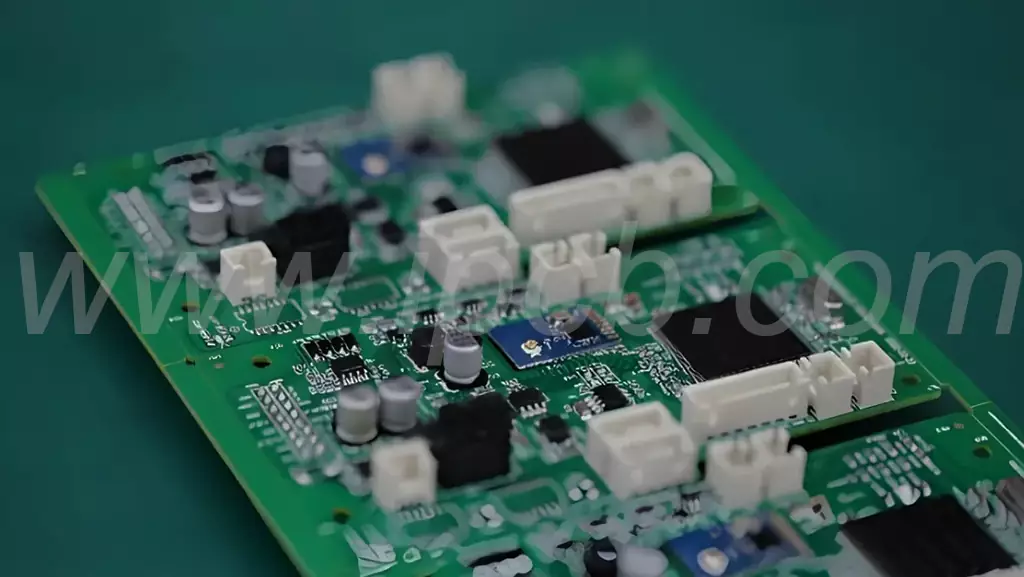
Automotive pcb assembly is the process of assembling automotive printed circuit boards, which has more stringent quality requirements than PCBA in other fields. This is mainly because the automotive electronic system is directly related to the performance and safety of the vehicle.
Automotive pcb assembly process:
Raw material preparation
According to the special needs of automotive electronics, select the appropriate circuit board substrate. Due to the complex automotive environment with high temperature variations, strong vibration and electromagnetic interference, substrate materials with high heat resistance, high mechanical strength and good electromagnetic compatibility are usually used, such as specially modified FR-4 materials or high-performance flexible substrates. These substrates must meet strict industry standards to ensure stable operation under harsh operating conditions. At the same time, all kinds of electronic components, including resistors, capacitors, inductors and various chips, are accurately purchased according to the circuit design. Component quality directly affects the reliability of the PCBA, procurement needs to meet automotive-grade specifications, with a wide temperature range and high reliability of the product. For example, the chip applied to the engine control system needs to work stably under the extreme temperature environment of -40℃ to 125℃. Purchased components also have to pass strict factory inspection, including appearance integrity and electrical parameter testing, to prevent substandard products from entering the production process.
SMT SMD Processing
Solder Paste Printing is to evenly print the formulated solder paste onto the PCB pads through the stencil. Automotive electronics PCB requires very high precision of solder paste printing, because any small error may cause subsequent soldering defects, affecting the overall performance. Stencils are usually produced using laser cutting or etching technology, with different apertures and shapes designed for different devices to ensure precise solder paste dosage. For example, for tiny packages such as 0201, small mesh holes are used to control the amount of solder paste to avoid short circuits; for large pads such as BGA chips, larger mesh holes are used to ensure sufficient solder paste. Subsequently, the electronic components are quickly and accurately placed onto the solder-paste covered pads by a high-precision mounter. The mounter identifies, picks up and locates the components according to the programme, and the placement accuracy reaches micron level to meet the dense component arrangement of complex circuit boards such as car navigation and self-driving controllers. After placement, it enters the reflow process, where the temperature profile is precisely controlled by a multi-temperature zone reflow oven, so that the solder paste is melted by heat and then solidified to form a solid solder joint. Reflow soldering temperature design needs to take into account the heat resistance of different components and substrate materials, to avoid too high a temperature damage to the components or too low a temperature to affect the quality of welding.
THT Plug-in Processing
Some automotive PCB assembly also requires through-hole plug-in technology (THT). For larger power, high mechanical strength requirements or not suitable for SMT components, such as large electrolytic capacitors, relays, etc., must be achieved through the plug-in process. When inserting, the operator needs to insert the component pins firmly into the pre-drilled holes, keep the insertion depth moderate and the pins perpendicular to ensure a good connection with the internal circuit. This process combines manual and tooling assistance to ensure precision and consistency. After completing the insertion, wave soldering equipment is used for soldering. Liquid solder flows through the waveform, and the PCB passes through the waveform so that the pins and pads are fully wetted and soldered. Wave soldering key control of the solder temperature, wave height and transmission speed, to ensure that the solder joints are full and no welding, to prevent short circuits caused by excessive solder.
Testing and debugging
Appearance Inspection: Carry out a comprehensive appearance inspection of the completed automotive PCB assembly to see whether there are missing components, offset, damage, solder joints, whether there is a weak solder, short circuit, leakage and other issues. With the help of magnifying glasses, microscopes and other tools, inspectors meticulously screen every detail to ensure that the PCB board assembly appearance meets the quality requirements. For example, when inspecting automotive airbag control PCBAs, any defect in the solder joints may cause the airbag to fail to eject properly at critical moments, endangering life and safety, so the appearance inspection is crucial.
Electrical performance test: Using professional test equipment to detect the electrical parameters of PCBA, such as on-off test to confirm whether the circuit connection is normal, voltage and current test to verify whether the power supply module and the output of each functional circuit meets the design standards, and signal integrity test to ensure that the transmission of high-speed digital signals is error-free. Automotive PCB assembly, for example, need to test the frequency response of the audio signal, distortion and other parameters to ensure that the sound quality is clear and pure. Only PCBAs that have passed the electrical performance test can proceed to the next step.
Functional test: Simulate the actual operating environment of the car to test the function of the PCB board assembly. It is installed into the special test tooling and verified according to the operation process of automotive electronic equipment in actual use. For example, to test the PCBA of the electric power steering system, simulate the working conditions under different speeds and steering angles, and observe whether the PCB board assembly can accurately control the power-assisted motor and achieve smooth steering. Through the function test, we can find some problems that are difficult to detect in the electrical performance test, and ensure that the PCBA meets the actual needs of automotive use.
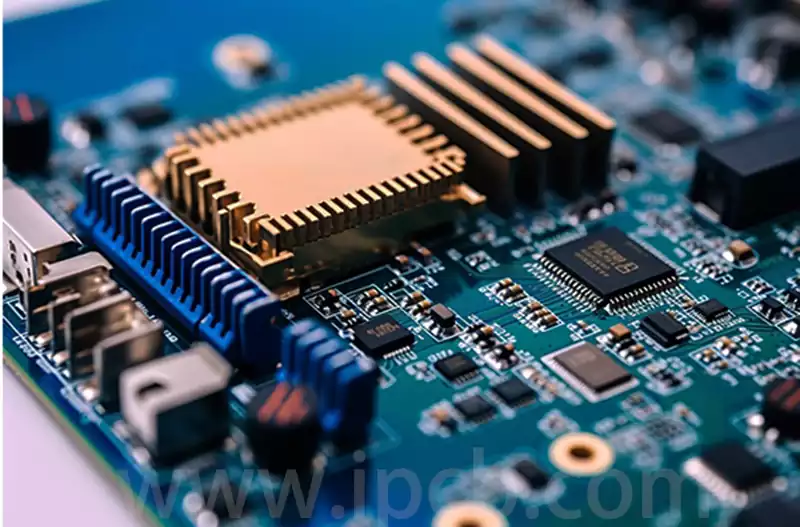

Automotive pcb assembly processing process should pay attention to:
Familiar with the working principle of the circuit: before carrying out inspection and repair, the technician must have a comprehensive understanding of the function of the circuit. Internal structure. The main electrical parameters. The role of each pin and the normal voltage and waveform. This is the basis for problem solving.
Power and thermal management: power integrated circuits must have a good thermal design, not in the absence of heat sinks in the case of high power operation, to avoid overheating caused by circuit damage or performance degradation.
Soldering iron insulation safety: soldering to ensure that the soldering iron is not charged, the iron case must be grounded. For static electricity and sensitive components such as MOS circuits, it is recommended to use 6~8 volts low voltage soldering iron to ensure safety.
Welding quality control: solder joints must be firm and reliable, to prevent solder buildup and air holes caused by false welding, welding time should be controlled within three seconds, recommended the use of 25 watts of endothermic soldering iron. After completing the welding, it is necessary to carefully check whether there is a pin short circuit.
Selection of test instruments: When measuring DC voltage, a multimeter with an internal resistance of more than 20KΩ/V should be used to reduce the measurement error.
Avoid pin short circuit: When measuring voltage or testing waveforms with an oscilloscope, it should be operated carefully to prevent short circuit between pins caused by sliding of the meter pen or probe, especially when testing flat-packed CMOS components.
Comprehensive judgement of the circuit state: As the circuit is mostly directly coupled, a part of the anomaly may lead to multiple voltage changes, so even if the measured pin voltage is approximately normal, can not easily conclude that the circuit is intact, the damage should not be rash judgement, the need for comprehensive analysis.
The development of automotive pcb assembly production and processing:
- Autonomous driving and new energy vehicles have greatly increased the use of automotive printed circuit boards. With the gradual transition of traditional cars to automatic driving cars, as well as policy support for the promotion of new energy vehicles, in order to adapt to the application of new technologies, the demand for automotive PCB electronic control boards continues to increase, and the use of automotive PCB circuit boards is becoming more and more widespread. It is predicted that in the future, along with the improvement and popularisation of technicality, the standard of automotive intelligent system will be further improved.
- Millimetre-wave radar has created a great demand for high-frequency PCB circuit boards. At this stage, millimetre-wave radar is in a high-frequency development trend, and the average value of bikes using millimetre-wave radar is expected to increase again in the future. And radar high-frequency circuits have high demand for PCB boards and manufacturing process. As a result, automotive radar pcb board will pcba processing and manufacturing industry to produce higher added value.
- New energy vehicle power battery BMS technology upgrade potential battery management system (BATTERYMANAGEMENTSYSTEM), battery management system (BMS) is the link between the battery and the user, the main object is the secondary battery, mainly in order to be able to improve the battery’s utilisation rate, to prevent the battery from overcharging and over-discharging.
With the continuous advancement of automotive intelligence and electrification, the importance of automotive PCB assembly is becoming increasingly prominent. In the face of the rapid development of autonomous driving, millimetre wave radar and new energy vehicle battery management systems and other emerging technologies, automotive PCB processing continues to improve the level of technology to meet the needs of higher frequency and more complex systems. In the future, automotive PCB assembly will continue to develop in the direction of high precision, high reliability and intelligence, helping the automotive industry to achieve a safer, more efficient and intelligent travelling experience.