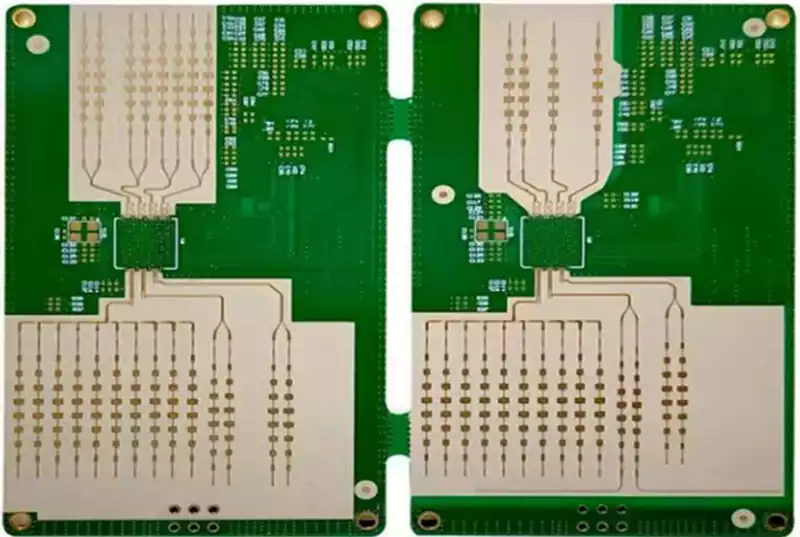
FR-4 material, derived from the abbreviation Flame Retardant 4, is a widely used composite material in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs). It consists of layers of woven glass fabric impregnated with epoxy resin, which are then compressed and heated to form a rigid board.
FR-4 material is known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, mechanical strength, and dimensional stability, making it a popular choice for various electronic applications.
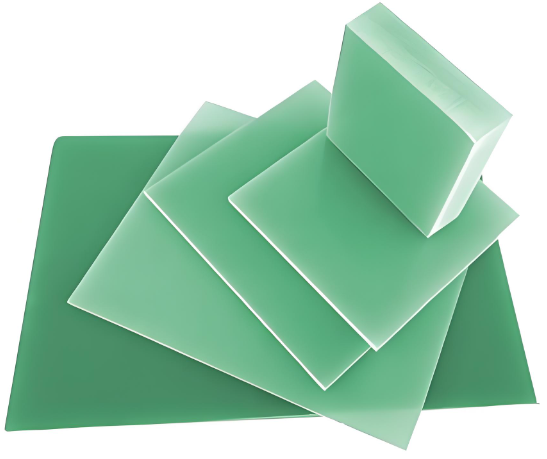

Composition and Manufacturing Process
FR-4 material is typically composed of a substrate made of woven glass fabric impregnated with an epoxy resin binder. The glass fabric provides mechanical strength and rigidity, while the epoxy resin acts as a bonding agent, providing adhesion between the layers and enhancing the material’s overall properties.
During the manufacturing process, layers of glass fabric and epoxy resin are stacked together and then subjected to heat and pressure, resulting in a solid, homogeneous material with uniform properties throughout its thickness.
Key Properties of FR-4 Material
FR-4 material exhibits several key properties that make it well-suited for use in electronic applications:
- Electrical Insulation: One of the most important properties of FR-4 material is its excellent electrical insulation. The combination of glass fabric and epoxy resin results in a material with high dielectric strength, which effectively prevents the flow of electrical current and minimizes the risk of short circuits in electronic devices.
- Mechanical Strength: FR-4 material has high mechanical strength and rigidity, making it capable of withstanding mechanical stress and vibration. This property is essential for ensuring the structural integrity of PCBs and other electronic components, especially in applications where the boards may be subject to bending or flexing.
- Thermal Stability: FR-4 material exhibits good thermal stability, allowing it to maintain its mechanical and electrical properties over a wide range of temperatures. This property is particularly important in electronic devices that may be exposed to elevated temperatures during operation, such as power electronics or automotive applications.
- Chemical Resistance: FR-4 material is resistant to a wide range of chemical substances, including acids, bases, and solvents. This property ensures that the material remains stable and does not degrade when exposed to harsh chemical environments, making it suitable for use in various industrial and automotive applications.
Applications of FR-4 Material
FR-4 material finds widespread use in various electronic applications, including:
- Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): PCBs are the most common application of FR-4 material. The material’s excellent electrical insulation properties and mechanical strength make it ideal for use as a substrate in the manufacture of PCBs for consumer electronics, telecommunications equipment, industrial controls, and other electronic devices.
- Electronic Enclosures: FR-4 material is also used to manufacture enclosures and housings for electronic devices. Its combination of mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance makes it suitable for protecting sensitive electronic components from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations.
- Insulating Components: FR-4 material is often used to fabricate insulating components such as insulators, spacers, and mounting pads in electronic assemblies. Its high dielectric strength and dimensional stability make it an excellent choice for applications where electrical insulation and mechanical support are required.
Future Trends and Developments
As electronic devices become smaller, more complex, and more integrated, the demand for advanced materials with enhanced properties is expected to increase. In response to this demand, researchers and manufacturers are exploring ways to improve the performance of FR-4 material and develop new materials with even better properties. Some of the future trends and developments in FR-4 material include:
- Advanced Formulations: Researchers are investigating new formulations of epoxy resins and glass fibers that can further enhance the mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of FR-4 material. By optimizing the composition and processing parameters, it may be possible to develop FR-4 materials with improved performance and reliability.
- Nanocomposites: Nanocomposites, which consist of nanoscale filler particles dispersed in a polymer matrix, offer the potential to further enhance the properties of FR-4 material. By incorporating nanoscale fillers such as carbon nanotubes or graphene into the epoxy resin matrix, researchers hope to improve the material’s mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and flame retardancy.
- Green and Sustainable Materials: With increasing awareness of environmental issues, there is growing interest in developing green and sustainable alternatives to traditional FR-4 materials. Researchers are exploring the use of bio-based resins, recycled fibers, and other environmentally friendly materials to reduce the environmental impact of electronic devices.
- Multifunctional Materials: Future FR-4 materials may incorporate additional functionalities such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, thermal management, or self-healing properties. By integrating multiple functions into a single material, designers can simplify the manufacturing process and reduce the overall cost and complexity of electronic devices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, FR-4 material is a versatile and widely used composite material that offers a unique combination of properties suitable for a wide range of electronic applications. Its excellent electrical insulation, mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance make it an ideal choice for use in printed circuit boards, electronic enclosures, and insulating components. With ongoing research and development efforts, it is likely that the performance of FR-4 material will continue to improve, enabling new and innovative electronic devices in the future.