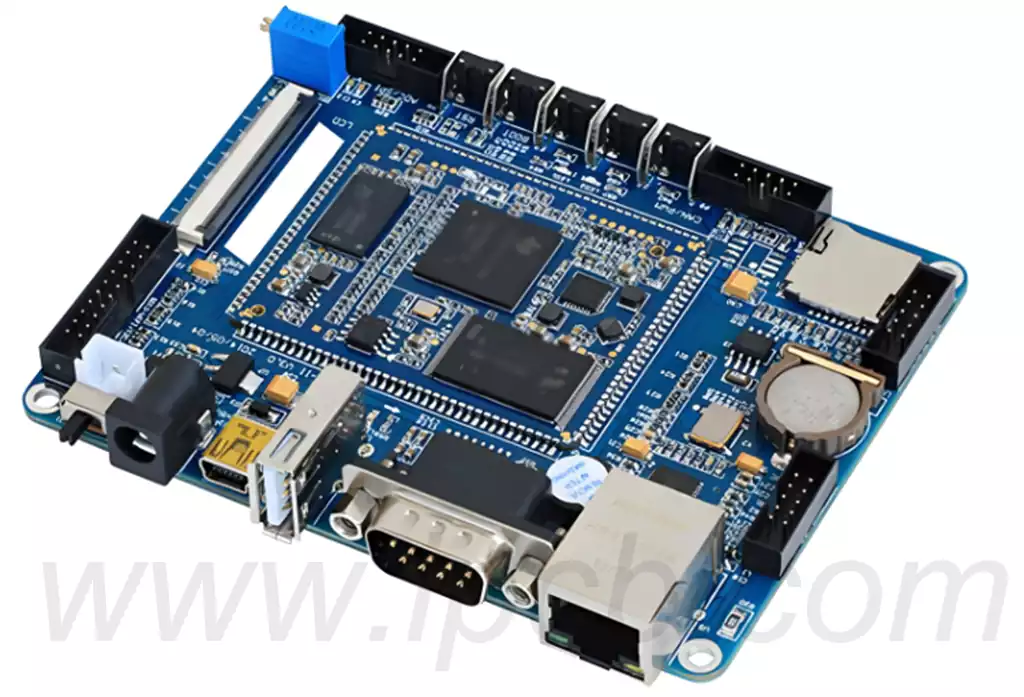
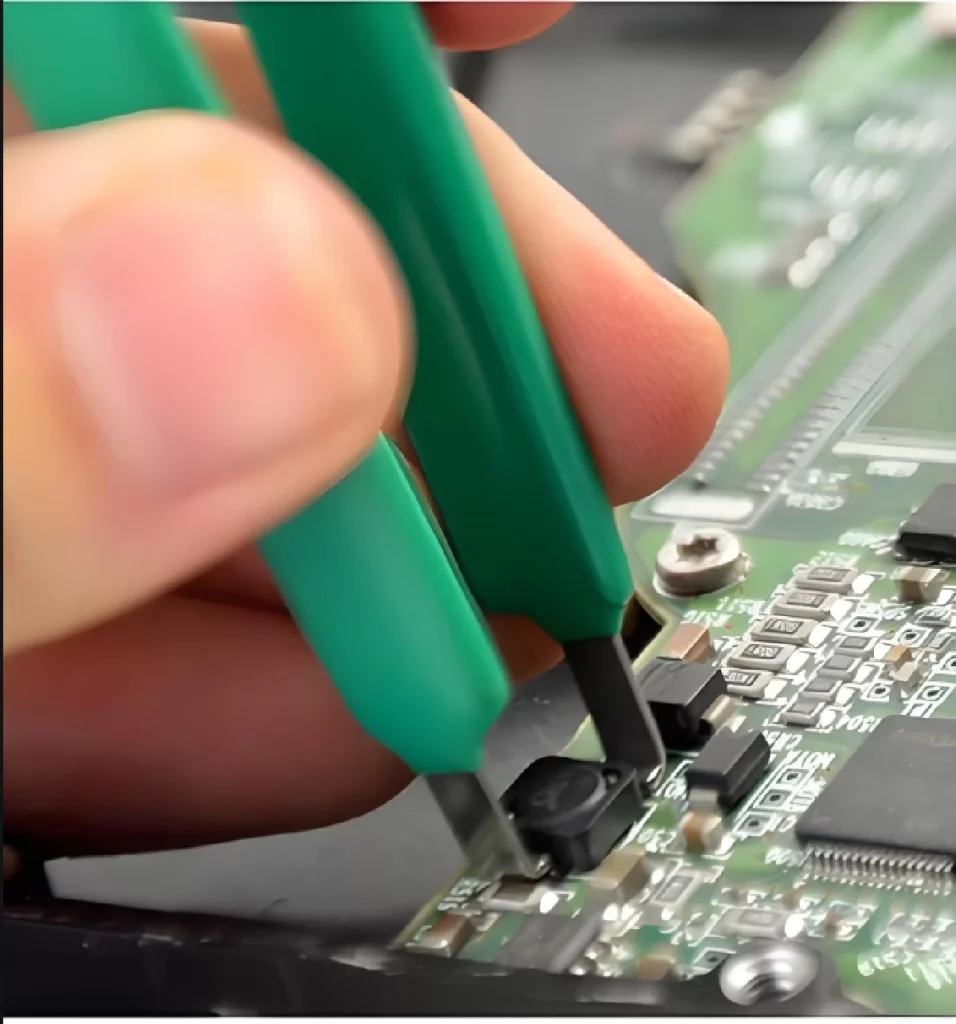
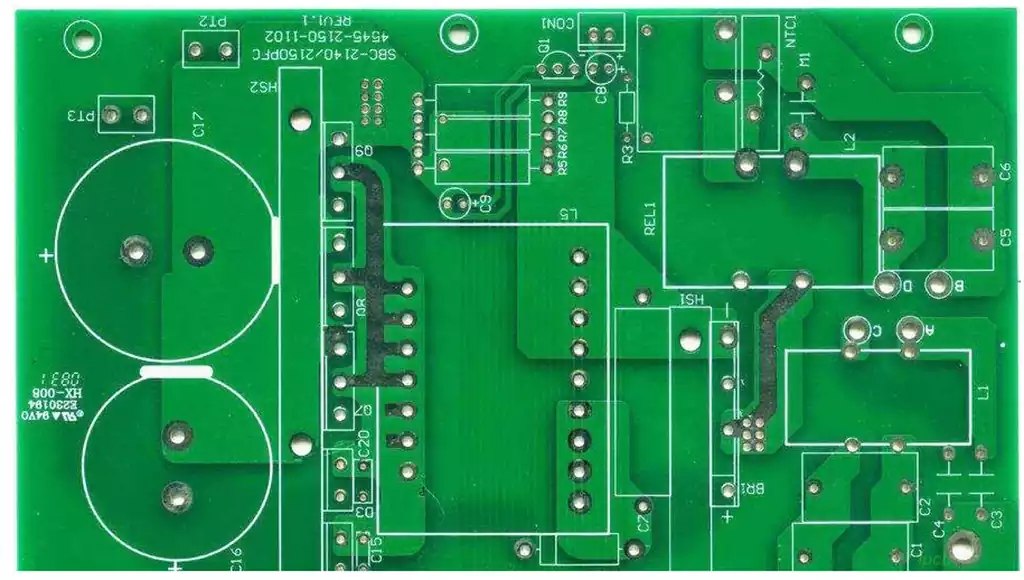
Circuit board component identifier is markings on a circuit board that distinguish components, connecting wires, and other information. They can be in the form of text, symbols, numbers, or colors to facilitate identification and assembly by engineers. The correctness and clarity of the circuit board identifiers are critical to the proper functioning of the circuit board.
Types of circuit board marking
- Component identification: including component model, specification, size and other information, to the general standard symbols or alphanumeric way identification, in order to facilitate engineers to identify.
- Connection line marking: indicates the use of the connection line or connection object, with general standard symbols, numbers or alphanumeric identification. The correctness of the connecting line marking is closely related to the correctness of the wiring of the circuit board production.
- Path marking: indicates that the circuit board signal or power movement path, in the form of general standard symbols or lines for identification. The correctness of the path marking is closely related to the design layout and manufacturing quality.
- Power marking: indicates the maximum power that the components can withstand or the circuit board to withstand the total power to the general standard symbols or alphanumeric form of identification. The correctness of the power marking is closely related to the safety of the circuit board operation.
- Weld marking: indicates the welding position, weld form, current direction and power and other information to the general standard symbols, numbers or alphanumeric identification. The correctness of the solder joint marking is closely related to the quality of welding.
Common electronic components identification code.
Resistor (R) – Resistors are a common type of electronic component used to limit current and regulate voltage in circuits. Common resistor codes include: R1, R2, R3 and so on.
Capacitor (C) – Capacitors are used to store charge and regulate voltage in a circuit. Common capacitor codes include: C1, C2, C3, etc.
Inductors (L) – Inductors are used to store energy and regulate current in a circuit. Common inductor codes include: L1, L2, L3, etc.
Diode (D) – Diodes are used to control the direction and magnitude of current. Common diode codes include: D1, D2, D3, etc.
Transistor (Q) – Transistors are used to amplify and control current. Common transistor codes include: Q1, Q2, Q3, etc.
Integrated Circuit (IC) – An integrated circuit is a chip that integrates a variety of electronic components together. Common IC codes include: IC1, IC2, IC3, and so on.
Power supply (VCC, VDD) – power supply is used to provide the electrical energy required by the circuit, common power supply codes include: VCC, VDD, etc..
Field Effect Tube (FET) – Field Effect Tube is used to control current and voltage, common FET codes include: FET1, FET2, FET3, etc.
Triode (T) – Triode is used to amplify and control the current, common triode codes include: T1, T2, T3, etc.
Electronic Switches (SW) – Electronic switches are used to control the on/off of a circuit. Common electronic switch codes include: SW1, SW2, SW3, etc.
Filter (FL) – Filters are used to filter out noise and noise in a circuit. Common filter codes include: FL1, FL2, FL3, etc.
Transformer (T) – Transformers are used to change the voltage and current in a circuit board. Common transformer codes include: T1, T2, T3, etc.
Circuit Protectors (P) – Circuit protectors are used to protect circuits from damage, common circuit protector codes include: P1, P2, P3 etc.
Signal Generator (SG) – Signal generators are used to generate various signal waveforms. Common signal generator codes include: SG1, SG2, SG3, etc.
Sensor (S) – Sensors are used to sense and collect various physical quantities, common sensor codes include: S1, S2, S3, etc.
Interface chip (I/O) – interface chip is used to connect the communication between different devices, common interface chip code includes: I/O1, I/O2, I/O3, etc..
Clock chip (CLK) – clock chip is used to generate a variety of clock signals, common clock chip code includes: CLK1, CLK2, CLK3, etc..
Isolator (ISO) – Isolators are used to isolate the interference between different circuits, common isolator codes include: ISO1, ISO2, ISO3, etc.
The role of circuit board component identifier
Product Traceability: The circuit board identifier can help manufacturers track information such as the origin of the product, production batch and production date, ensuring product quality and tracing the source of problem products.
Maintenance support: In the maintenance process, by reading the board identification code, maintenance personnel can quickly understand the board model, configuration and maintenance history and other information, so as to more efficiently locate and solve the problem.
Inventory Management: The board identifier helps manufacturers to manage their inventory. Through the identifier, it is easy to count and track information such as inventory quantity, storage location and inventory time, thus reducing inventory costs and improving management efficiency.
Supply Chain Management: In the supply chain, the circuit board identification code can ensure product traceability and transparency throughout the supply chain, helping to establish a closer relationship between manufacturers and suppliers.
In the world of electronics, the Circuit board component identifier is like a key that unlocks the mystery of efficient circuit board operation. Its importance lies not only in the convenience it provides to engineers, but also in the direct impact its accuracy and clarity has on board performance and stability.