A single sided pcb is a circuit board that has a copper-clad layer on one side only and no conductive layer on the other side. It relies on a layout such as open wires or common wires in order to realize the electrical connectivity of flat circuits. Compared to double-sided boards, single-sided boards are simpler to produce and therefore more economical.
Single-sided pcb carries a variety of electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, and so on. These components are connected to each other through conductive lines printed on the board to form a complete circuit system. This design allows electronic devices to work as intended, bringing great convenience to people’s lives and work.
With its simplicity, economy and reliability, it has a wide range of applications in various fields of the electronics manufacturing industry:
Single sided printed circuit boards are a key component in all types of consumer electronics, such as cell phones, tablet PCs, TVs, cameras and stereos. It serves as a platform for circuit connections, signal transmission and power supply by precisely soldering electronic components to ensure the normal operation of the device.
In the communications industry, whether it is a cell phone base station, communications equipment or satellite communications, etc., the use of these circuit boards is required to realize the electrical connection of complex circuits and high-frequency signal transmission, to ensure that the communication protocols and network connections are stable and reliable.
In the automotive electronics industry, single sided pcb also play an indispensable role. Modern automobiles in a variety of electronic control units (ECUs), instrument panels, in-car entertainment systems, etc., are dependent on single-sided printed circuit boards for signal transmission and power supply, to achieve the vehicle’s intelligent and automated control.
Single-sided pcb is also increasingly used in industrial automation and medical devices. For example, they play a key role in PLCs (automated logic controllers), industrial robots, automated production lines, as well as medical monitoring equipment, medical imaging equipment, diagnostic instruments, and other devices.
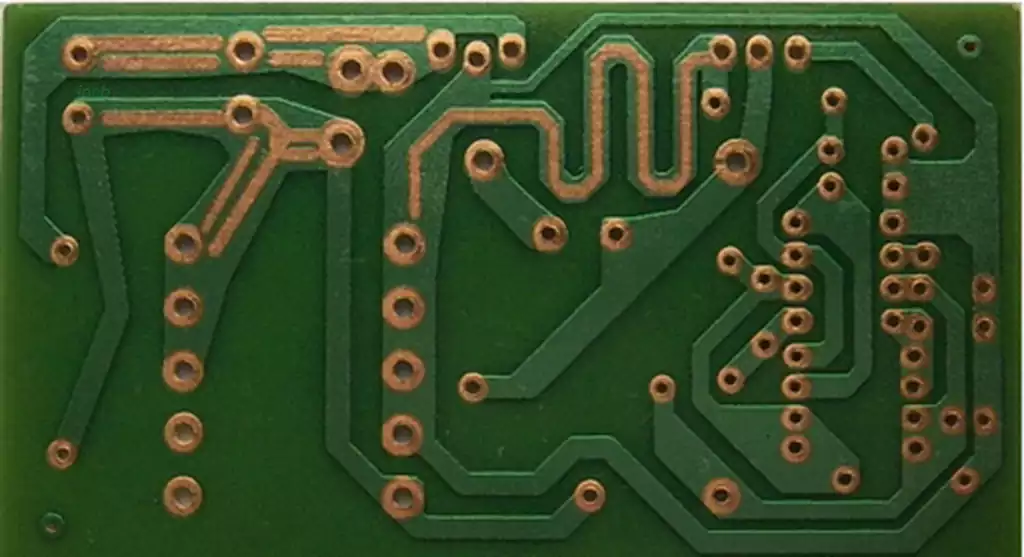
The main types of data used for single sided pcb include the following:
- phenolic paper substrates, i.e. cardboard, plastic board, V0 board, flame retardant board, red letter copper-clad board or 94V0. Of these, FR-1 (flame retardant) and XPC (non-flame retardant) are the two most commonly used phenolic paper-based base laminates. Their identification is quite intuitive, and they can be easily distinguished simply by the color of the letters on the back of the pcb board: FR-1 has red letters, while XPC has blue letters. In terms of price, this substrate is more affordable than the other types.
- epoxy fiberglass cloth substrate, also known as epoxy board, fiberglass board, fiberboard or FR4. It is a substrate made of epoxy resin as the binder and electronic grade fiberglass cloth as the reinforcing material. Its bonding sheet and thin copper-clad core play an important role in the production of multilayer printed circuit boards. Due to its relatively high operating temperature and low environmental impact on its performance, it has significant advantages over other resin-based fiberglass cloth boards in terms of processing technology. Although these products are mainly used for double-sided printed circuit boards, they are about twice as expensive as phenolic paper substrates and are commonly used with a thickness of 1.5MM.
- composite substrates, often referred to as powder board, etc., also known in some areas as 22 F. It mainly includes CEM-1 and CEM-3 two kinds of composite copper-clad laminate. The former is made of wood pulp fiber paper or cotton pulp fiber paper as the core reinforcing material and glass fiber cloth as the surface reinforcing material, both of which are immersed in flame-retardant epoxy resin; whereas the latter is made of fiberglass paper as the core reinforcing material and glass fiber cloth as the surface reinforcing material, which are also immersed in flame-retardant epoxy resin. These two types of laminates are the most common composite substrate laminates and are also known as CEM-2, CEM-3, and so on. In terms of price, these types of laminates compared to FR4 type laminates are more
Selection Strategy
When selecting a single panel, we need to consider the following key factors:
- The complexity of the pcb layout: If the layout of the circuit board is relatively simple and does not require too many line crossings and layers of superposition, then the single-panel is a suitable choice;
- Process speed and cost requirements: Since the single-panel production process is relatively simple and fast, it is particularly suitable for scenarios that require fast delivery or limited budget;
- the size of the available space: compared with double-sided panels, single-sided panels have limitations in connecting components, so the layout of components needs to be fully considered in the design process to achieve a higher density of electronic components in a limited space.
As the cornerstone of the electronics manufacturing industry, the importance and status of single sided pcb cannot be overstated. In the future development, it will continue to play its key role in providing a strong guarantee for the performance and reliability of electronic equipment.