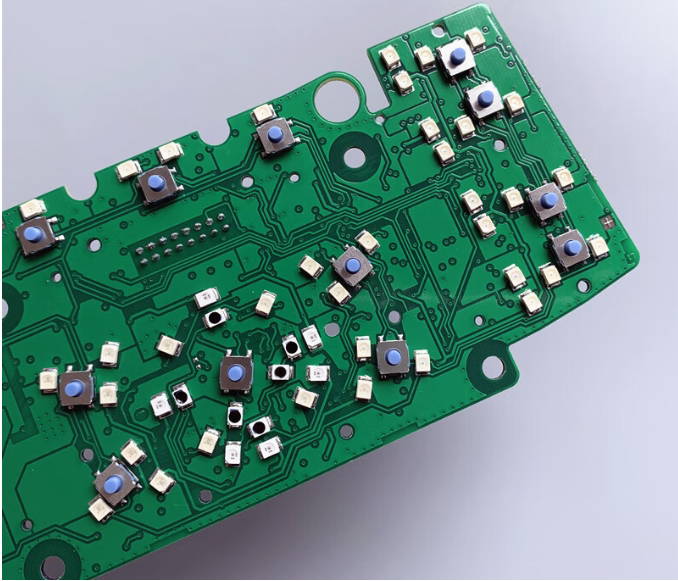
PCB buttons are everywhere we live and work, from mobile phones and TV remotes to computer keyboards, keys are an important medium of interaction between us and our devices.
PCB buttons are switching elements embedded in a printed circuit board (PCB), typically used to receive input commands from the user.When the user presses the button, it functions to control electrical signals by changing the state of the circuit.PCB buttons are able to achieve a variety of operations, such as switching on and off, volume adjustment, mode switching, etc., and are widely used in various types of electronic products.Key switches are usually composed of a base, a piston and a contact.The base is the main body that carries the entire switch, while the piston plays the role of pressing and popping up.The contacts are two metal plates that contact each other when the key is pressed, forming a closed circuit that sends a signal.
A pcb button is made up of pushbutton switches, connecting wiring, and control elements.The key switch is an important component that acts as a trigger signal.When the key is pressed, the metal contacts inside the switch are connected to the signal line, thus changing the state of the circuit.This process may seem simple, but the principle behind it is very precise.
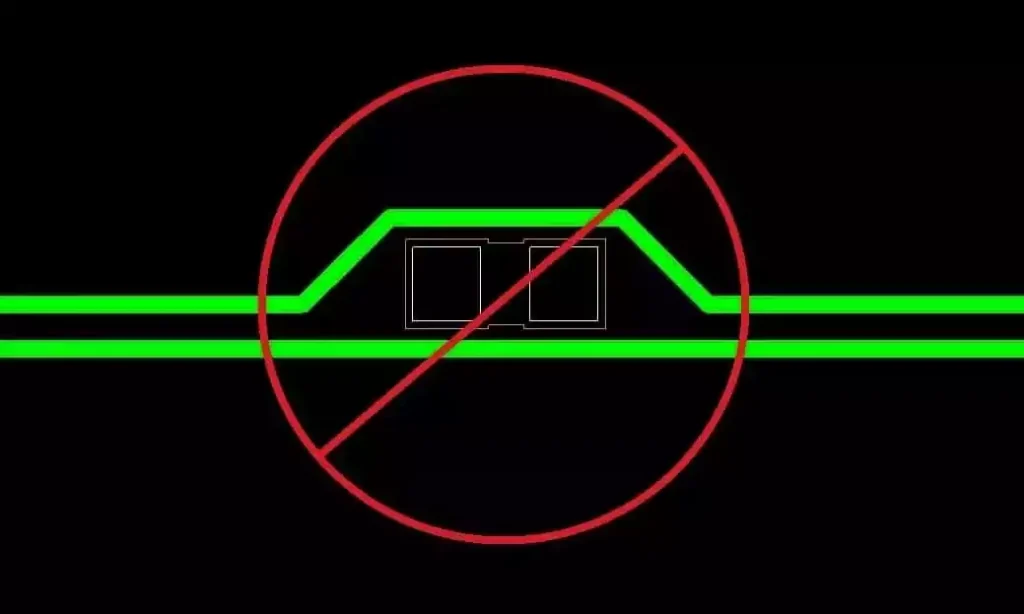
Each pcb button has a soldering point that corresponds to it.The soldering point is the key part that connects the keyswitch to the circuit board and ensures that the keyswitch works and sends signals.In addition to this, the circuit board has one or more main wires spanning the entire board,called trunk wires.The backbone is responsible for integrating and transmitting the signals from the individual keyswitches and ultimately handing them over to the control elements for processing.
The choice of materials used for pcb buttons has a significant impact on their performance in terms of durability,tactility,conductivity and signal integrity.
1.The materials used for PCB buttons must have good durability to withstand frequent use.In this regard,the properties of different materials are as follows:
Silicone: Silicone PCB buttons have excellent abrasion and corrosion resistance and are able to withstand multiple presses without wear and tear for a long service life.
Plastic: Although commonly used for low-cost production, plastic keypads are less resistant to abrasion and less stable over long periods of time, and may degrade in performance over time.
Metal: Metal pushbuttons (e.g.stainless steel) offer extremely high durability, the ability to maintain functionality in harsh environments, and excellent electrical conductivity.They are usually able to withstand a very high number of presses without failure and are commonly used in applications under harsh conditions.
2.The tactile feel of a keypad is an important aspect of the user experience, and the material used directly affects this characteristic:
Metal Domes: These pcb buttons provide crisp tactile feedback and a noticeable clicking sound, allowing the user to clearly perceive when a press has been successful.
Polymer domes: Polymer domes provide a softer touch than metal and are suitable for applications that require a quieter, softer touch.This reduces operating noise and is suitable for certain user environments.
Rubber: Rubber pcb buttons are popular for their comfortable feel and abrasion resistance.They often provide clear tactile feedback and are water and dust resistant, making them suitable for use in wet environments.
3.The choice of material for pcb buttons also affects their conductivity and signal integrity, which is especially important for high frequency applications:
Conductive Materials: Common conductive materials include silver, copper, and carbon.Silver provides the best conductivity, but is more expensive and is usually used in high-end keypad designs.
Substrate: The substrate material of the key (e.g.polyester or polycarbonate) plays a key role in moisture resistance and thermal stability.Choosing the right substrate material can reduce signal loss and improve signal integrity, especially in high frequency applications.
Dielectric Constant and Loss Factor: The dielectric constant (Dk) and loss factor (Df) of a material affects how well an electrical signal travels through the board.Materials with low dielectric constants and low loss factors are more favourable for stable signal transmission.
4.The selection of materials should also take into account the environment in which the board will be used:
Chemical resistance: Some materials such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are resistant to a wide range of chemicals and are suitable for use in chemical environments, whereas conventional polyesters may degrade under the influence of some chemicals.
Temperature and humidity: Choosing materials that can withstand high temperatures and low humidity is essential to extend the life of the keypad and avoid performance degradation in extreme environments.
Optimising the performance of pcb buttons cannot be achieved without in-depth research and careful selection of material science.In the future, with technological innovation and advances in material science, we are confident that we will be able to usher in more durable,comfortable and efficient keypad designs that will provide a better user experience.