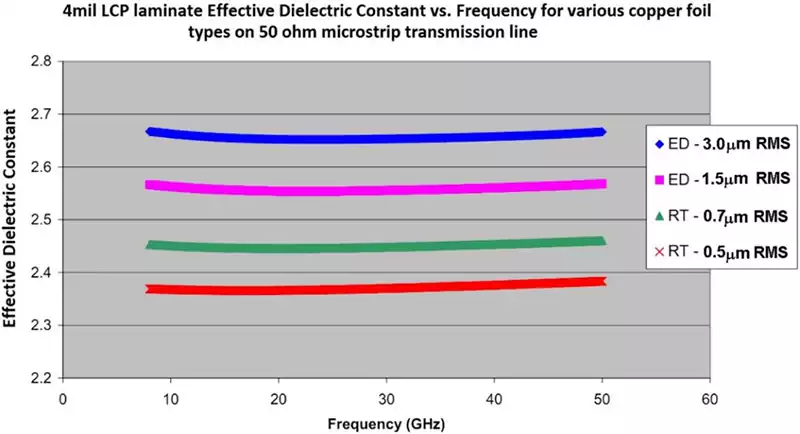
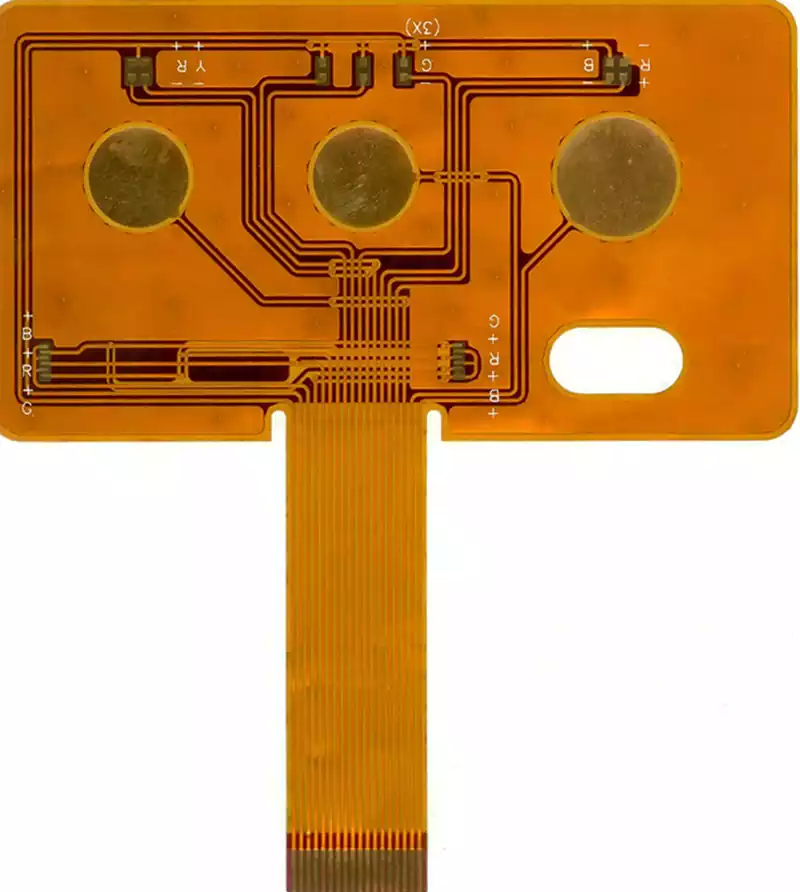
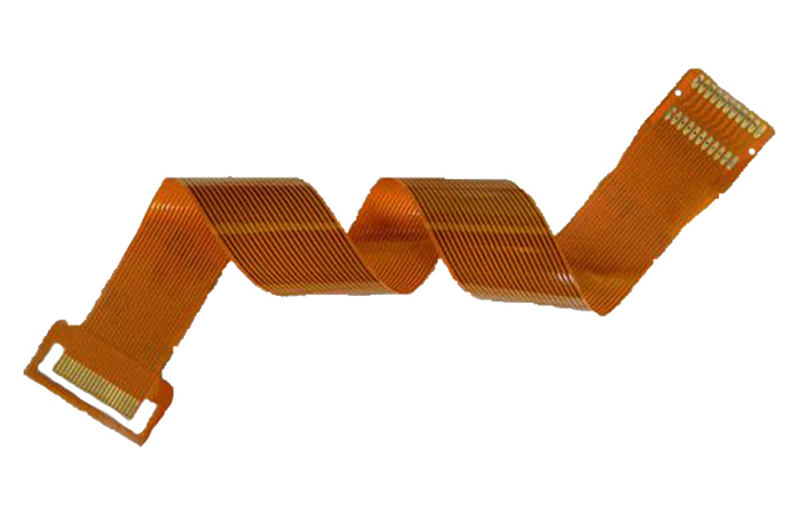
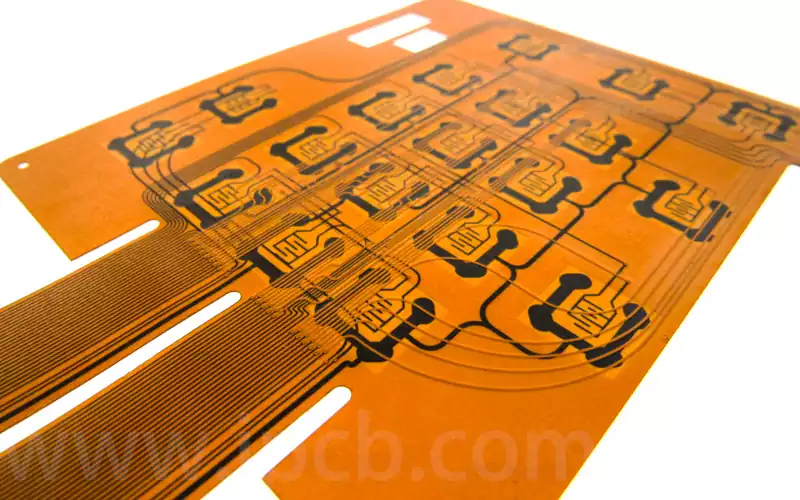
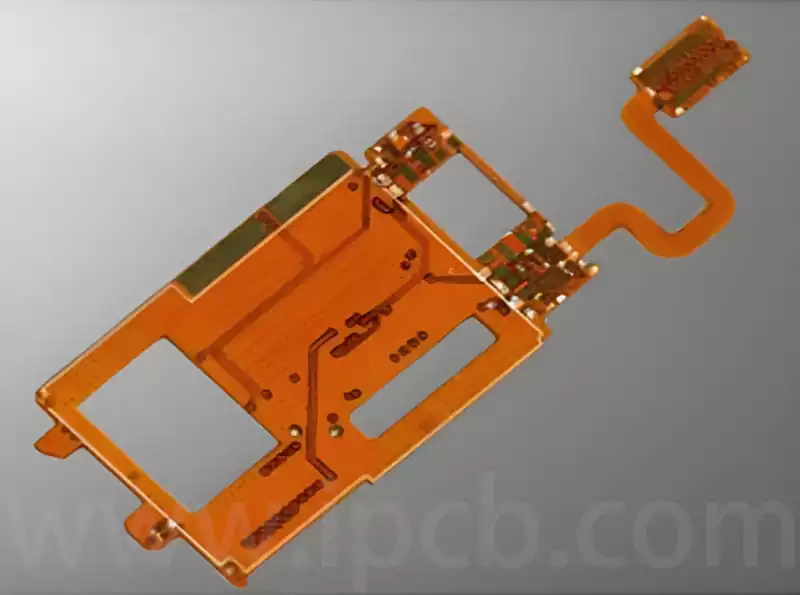
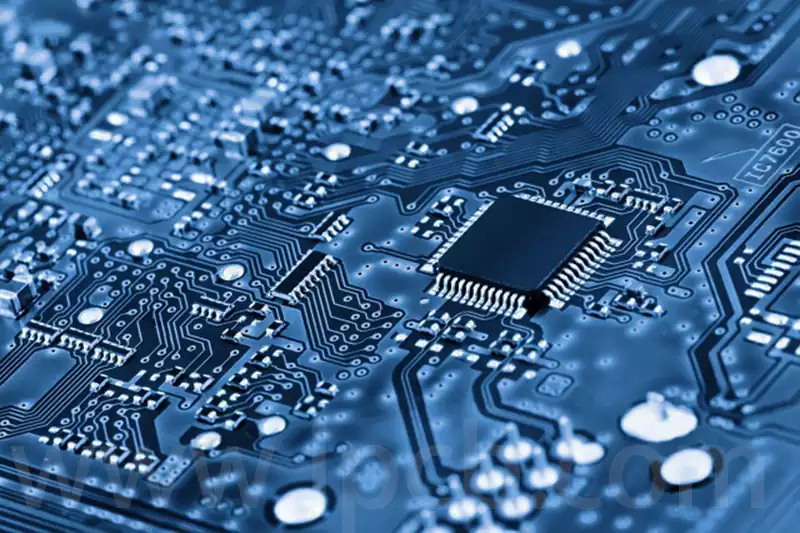
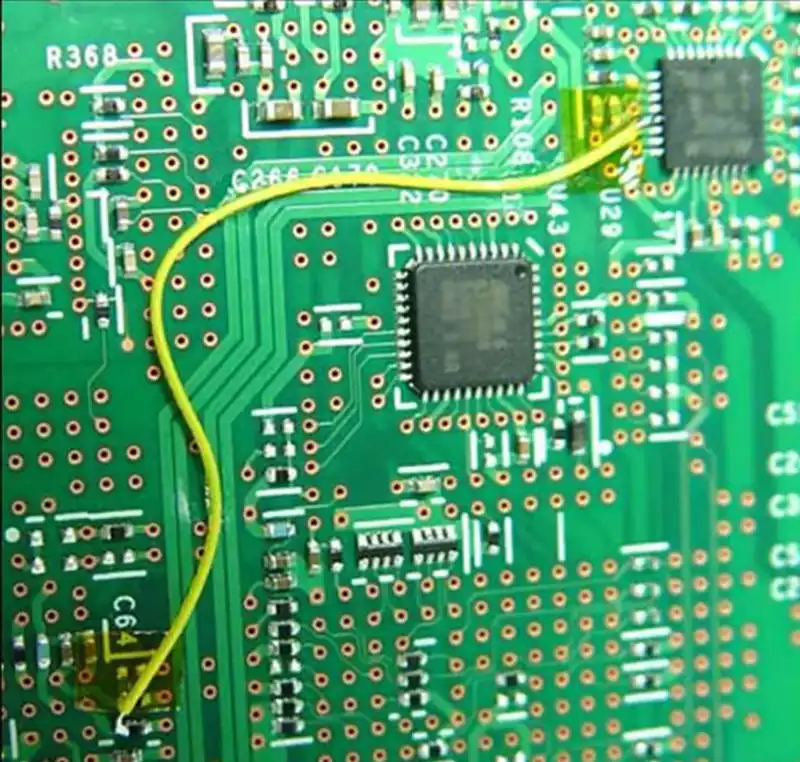
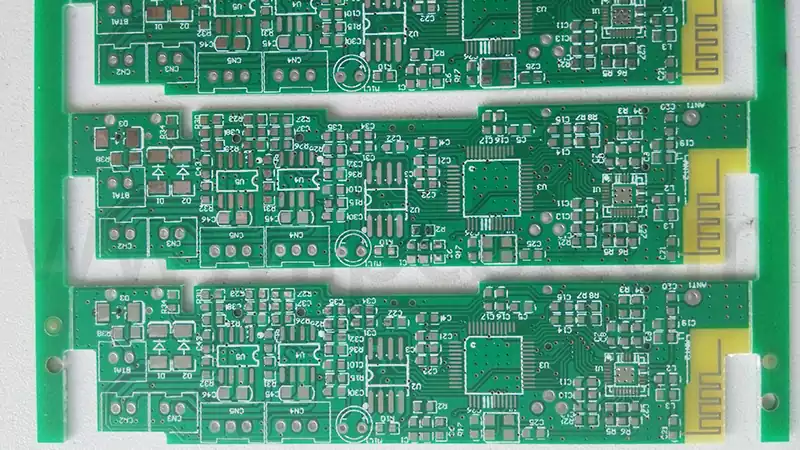
The Difference Between Rigid PCB and Flexible PCB
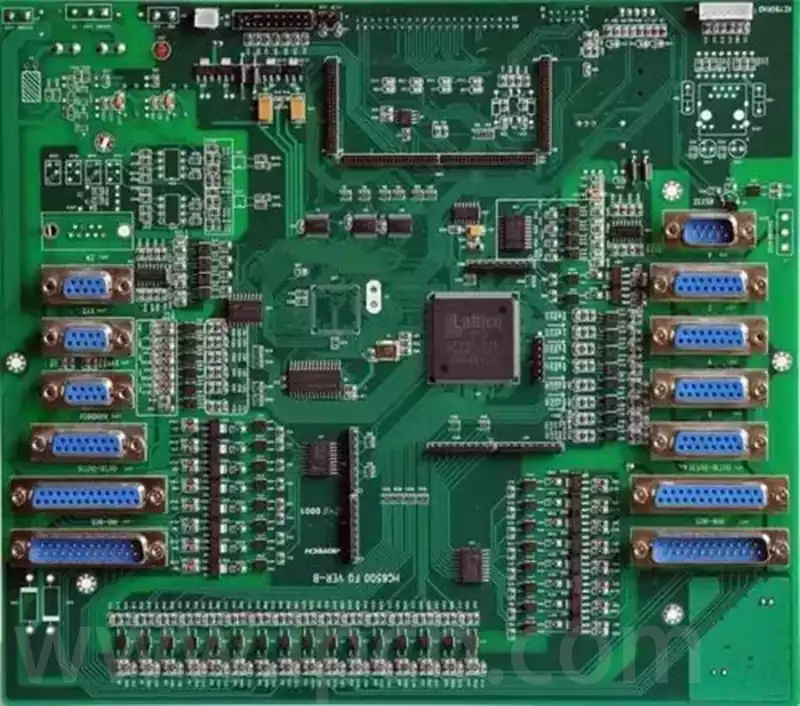
Rigid PCB, commonly referred to simply as PCBs, are what most people envision when thinking of circuit boards. These boards utilise conductive tracks and other components arranged upon a non-conductive substrate to connect electrical components. In rigid circuit boards, the non-conductive substrate typically incorporates glass cloth, which enhances the board’s strength and imparts rigidity. Rigid […]