Circuit boards are an integral part of modern electronic equipment, and they are usually subjected to a variety of processes during production, such as drilling, surface treatment, gold sinking, soldering, etc., as well as being exposed to a variety of contaminants and chemicals. Therefore, cleaning circuit boards is necessary to remove surface contaminants and improve the reliability and performance of circuit boards.
How do circuit boards get dirty?
Over time, printed circuit boards can become dirty with dust, water and other contaminants, which can prevent equipment from operating effectively. Some of these contaminants may cause temporary damage, while others may cause permanent damage to the equipment. If an electronic device has a built-in fan, it may draw in airborne debris, creating unwanted material that can lead to overheating and component failure. Liquids are one of the common ways that electronic devices are affected. Once the liquid comes into contact with other electrical components of the printed circuit board, it can cause a short circuit. This can damage the circuitry and impair the operation of the device.
Residues from the manufacturing process
The issue of residue and contaminants on pcb substrate is becoming a growing problem affecting PCB reliability as the spacing between neighboring conductors decreases. Electrochemical migration is the migration of ions through a dielectric (e.g. flux residues) under the influence of an electromagnetic field. When these printed circuit boards are operated under stress voltages, intermittent failures may occur, thus reducing reliability.
Creep corrosion is a phenomenon in which crystals of copper or silver sulfide are generated on the surface of a circuit board. When sulfur in the air combines with copper or silver, copper or silver sulfide is formed. These compounds can grow in the guides and cause shortcuts between open thin leads or spaced leads, resulting in poor quality printed circuit board manufacturing.
Influence of the working environment
The durability of solder joints can be affected if the printed circuit board is packaged in a sealed box or bag to prevent contamination. Some of the operating conditions that affect the working of printed circuit boards are the exposure of electrical components to air, which can lead to corrosion. Even if the operator is required to perform additional soldering on the electrical components, it is important for the user to ensure that there is no additional flux residue. Without proper cooling techniques, printed circuit boards in high-performance application equipment can get hot. This can also affect the working of the printed circuit boards, which need to be cleaned regularly.
Improper use
Sometimes, users do not use the electronic equipment recommended by the manufacturer. Manufacturers always provide operators with user manuals to use electronic equipment in the best environment for high performance. However, this is not the case for everyone as each person’s usage is different. The printed circuit boards are likely to get damaged when the operator uses the electronic equipment in higher power or humid environments.
Methods of Circuit Board Cleaning
Commonly used circuit board cleaning methods include mechanical cleaning, ultrasonic cleaning, aerosol cleaning and chemical cleaning. Among them, the mechanical cleaning method is simple and easy to implement, but the cleaning effect is not as good as other methods. Ultrasonic cleaning can thoroughly clean the surface of the circuit board, but the need for specialized equipment and cleaning agents, and there is a long cleaning time, cleaning agent residues and other issues. Aerosol cleaning can clean small pcb components, but the cleaning effect is comparable to ultrasonic cleaning. Chemical cleaning can be precise for different oil cleaning, but need to be used with caution to avoid damage to the circuit board.
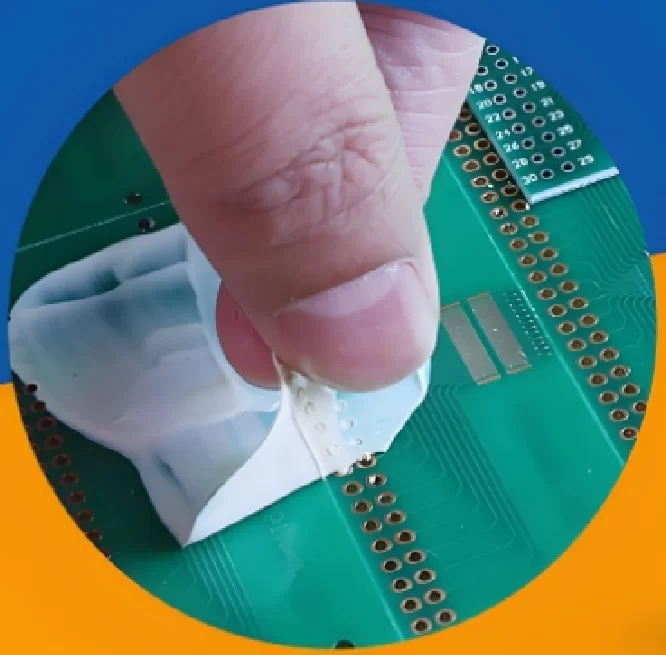
How to clean a circuit board
- Prepare cleaning agent. It is recommended to choose anhydrous alcohol or special pcb plate cleaner.
- Disassemble the circuit board. Remove the circuit board from the device for cleaning.
- Clean the surface. Spray the cleaning agent with a special brush or sprayer to thoroughly clean the surface of the circuit board, taking care not to get wet or bump the board.
- Soak cleaning. Soak the circuit board in the cleaning agent until the oil is dissolved, you can gently scrub.
- Cleaner removal. Remove the circuit board from the cleaning agent, wipe dry with a clean paper towel or water, make sure the board is completely dry.
Precautions
- When choosing a cleaning agent, you should choose a cleaning agent that is suitable for the circuit board material and oil type.
- Pay attention to personal safety during the cleaning process, the use of chemical cleaning agents need to wear protective gloves and masks and other protective equipment.
- After cleaning the circuit board should be thoroughly dry, so as not to leave traces of water or residual cleaning agent on the pcb board.
- Avoid the use of acidic and alkaline cleaning agents and other substances that may cause damage to the circuit board.
- If you are not sure of the cleaning method or do not have the appropriate cleaning conditions, it is recommended to seek professional help.
The cleanliness of circuit boards is critical to the performance and reliability of electronic equipment. Regular of cleaning circuit boards, selecting the appropriate cleaning method and cleaning agent is the key to maintaining the performance of the equipment and extending its service life.