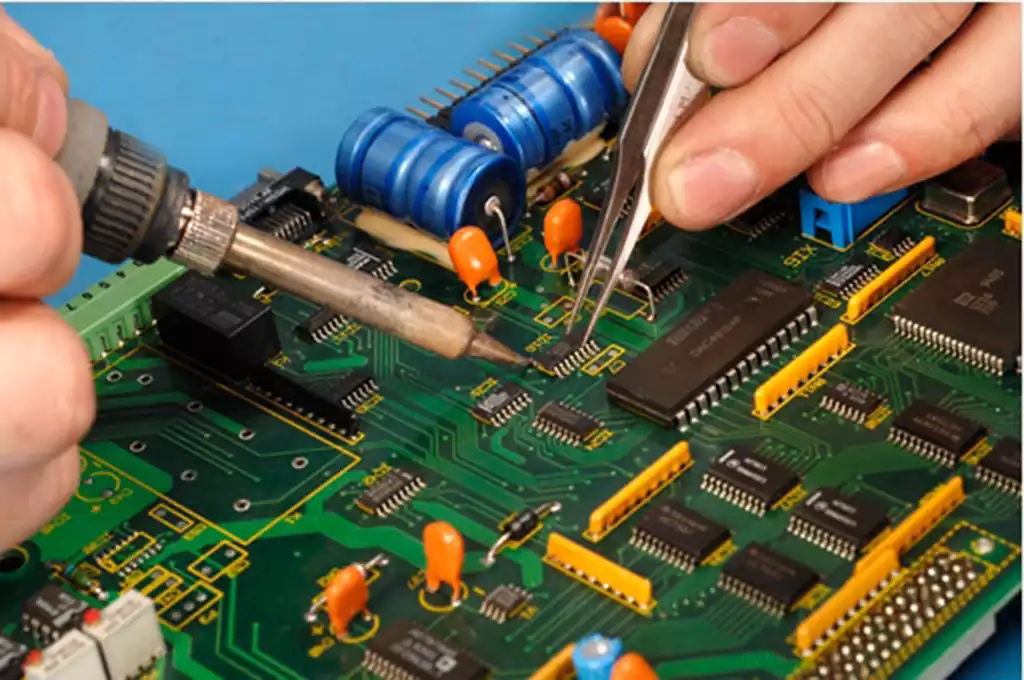
FPC Bonding (Flexible Printed Circuit Board Bonding) is a technology that electrically and mechanically connects flexible circuit boards (FPC/FPCB) to other electronic components, rigid circuit boards (PCBs), or components such as displays through a specific process. This process is widely used in consumer electronics (e.g., mobile phones, tablets, wearable devices), automotive electronics, and medical devices to meet the demand for thin and light, high-density wiring, and bendability.
Commonly used FPC Bonding techniques include the following:
Hot Bar Soldering
This process uses a heated soldering head (Hot Bar) to connect the pads on the FPC to the pads of the PCB or component by molten solder. It is characterised by the ability to achieve highly accurate and small sized solder joints, and is widely used for connecting display wiring. Key process parameters include temperature, pressure and heating time.
ACF Bonding (Anisotropic Conductive Film)
uses an adhesive film containing conductive particles that are heated and pressurised to conduct in the vertical direction while maintaining insulation in the horizontal direction. This technology is mostly used for bonding between LCD or LED displays and driver circuits, as well as touch panels. The advantages are that it is environmentally friendly, lead-free and suitable for micro-pitch pad connections.
Laser soldering
uses a laser beam to make a solder connection by localised heating to melt the solder. This is a non-contact process with high soldering accuracy, suitable for high density and miniaturised electronic devices.
Conductive Adhesive Bonding (Conductive Adhesive)
The FPC is bonded to the substrate by means of a conductive adhesive, such as a silver-containing paste, which forms a conductive path after curing. This method is suitable for temperature-sensitive components or applications where flexibility of the connection needs to be maintained.
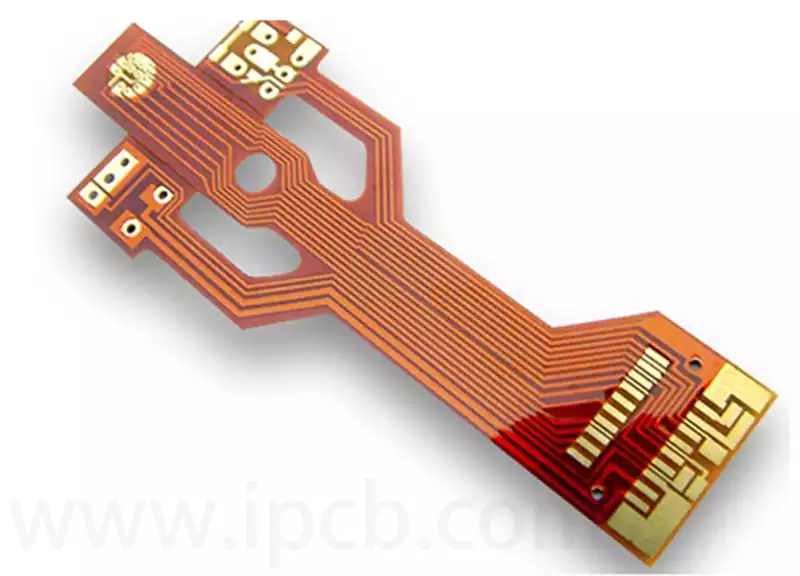
FPC Bonding Process Flow:
Pre-Preparation
Before carrying out the FPC bonding process, adequate preparation must be carried out. This includes the preparation of the required production materials such as the FPC body, PSA (Pressure Sensitive Adhesive) and other relevant auxiliary materials. At the same time, production equipment is thoroughly checked and calibrated to ensure that it is operating at its optimum level. Environmental conditions also need to be strictly controlled to maintain appropriate temperature, humidity and cleanliness to prevent environmental factors from adversely affecting the lamination process.
PSA Lamination Process
PSA lamination is a key step in the FPC lamination process, covering precise positioning, pressure application and heat curing. First of all, it is necessary to ensure that the FPC and the target component are accurately aligned with each other, and this process is generally completed by using high-precision positioning equipment and visual inspection systems. Subsequently, by applying appropriate pressure, the PSA is evenly distributed at the interface between the FPC and the component to form a strong bonding layer. Factors such as pressure size, distribution method and maintenance time play a decisive role in the final lamination effect. Finally, heat curing treatment is performed to further enhance the bonding performance and stability of PSA.
Throughout the lamination process, quality defects such as bubbles, misalignments and wrinkles should be closely monitored and avoided. Strict quality control measures, including regular equipment inspections, monitoring of environmental parameters and timely adjustment of process parameters, are required to ensure the quality of the lamination.
Quality inspection after lamination
After completing the lamination of FPC and PSA, a comprehensive quality inspection must be carried out to ensure that the product meets the design and performance standards. The main inspection content includes appearance testing, such as confirming that the lamination surface is flat, no bubbles and foreign objects; dimensional measurements to ensure that the product dimensions in line with the specification requirements; functional testing, to verify that the lamination of the FPC can operate normally and meet the performance indicators.
In addition, for specific needs, more in-depth reliability tests can be conducted, such as weathering tests and mechanical strength tests. These tests help to assess the performance of the product under various harsh conditions and provide a guarantee for its long-term stable use.
FPC bonding process focus and difficulties
Moisture proof and pre-baking
FPC material is highly hygroscopic, moisture will lead to blistering and delamination damage during subsequent heating, strict vacuum packaging and pre-baking is the key link to prevent this problem.
Fixture design and clamping method
The fixture not only undertakes the mission of fixing FPC, but also needs to solve the problem of FPC unevenness, reasonable choice of pallet material (e.g. aluminium alloy) and adhesion method directly affects the production efficiency and yield.
Control of printing tin problem
FPC surface unevenness may cause tin, tin less, tin more problems in solder paste printing. The use of notch design to eliminate the influence of the thickness of the backing layer around the pad area, precise control of the position of the silicone adhesive and the distribution of high-temperature adhesive paper are commonly used strategies.
Board assembly and placement automation
Due to the small number of FPC components, board assembly is often used for placement operations. Reasonable configuration of the number of boards can improve the efficiency of the placement machine, and at the same time, by reducing the number of MARK points and the use of blue light camera to improve the quality of visual recognition, improve the placement accuracy and speed.
Cost and equipment investment considerations
REEL TO REEL continuous production technology is suitable for mass production, equipment specialisation is high and expensive, while the fixture attachment method is widely used for its low cost and easy operation, which should be selected according to the production scale.
FPC Bonding as an important process to connect flexible circuit boards and other electronic components, solid technical basis and strict process control is to ensure product performance and reliability of the key. With the development of electronic products in the direction of thinness, high density and diversification, FPC Bonding process continues to innovate and improve in order to meet the increasingly stringent application requirements.