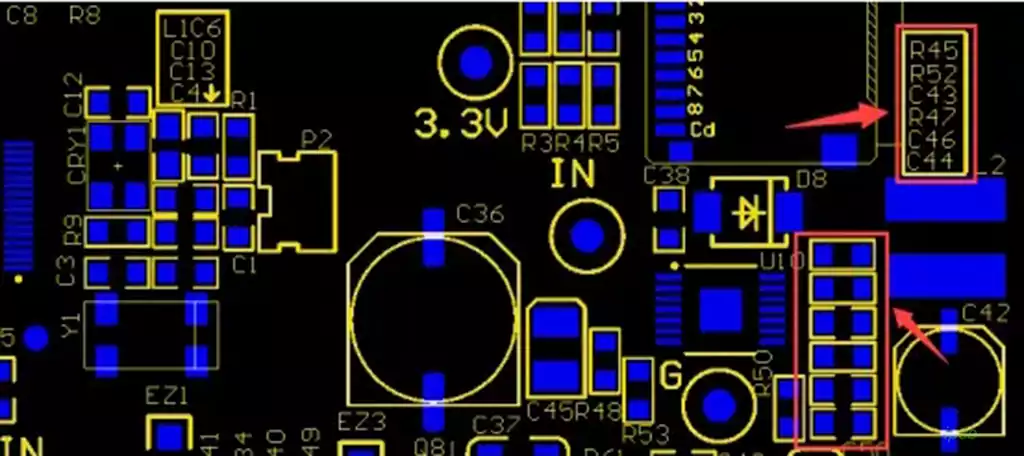
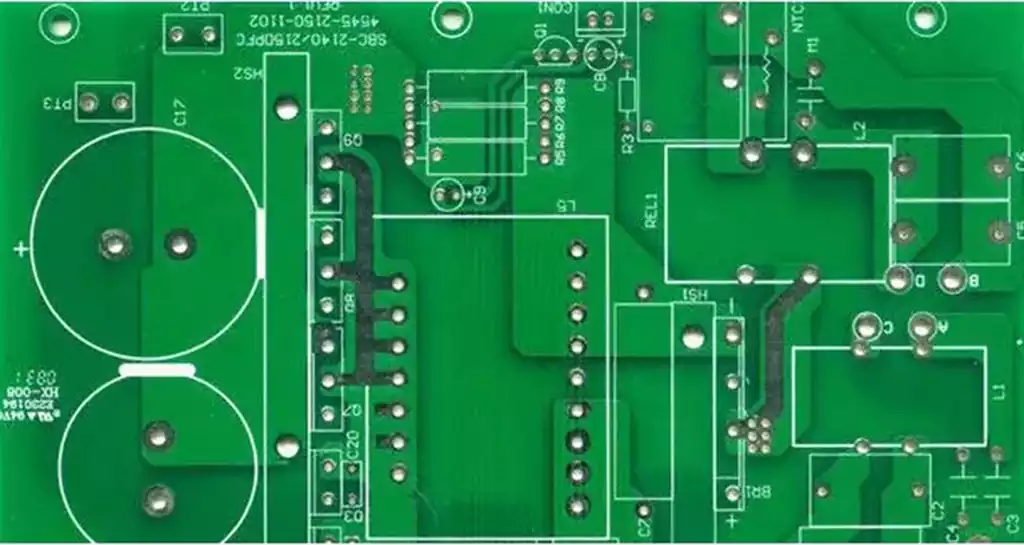
Computer board components refer to the hardware parts that make up a computer system, focusing mainly on the motherboard and the other components it connects to (such as the CPU, memory, storage, and expansion cards). These components work together to perform computing tasks and data processing, and are the foundation of a properly functioning computer.
What are the main computer board components?
1.Computer base components
The basic electronic components of a computer mainly include the motherboard, CPU, memory, graphics card, power supply, hard disk and so on. These components together constitute the core hardware part of the computer, enabling it to complete a variety of computing and processing tasks.
- Motherboard
The motherboard is the largest circuit board in a computer system and is responsible for connecting all other components and providing power and data transmission channels. The motherboard integrates many important chips, such as the BIOS and chipset, which determine the performance and expandability of the computer. - CPU (Central Processing Unit)
CPU is the computing core of the computer, responsible for processing all data within the computer, similar to the human brain. Its performance directly affects the speed and efficiency of the entire computer. - Memory
Memory is a temporary storage device used to hold data and programs, which affects the computer’s operating speed and multitasking ability. The capacity and speed of RAM is an important factor in determining the smoothness of a computer’s operation. - Graphics Card
Graphics cards are responsible for processing and outputting images, especially in gaming and professional graphic design, the performance of the graphics card is critical. Modern graphics cards not only support 2D graphics, but can also handle complex 3D images. - Storage Devices
Storage devices include hard disks, solid state drives (SSDs), etc., which are used to store operating systems, software, and user data. The storage speed and capacity of the hard disk will have an impact on the system’s boot time and file reading speed. - Power Supply
A power supply converts power from the grid into the voltage and current required by the computer’s components to ensure stable computer operation. The power and efficiency of the power supply is also closely related to the performance of the system.
Principles of computer board components design
- Ensure functional modularity
Computer board component design should try to split the functions as much as possible, keeping each component responsible for a single and well-defined function. This design concept helps to improve maintainability, making subsequent changes and debugging easier, as well as better enabling module reuse. - Choosing the right package
When choosing a component package, the actual application needs and performance requirements should be taken into account. Different package types will affect the size, thermal performance, and electrical characteristics of the component, so it is crucial to choose the right package. - Consider thermal management
In the design process, the thermal management of the computer board component must be emphasized. In high-power applications, component heating may affect the performance of the entire board, and proper thermal design can significantly improve system stability and reliability. - Keep wiring simple
The wiring design should be kept as simple as possible to avoid unnecessary complexity and redundant connections. Minimize cross-connections, thereby reducing electromagnetic interference and signal attenuation. - Determine a reasonable layout
Computer board components should be reasonably laid out to optimize the signal path and maintain good electrical performance. The interactions between components should be considered in the layout to avoid mutual interference between high-frequency signal lines and low-frequency signal lines. - Consider manufacturability
Component design should not only consider the function and performance, but also must take into account the feasibility of manufacturing. Choosing common materials and standardized production processes can reduce manufacturing costs and improve production efficiency. - Design Test Points
Reserving test points is an important consideration during the component design phase. Test points should facilitate subsequent functional verification and troubleshooting for product quality control. - Ensure maintainability
The design should take into account the maintainability of the components, and in the case of hardware failure, it can be easily replaced or repaired. Reasonable design can reduce the repair time and lower the overall maintenance cost.
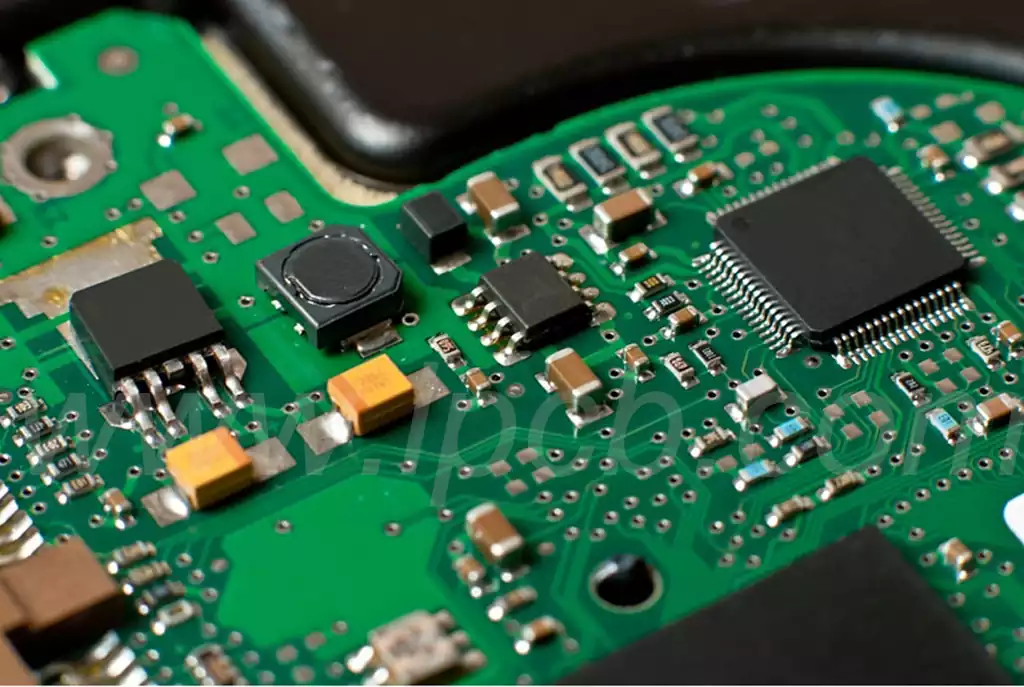
When assembling a computer, what are the factors to consider when choosing a motherboard?
- Compatibility
When choosing a motherboard, the most important thing is to ensure its compatibility with the CPU and other hardware. Different CPUs need to be matched with corresponding motherboard chipsets, for example, Intel’s CPU can only use Intel’s motherboard, while AMD’s CPU needs AMD’s motherboard. - Number of slots and ports
The number of slots and ports on the motherboard is another important consideration. Choosing a motherboard with enough memory slots, PCI-E slots, and various expansion ports will facilitate future upgrades. Ideally, choose a motherboard with at least four memory slots to support more memory upgrades. - Motherboard Size
The size of the motherboard also needs to be chosen based on the size of the case. Common motherboard sizes include ATX and Micro-ATX. Choosing the right size motherboard ensures that it can be installed smoothly in the chassis and ensures good heat dissipation. - Functions and Features
Different motherboards have different functions and features that should be considered according to individual needs, such as network interfaces, audio processing capabilities, type and number of USB ports, and whether it supports fast storage interfaces such as M.2. - Quality and Reliability
The quality of the motherboard and the reputation of the manufacturer should not be ignored. Choosing a motherboard with a well-known brand name usually results in better stability and reliability, and reduces the possibility of subsequent failures. - BIOS and Firmware Support
The BIOS and firmware support of the motherboard is also an area of concern. Good BIOS support ensures the stability of the system during startup and operation, and also provides better functionality and scalability. - Budget and price/performance ratio
Finally, budget is also a factor that must be considered when choosing a motherboard. A reasonable budget allocation can help users ensure that their needs are met while staying within their means.
When designing computer board components, how to choose the right material
- Determine the application scenario
Before choosing the right material, it is important to first define the application scenario of the board.This includes consideration of its operating environment (e.g., temperature and humidity), the electrical characteristics of the intended use, and specific performance requirements. This step is critical to ensure that the selected material meets the needs of the actual use. - Evaluate material properties
Different materials have their own properties,such as heat resistance, insulation, and electrical conductivity. In circuit board design, common materials include FR-4, polyimide, aluminum substrate and so on. The following physical properties should be considered when selecting materials, such as glass transition temperature (Tg), dielectric constant (Dk) and loss tangent (Df). - Adaptation of operating frequency and data transfer rate
When selecting materials, the operating frequency and data transfer rate of the board should be considered. High-frequency circuits usually require materials with low dielectric constants to minimize signal propagation delays and losses. The thickness of the material and its resin-to-glass ratio should also be strictly controlled at the design stage to ensure that the desired electrical performance is achieved. - Consider cost and reliability
Cost is an important factor in material selection, and designers need to find a balance between cost and performance. For example, although FR-4 is more economical, polyimide may be a more appropriate choice for high temperature or high frequency applications. Ensuring that the chosen material maintains good reliability over its expected life cycle is critical to the success of the design. - Conduct field testing and validation
After selecting a material, it is recommended that the necessary field testing and validation be performed. This can help ensure that the selected material performs well in real-world applications and meets the expected performance criteria. Adjusting the material selection based on test results can also significantly improve the overall performance of the board!
Choosing the right Computer board components and materials is critical when designing and assembling computers. By having a deep understanding of the performance of each piece of hardware and how it interacts with each other, users are able to build efficient and stable computing systems. At the same time, choosing board materials that take into account application scenarios, material properties, cost, and reliability, as well as taking the risk of field testing and validation, ensures optimal performance and long-term stability. Proper component and material selection can bring significant improvements in overall system efficiency and longevity, creating a better computing experience.