, computers, automotive electronics, and so on.
The main difference between PCB and PCBA: PCB is a printed circuit board, which is a support for electronic components or a board where electronic components are interconnected, and PCBA is a printed circuit board assembly, which is the process of soldering electronic components to a PCB board.
Process: PCB manufacturing mainly includes circuit design, PCB board drawing design, PCB template production, etching copper foil, drilling, tin spraying, and board-making processes. The manufacture of PCBA, on the other hand, requires component placement, soldering, testing, and other processes.
Application: PCB is mainly used to support and connect electronic components, while PCBA integrates electronic components into a complete circuit system, which can be used in the manufacture of various electronic products, such as cell phones, computers, tablets, and so on.
Status: PCB is an empty printed circuit board with no parts on it. PCBA is processed on the empty PCB, installing resistors, capacitors, chips, and other components to form a board with certain functions.
Equipment and tools: PCBA manufacturing requires the use of placement equipment, welding equipment, testing equipment, etc., while PCB manufacturing requires the use of circuit board production equipment, etc.
Standardization: PCBA design can be standardized to facilitate interchangeability, facilitate mechanization, automated production, improve labor productivity and reduce the cost of electronic equipment.
The manufacturing process of PCBA mainly includes the following steps: PCB board making: first of all, make PCB board according to the design requirements, including choosing suitable materials, designing circuit diagrams, making drilling diagrams, and so on. This step is the foundation of PCBA manufacturing, which is needed to ensure the quality and reliability of the PCB board.
Material inventory: organize the BOM list, the PCBA board needs to be used in the material components and other inventory and preparation. This step is to ensure that all materials are ready and meet the requirements.
SMT mounting: electronic components mounted on the surface of the PCB board. Mainly includes paste, patch, reflow soldering, and other steps. This step requires the use of automated equipment such as a mounter to ensure the accuracy and reliability of component placement.
Optical Inspection: Through automatic optical inspection equipment, the PCB board is scanned to check whether the position, direction, and polarity of the components meet the requirements. This step is to ensure that the quality of the PCB board before welding meets the requirements.
Welding: Through wave soldering, reflow soldering, etc., the components are welded together with the PCB board. This step needs to control the temperature, time, and other parameters to ensure the quality and reliability of welding.
Cleaning: Clean the soldered PCB board to remove residue and dirt to ensure the cleanliness and reliability of the board.
Inspection and repair: The cleaned PCB boards is inspected, including an electrical performance test, appearance inspection, and so on. Repair or replace the unqualified components. This step is to ensure that the quality of the soldered PCB plate meets the requirements.
Aging test: The soldered pwb is subjected to an aging test to simulate the actual working conditions of the load and temperature and other environmental factors to check the reliability and stability of the product. This step can detect potential problems and repair them in time to improve the quality and reliability of the product.
Packaging: Packaging the PCBA boards that have passed the aging test, ready to be delivered to the customer. The packaging process needs to be carried out by customer requirements to ensure that the product is safe and intact.
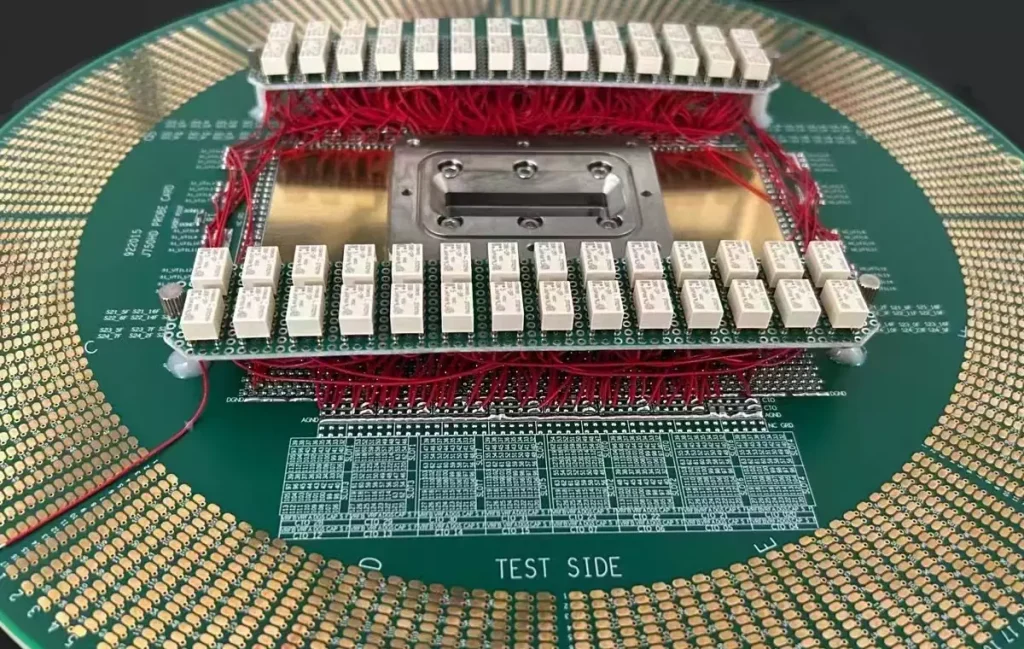
PCBA testing is the process of functional verification and performance testing of assembled printed circuit boards (PCBA). The purpose of the test is to ensure that the assembled circuit board in normal operation and meets the specifications.PCBA test is the most critical quality control link in the whole PCBA processing process, which determines the final performance of the product.
What is PCBA test?
PCBA test mainly includes the following aspects of the test:
Functionality test: Check whether each component on the board works normally and whether the function of the board meets the design requirements.
Electrical performance test: test the circuit board’s electrical performance parameters, such as voltage, current, resistance, capacitance, inductance, etc. whether to meet the design requirements.
Reliability and life test: Through various environmental tests and stress tests, simulate the actual working conditions of the load and temperature and other environmental factors to check the reliability and stability of the product.
Compatibility Test: Test the compatibility of the board with other equipment or systems to ensure that the board can work properly.
Automation Testing: Tests are conducted using automated test equipment to improve testing efficiency and accuracy.
PCB assembly is an important part of electronic product manufacturing, requiring strict control of process parameters and operating procedures. By mastering the key steps and precautions, you can improve the efficiency and quality of PCBA, reduce the defective rate, and enhance the overall performance and reliability of the product.