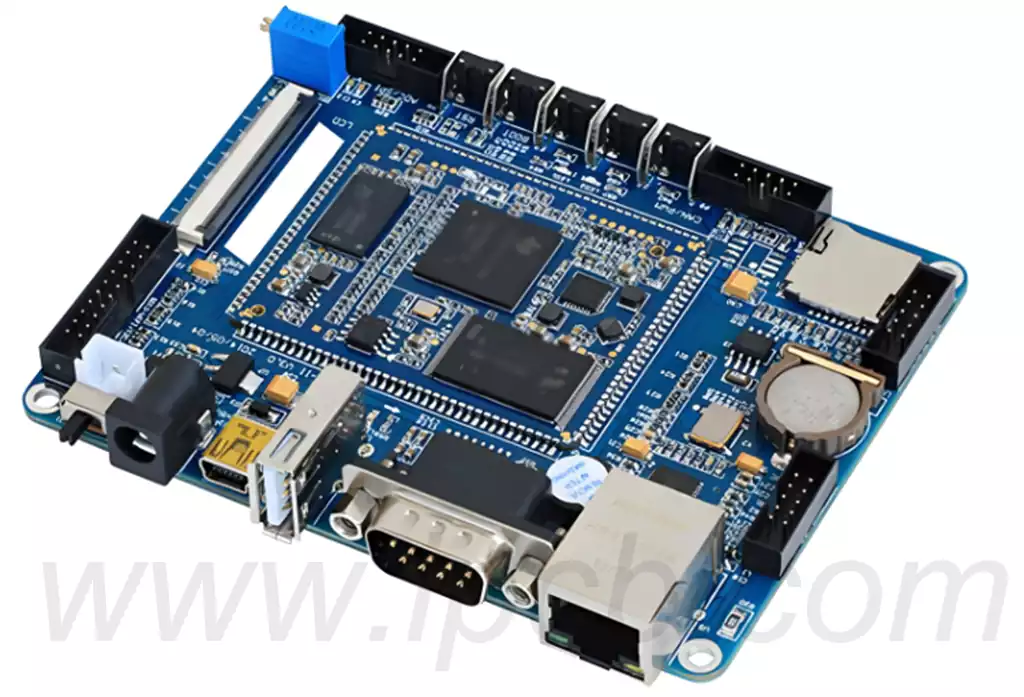
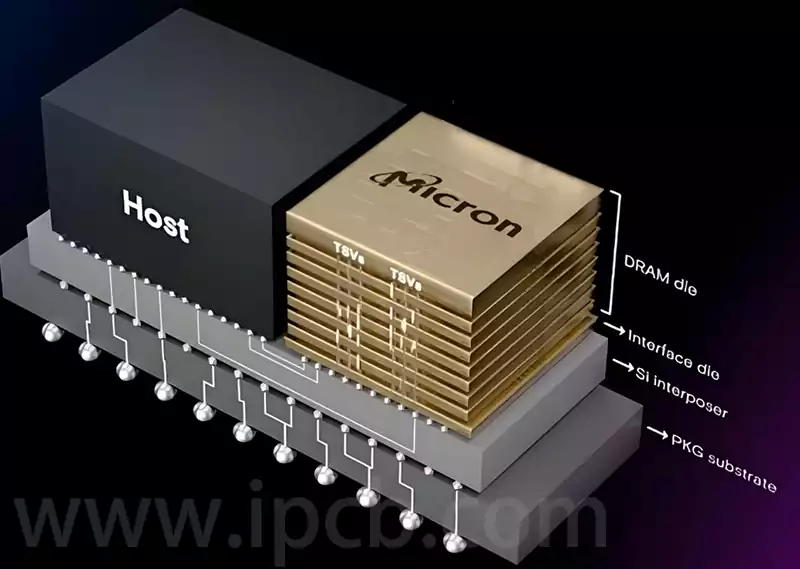
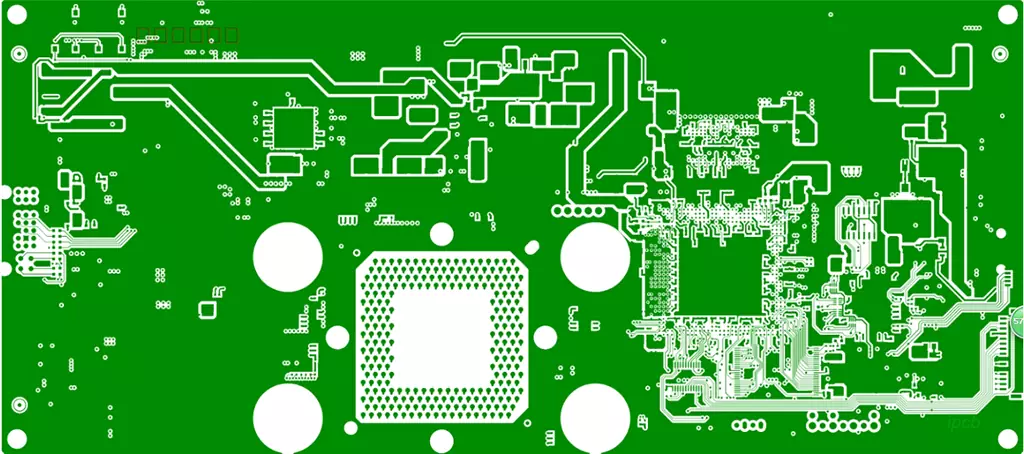
High speed digital pcb is circuit boards that can support high speed digital signal transmission, and are usually used in scenarios where the frequency of digital logic circuits reaches or exceeds 45MHz-50MHz, or where the delay of digital signals in circuits on the transmission line is greater than 1/2 rise time.
Compared to traditional analogue circuit boards, high speed digital pcb offers the following advantages:
- Higher operating frequency: high speed digital pcb can operate at higher frequencies, thereby improving the response speed of the circuit;
- Lower power consumption: high speed digital pcb can reduce power consumption by optimising circuit design and layout;
- Higher reliability: high speed digital pcb can improves circuit reliability by reducing the delay time of signal transmission and noise interference.
Applications of high speed digital pcb :
Communication
In the field of communication, high speed digital pcb has been playing an important role as a key component in achieving signal transmission and data processing. With the development of communications technology, the transmission speed and data processing capacity requirements are increasingly high, high-speed circuit boards become one of the important means to achieve this goal. For example, fibre-optic transceivers based on high-speed circuit boards have become one of the mainstreams of fibre-optic communications, with advantages such as high-speed transmission, low power consumption and high stability.
Networking
In the field of networking, high speed circuit boards are mainly used in network equipment to support high-speed data transmission and information processing. For example, in network equipment such as routers and switches, high-speed circuit boards are widely used to transmit and process high-speed data to achieve high-performance network functions. In addition, in data centres, high-speed circuit boards are also widely used for data transmission and processing to support applications such as cloud computing and big data.
Medical
In the medical field, high-speed circuit boards are mainly used in medical equipment to support high-speed information transmission and processing of medical images, medical data, and other information. For example, in MRI, CT and other medical equipment, high-speed circuit boards are widely used for image data acquisition, processing and transmission to achieve efficient and accurate medical diagnosis and treatment.
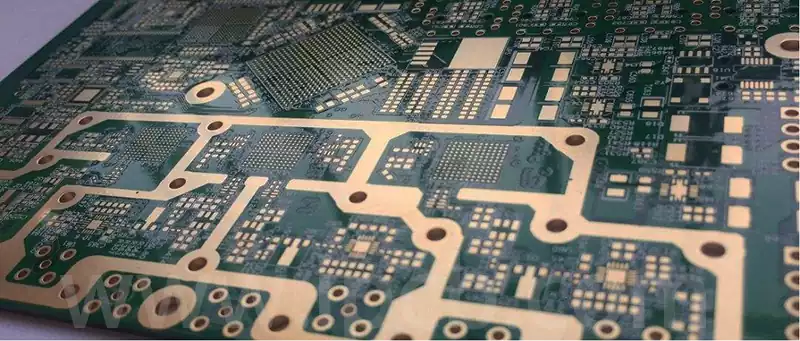
Signal Integrity in high speed digital pcb design
Signal integrity (SI) is the key to ensuring that digital signals are transmitted in circuits with the expected behaviour. Signal integrity problems occur when signals fail to respond at the correct timing and voltage levels. These problems are not caused by a single factor, but are the result of a combination of board-level design factors.
Manifestations of Signal Integrity Problems
Signal integrity problems can lead to a number of negative consequences, including signal distortion, timing errors, incorrect behaviour of data, address, and control lines, and even system misoperation or crash. Major signal integrity problems include:
Delay: Deviations in signal transmission timing that can be caused by differences in the length of the transmission path, load differences, and crosstalk.
Reflection: The phenomenon that occurs when a signal encounters an impedance mismatch on a transmission line, and is one of the two main factors triggering signal integrity problems.
Crosstalk: Electromagnetic coupling between different signal lines, resulting in mutual interference of signals, is also one of the two main factors causing signal integrity problems.
Ringing and Oscillation: The distortion of signal edges, manifested as multiple overshoots and undershoots before the signal reaches a steady state, usually caused by wiring problems, incorrect termination or semiconductor device problems.
Ground Bounce: Refers to Synchronous Switching Noise (SSN), which is caused by multiple signals switching at the same time resulting in current transients that cause voltage fluctuations in the ground plane or power plane.
Factors Affecting Signal Integrity
Poor signal integrity is rooted in the interaction of multiple factors:
IC Switching Speed: The fast switching speed of integrated circuits (ICs) is a significant factor in signal integrity problems.
Wiring and termination: Improper board wiring layout, incorrect termination, and incorrect wiring of high-speed signals can cause signal integrity problems.
Signal Characteristics: The characteristics of the signal itself, such as rise time and swing, can also affect the degree of signal distortion.
System impedance: Mismatch between the impedance on the transmission line and the load impedance can lead to signal reflection and distortion.
Transmission Delay: The delay of the signal on the transmission path affects the timing of the signal, especially more significant in high-speed circuits.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): External EMI or electromagnetic noise generated within the circuit can affect the quality of the signal.
Voltage fluctuations: Power and ground noise or voltage fluctuations can also cause signal distortion.
Importance of high speed digital pcb in modern circuit design
As technology advances, high speed digital pcb is becoming increasingly important in modern circuit design. High speed digital pcb can improves the response speed and reliability of the circuit, thus meeting the requirements of modern circuits for speed and performance. In addition, high speed digital pcb can also reduces power consumption, thereby reducing the waste of energy, in line with the requirements of the modern society of energy saving and environmental protection.