In today’s high-tech era, electronic components are ubiquitous, they are the cornerstone of a variety of electronic devices and systems, which often consist of several parts, and can be common in similar products.
There are various types of electrical components, which can be classified according to different classification standards. It can be divided into resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, transistors, etc. according to their functions. According to packaging, it can be divided into direct insertion type and surface installation type. The commonly used devices in electronic circuits include resistors (including potentiometers), capacitors, inductors, transformers, diodes, transistors, optoelectronic devices, electroacoustic devices, display devices, thyristors (thyristors), field-effect transistors, IGBTs, MOSFETs, relays and reed coils, switches, fuses, oscillators, connectors, various sensors, etc. Different types of electronic components have different characteristics and applications, and they play different roles in circuits.
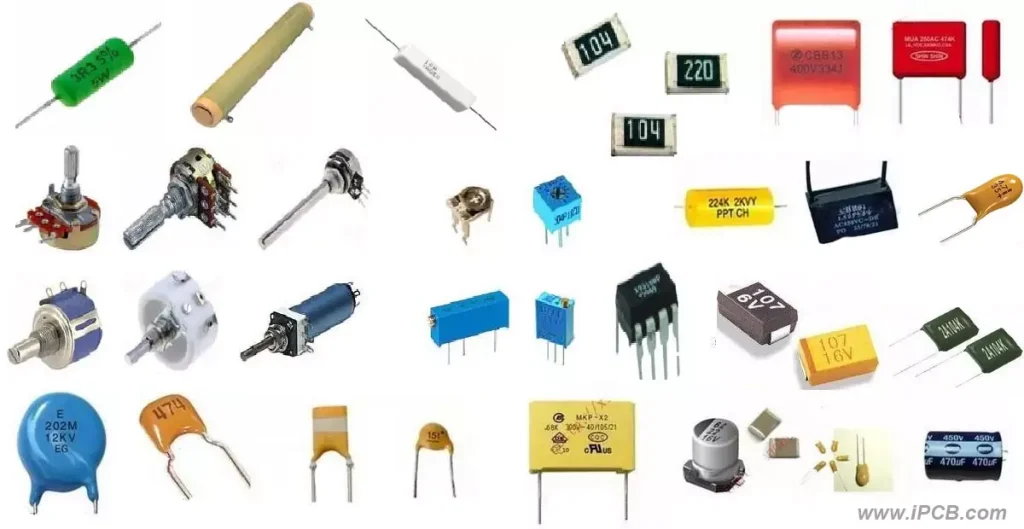
The characteristics and applications of Electrical Components
Resistor: A resistor is used to limit the current components, commonly used in voltage division and current limiting circuits. Resistors of different resistance values have different voltage and current characteristics and are suitable for different circuit requirements.
Capacitor: A capacitor is a component used to store charge and has the characteristic of isolating through and through. It is often used in filtering, decoupling, resonance, and other circuits to ensure circuit stability and reduce noise interference.
Inductance: Inductance is used to store magnetic energy components, and has the characteristics of isolation straight through the intersection. It is commonly used in filtering, oscillation, and anti-jamming circuits, to realize the frequency selection of the signal and the role of noise suppression.
Diode: A diode is a unidirectional conductive element, commonly used in rectifiers, voltage regulators, switches, and other circuits. Through different connections, diodes can realize the function of forward conduction and reverse cutoff.
Transistor: Transistor is a semiconductor device, with amplification and switching. It is commonly used in amplification circuits, switching circuits, and oscillation circuits, and is one of the core components in modern electronic equipment.
Chip: abbreviated as IC, also known as integrated circuit. It is a device with certain functions that integrates transistors, resistors, capacitors, and other components on a silicon substrate using special processes.
Relay: A relay is an electrical control device. In fact, it is an “automatic switch” circuit that controls the operation of large currents with small currents, playing a role in automatic regulation, safety protection, and switching circuits.
Oscillator: An electronic component used to generate repetitive electronic signals (usually sinusoidal or square waves). It is an energy conversion device that can convert direct current into an electronic circuit or device with a certain frequency of AC signal output. The circuit it consists of is called an oscillation circuit.
Sensor: It is a detection device. Measurement information can be converted into electrical signals or other forms of information output to meet the requirements of information transmission, processing, storage, display, recording, and control. According to their basic perceptual functions, they are usually divided into ten categories: thermal sensitive elements, photosensitive elements, gas sensitive elements, force sensitive elements, magnetic sensitive elements, humidity sensitive elements, sound sensitive elements, radiation sensitive elements, color sensitive elements, and taste sensitive elements.
Rectifier bridge: The rectifier tube is sealed inside the shell, and the rectification work is completed through the unidirectional conduction principle of the diode, converting alternating current into direct current.
Optical coupling: The transmission of electrical signals using light as a medium. It has a good isolation effect on input and output electrical signals and is widely used in digital circuits.
Connector: Generally refers to electrical connectors. A device that connects two active devices and transmits current or signals. Like common sockets.
LED: It mainly consists of several components of elements such as arsenic (AS), aluminum (AL), gallium (Ga), indium (IN), phosphorus (P), nitrogen (N), strontium (Sr), LED is the light-emitting component of LED, the core component of LED.
Transistor: also known as a transistor, with three pins, commonly referred to as a transistor. It has a current amplification function and is widely used, such as switch control, signal amplification, etc.
Microswitch: A microswitch is a contact mechanism with small contact intervals and a quick action mechanism that operates with a specified stroke and force. It is covered with an outer shell and has a driving rod on the outside. Because the contact distance between its switches is relatively small, it is called a microswitch, also known as a sensitive switch or quick action switch. Used for door switches, etc. in anti-theft systems.
Temperature switch: A temperature switch is a type of temperature switch that uses a bimetallic sheet as a temperature sensing element. When the electrical appliance is in normal operation, the bimetallic sheet is in a free state and the contacts are in a closed/disconnected state. When the temperature rises to the operating temperature value, the bimetallic element experiences internal stress and quickly acts, opening/closing the contacts, cutting off/connecting the circuit, and thus providing thermal protection.
Temperature fuse: Temperature fuse, also known as thermal fuse, is a temperature sensing circuit cut-off device. Temperature fuses can sense the overheating generated by abnormal operation of electrical and electronic products, thereby cutting off the circuit to avoid the occurrence of fires. Commonly used for: hair dryers, electric irons, rice cookers, electric stoves, transformers, electric motors, water dispensers, coffee pots, etc. The temperature fuse cannot be used again after operation and only operates once at the melting temperature.
Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) is a high-power electrical component, also known as a thyristor. It has advantages such as small size, high efficiency, and long lifespan. In automatic control systems, it can be used as a high-power driver to control high-power equipment with low-power controls. It has been widely used in AC/DC motor speed control systems, power regulation systems, and servo systems.
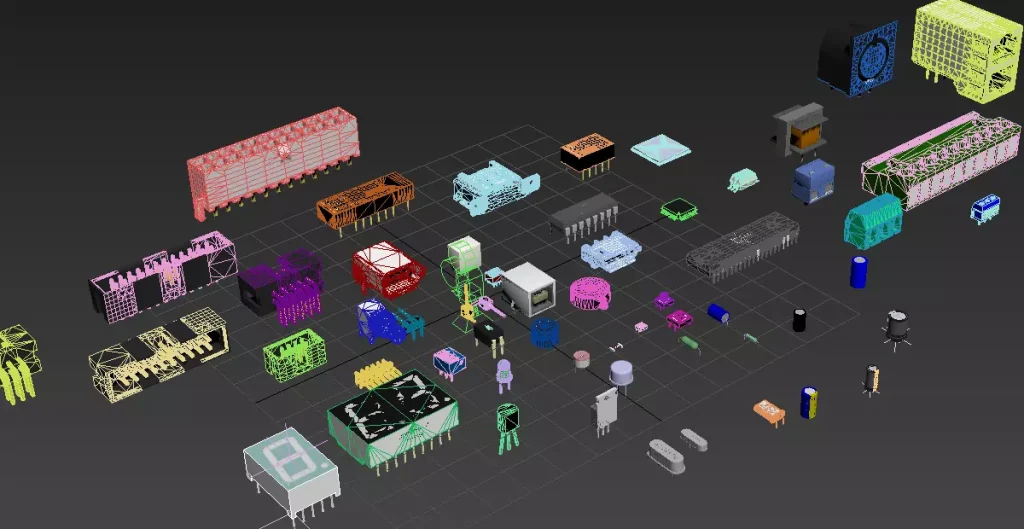

Electronic devices can be divided into active devices and discrete devices. Active devices require an external power source to achieve their basic characteristics and are a type of electronic device that consumes electrical energy. Discrete devices are mainly divided into semiconductor diodes and semiconductor transistors, such as basic circuit components, switch components, connectors, indicators or displays, sensors, etc.
With the continuous development of science and technology, the field of application is also expanding. In emerging industries such as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, electric vehicles, and other fields, electronic components play an increasingly important role.
For example, IoT devices require a large number of sensors and microcontrollers to realize intelligence. AI algorithms require high-performance processors and memories to realize efficient computing. and electric vehicles require high-efficiency power management chips and motor drivers to improve energy efficiency.
In addition, with the popularization of 5G technology, the application of electronic components in the field of communications will also usher in new opportunities. 5G technology’s high speed, large capacity, and low latency characteristics will promote the rapid development of the Internet of Things, intelligent transportation, telemedicine, and other fields, which require a large number of electronic components to support their implementation.