Lead-free vs lead solder debate has been ravaging behind the scenes in the electronic manufacturing industry. Over the years, PCB manufacturers have kept pace with industry challenges and responded with an influx of new technologies and practices. These include miniaturization of PCBs, flexible printed circuits, and the growing demand for green electronics. PCB manufacturing employs practices that use less energy, reduce carbon emissions, and utilize non-toxic and environmentally friendly materials. Here we will compare Lead Solder with lead-free solder and discuss how to choose between leaded and lead-free solder.
What is solder?
Solder is a metal alloy consisting of lead and tin melted using a hot iron and used to join two metals together. Solder is commonly used to make electronic products, and various types of solder are used to join different types of metals. The melting point of the solder must be lower than the melting point of the metals it joins together. Soldering begins with mounting the assembly onto a printed circuit board and applying heat to the joints. The assembler then applies solder to the connectors to adhere the parts to the board before cutting the component leads. There are two main types of solder commonly used: Lead Solder and lead-free solder.
Lead Solder
Lead Solder is also known as SnPb solder because it is a metal alloy based on tin (Sn) and lead (Pb). It has a lower melting point (183 °C or 361 °F) than lead-free solder, which makes it preferable to lead-free solder because it has a lower thermal effect on the PCB substrate and its electronic components. In addition to less thermal damage to the board, Lead Solder provides smooth looking joints that are brighter and cause fewer quality problems than lead-free solder. Lead Solders are used in most electronic manufacturing processes, such as PCB assembly, SMT component mounting, and so on.

Lead-free solder
Lead-free solder is an alternative to the more traditionally used 60/40 SnPb solder wire. Lead-free solders are solders that do not contain any toxic substances. They are also known as non-toxic solders because they do not contain heavy metal elements that can cause health problems. Typically, these versions will have a percentage of tin-copper, tin-silver, and tin-zinc alloys in place of the lead content: silver, copper, nickel, and zinc. The melting points of lead-free solders range from 50 to 200 °C or higher. Lead-free solder is not suitable for critical applications such as aerospace or medical products, but it is suitable for electronic assemblies.
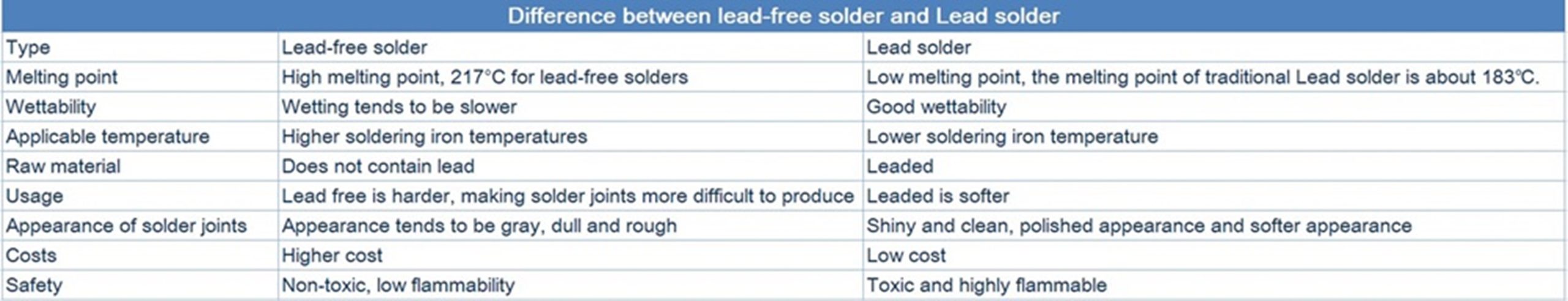
The difference between lead-free solder and Lead Solder
How to choose lead-free solder and Lead Solder?
It is very important to choose the right solder, which is related to the process and performance of the PCB. When choosing, you can consider the following aspects.
- Type:
There are different types of solder, including wire, rod, ball, paste and preforms. Each form has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, when using bar or sphere solder allows for better control over the amount of solder used. On the other hand, solder paste tends to spread, making it difficult to use in tight areas. Preformed solder eliminates the problems associated with spreading. It also provides better control over the amount of material applied. In addition, preformed solder does not produce toxic fumes like molten solder. - Cost:
Lead Solder costs less and lead-free solder costs more. - Safety:
If life comes first, use lead-free solder, there is no cadmium, mercury, arsenic and other harmful chemicals, and does not produce dangerous fumes - Wiring requirements:
Lead Solder works well when connecting two different types of metal surfaces. This includes copper and brass, but also includes aluminum and stainless steel. Lead-free solder, on the other hand, has a wider range of applications, including the use of tin and metals such as silver, nickel and gold. - Size:
In terms of size, Lead Solder is larger than lead-free solder. You’ll find them in sizes ranging from 0402 to 1 ounce. Lead-free solder, on the other hand, ranges from 0201 to 2 ounces, depending on the choices made by the PCB factory.
Application of lead-free soldering technology in circuit board assembly
- Welding process optimization
The melting point of lead-free solder is higher than that of lead-containing solder, so in the welding process, the welding temperature, time and other process parameters need to be adjusted. Reasonable control of welding parameters can effectively improve welding quality and reduce solder joint defects. - Flux selection
Lead-free soldering process, the choice of flux is critical. Lead-free flux should have good activity, can fully remove the oxides on the surface of the weld, improve the wettability of the solder. In addition, lead-free flux should also have a low corrosive and good thermal stability. - Soldering equipment upgrades
Lead-free soldering equipment puts forward higher requirements. Soldering equipment needs to have precise temperature control and good thermal uniformity to ensure soldering quality. In addition, some lead-free solder has higher requirements for nitrogen protection, so the application of nitrogen protection welding equipment is also becoming more and more widespread.
Advantages of lead-free soldering technology
- Environmental protection
Lead-free soldering technology reduces the use of lead and other hazardous substances, reducing the environmental pollution of electronic products, which is conducive to the protection of the ecological environment and human health. - High reliability
Lead-free solder has high mechanical properties and thermal cycling performance, making the solder joints more solid, improving the reliability of the circuit board. - Compatibility
Lead-free soldering technology is applicable to a variety of circuit board materials and components, with good compatibility. In addition, lead-free solder and leaded solder in the soldering process has a certain compatibility, to facilitate the transition and transformation of enterprises. - Cost advantage
With the popularization of lead-free soldering technology, the price of lead-free solder is gradually reduced. In addition, lead-free soldering technology can improve productivity and reduce the rate of defective products, thereby reducing the overall cost.
The application of lead-free soldering technology in circuit board assembly is an inevitable trend for the green development of the electronics industry. Although lead-free soldering technology puts forward higher requirements for processes and equipment, its advantages of environmental protection, high efficiency and reliability make it the mainstream of the industry’s development. With the continuous maturity of lead-free soldering technology, we believe that its application in the field of electronics will be more extensive, contributing to the sustainable development of China’s electronics industry.
In summary, soldering is an important process in electronics to create a lasting bond between two objects. As such, there are two types of solder: Lead Solder and lead-free solder. With advances in technology and concerns about environmental and health issues, lead-free solder has become a more common choice.
While Lead Solder has a lower melting point, higher wettability, cost efficiency, and a smoother, brighter appearance, it is toxic and damaging to the environment. Lead-free solder is safe but challenging to use, has a higher melting point, and is less reliable due to lower wettability. Choosing the right solder depends on the specific project and its requirements. Therefore, understanding the properties and differences between leaded and lead-free solders is critical to selecting the most appropriate solder for the project.