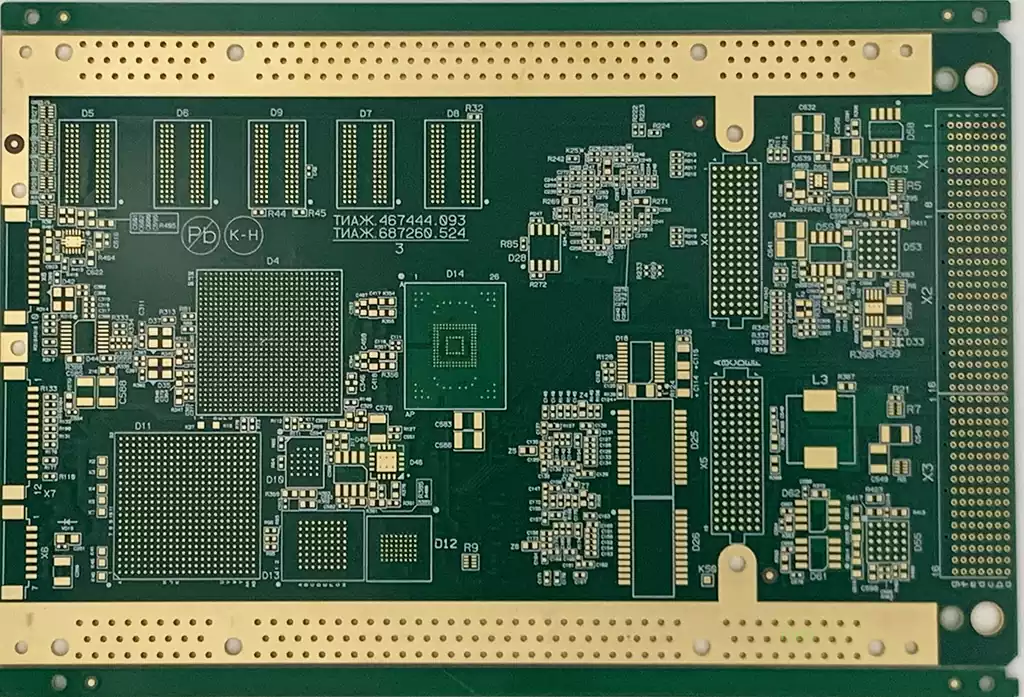
What is in a circuit board?PCB stands for Printed Circuit Board. It is a substrate used to support and connect electronic components and is a flat board made of insulating material on which electronic components are laid out and connected through structures such as conductive tracks, holes and pads. It is one of the most common components used in electronic devices to build and support electronic circuits.
Its working principle is to use the board base insulating material to isolate the surface copper foil conductive layer, so that the current flows along the pre-designed route in a variety of components to complete such functions as power, amplification, attenuation, modulation, demodulation, coding, etc.
What is in a circuit board?
Line and surface: the line is to do as a tool for conduction between the original, in the design of the design will be designed in addition to a large copper surface as a grounding and power supply layer. Line and surface are made at the same time.
Dielectric layer: Used to maintain the insulation between the line and each layer, commonly known as the substrate.
Hole: Through-hole can make more than two levels of the line with each other, the larger through-hole is used for parts insertion, and there are non-conductive holes are usually used as a surface mount positioning, fixed screws used in the assembly.
Anti-soldering ink: not all copper surface to eat tin on the parts, so non-tin-eating areas, will be printed a layer of copper surface insulation to eat tin substances (usually epoxy resin), to avoid non-tin-eating short circuit between the lines. According to different processes, divided into green oil, red oil, blue oil.
Screen Printing: This is a non-essential component, the main function is to mark the name of each part on the circuit board, the location of the frame, to facilitate maintenance and identification after assembly.
Surface treatment: Due to the copper surface in the general environment, it is easy to oxidize, resulting in the inability to tin (solderability bad), so it will be in the copper surface to eat tin to protect. Protection methods include spray tin, gold, silver, tin, organic solder, each with its own advantages and disadvantages, collectively referred to as surface treatment.
Working Layers
Circuit boards include many types of working layers, such as signal layers, protective layers, silkscreen layers, internal layers, etc. The roles of the various layers are briefly described below:
(1) protective layer: mainly used to ensure that the circuit board does not need to be tinned places are not tinned, so as to ensure the reliability of the circuit board operation. Top Paste and Bottom Paste for the top layer of soldermask and bottom layer of soldermask; Top Solder and Bottom Solder for the solder paste protection layer and bottom layer of solder paste protection layer.
(2) Signal Layer: mainly used to place components or wiring, Protel DXP usually contains 30 intermediate layers, i.e., Mid Layer1~Mid Layer30, the middle layer is used to arrange the signal lines, the top layer and the bottom layer is used to place components or copper.
(3) Silk Screen Layer: It is mainly used to print the running number of components, production number, company name, etc. on the circuit board.
(4) Internal layer: mainly used as a signal wiring layer, Protel DXP contains a total of 16 internal layers.
(5) Other layers: mainly includes four types of layers.
Drill Guide (Drill Orientation Layer): Mainly used for the location of drilling holes on the pcb board.
Keep-Out Layer (prohibit wiring layer): mainly used to draw the electrical border of the circuit board.
Drill Drawing (Drill Drawing Layer): Mainly used to set the shape of the drilled holes.
Multi-Layer: Mainly used to set the multi-layer.
Main functions
Provide mechanical support: PCB can support and fix electronic components to ensure the stability of the whole circuit.
Provide electrical connection: The wire layers and printed circuits provide the connection between the electronic components, enabling the various parts of the circuit to properly transfer current and signals.
Signal Transmission: Through the wires and lines on the PCB substrate, signals are able to be transmitted within the electronic device for proper electronic function.
Blocking short circuits: PCBs are designed to ensure that short circuits do not occur between different layers of wires, ensuring the stability and safety of circuit operation.
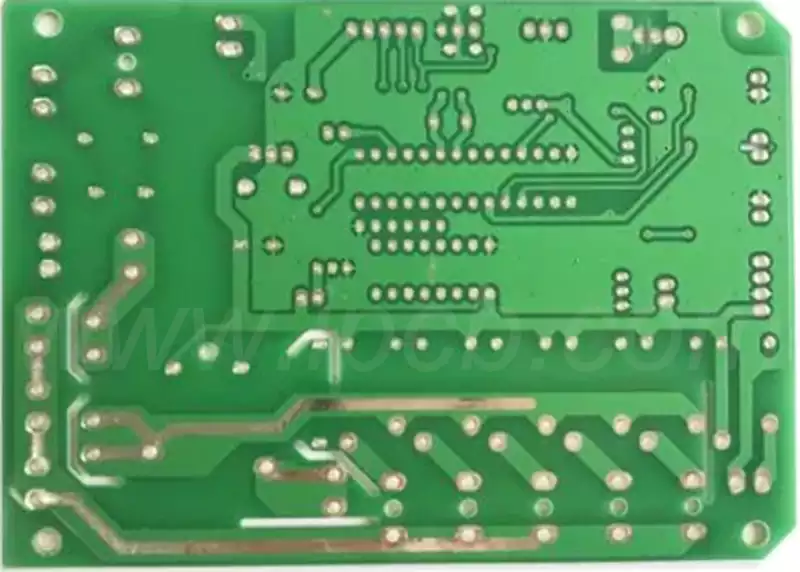
Classification
According to the number of layers to be divided into single-sided board, double-sided board, and multilayer circuit boards.
Multilayer board: refers to more than three layers of conductive graphics layer and the insulating material between them in order to separate the laminated and the conductive graphics between them according to the requirements of the interconnection of the printed circuit board. Multilayer circuit board is electronic information technology to high-speed, multi-functional, high-capacity, small volume, thin, lightweight development of the direction of the product.
Single-panel: In the most basic PCB, the parts are concentrated on one side, and the wires are concentrated on the other side. Because the wires are only present on one side, the PCB is called a single-sided circuit board. Single-sided PCBs are usually simple and inexpensive to produce, but the disadvantage is that they cannot be applied to products that are too complex.
Double-sided board: is an extension of the single-panel, when a single layer of wiring can not meet the needs of electronic products, we must use double-sided board. Both sides are copper-coated wire, and can be through the hole to conduct the line between the two layers, so that the formation of the required network connection.
Classified according to the substrate: flexible circuit boards, rigid circuit boards and rigid-flexible combination of boards.
Flexible PCB (Flexible Board)
Flexible PCBs are printed circuit boards made of flexible substrates with the advantage that they can be bent to facilitate the assembly of electrical components.FPCs are widely used in aerospace, military, mobile communications, laptop computers, computer peripherals, PDAs, digital cameras, and other fields or products.
Rigid PCB
It is made of paper base (commonly used for single-sided) or glass cloth base (commonly used for double-sided and multi-layer), pre-preg phenolic or epoxy resin, surface layer on one side or both sides of the adhesive copper-clad foil and then laminated and cured. This PCB copper-clad sheet, we call it a rigid board. Then made of PCB, we call it rigid PCB rigid board is not easy to bend, with a certain degree of toughness of the rigid substrate made of printed circuit boards, the advantage is that it can be attached to the electronic components to provide a certain degree of support.
Rigid-flex PCB (Rigid-flex PCB)
Rigid-flex PCB refers to a printed circuit board that contains one or more rigid and flexible areas, consisting of a rigid board and a flexible board laminated together. The advantage of rigid-flex PCBs is that they provide the support of rigid printed circuit boards, but also have the bending characteristics of flexible boards, enabling them to meet the demands of three-dimensional assembly.
HDI Board
High Density Interconnect abbreviation, that is, high-density interconnect technology, is a kind of printed circuit board technology. HDI board is generally manufactured using the multilayer method, the use of laser punching technology to punch holes through the layer, so that the entire printed circuit board formed in the buried, blind holes for the main way of interlayer connectivity. Compared to traditional multilayer printed circuit boards, HDI boards can improve the board wiring density, which is conducive to the use of advanced packaging technology; can make the signal output quality enhancement; can also make electronic products in the appearance of becoming more compact and convenient.
Circuit board, as the core building blocks of electronic equipment, its continuous innovation and development, is leading the electronics industry towards a smarter, more efficient future. It is not only the crystallization of technology, but also a powerful force for social progress.